Behind every product launch, construction milestone, or digital transformation, there’s one person quietly steering the chaos into order: the project manager. They connect strategy to execution, turning ideas into outcomes that matter.
But what exactly are the roles and responsibilities of a project manager?
A project manager’s duties go far beyond scheduling and status reports. They include defining goals, managing risks, and keeping teams aligned. They also ensure that timelines, budgets, and quality standards stay on track while motivating stakeholders and teams.
If you aspire to this role or are refining your leadership as a practicing PM, understanding these key project manager responsibilities is the first step to managing projects that deliver measurable impact. In this guide, let’s take a clear look at them.
Who is a Project Manager?
A project manager is the central figure responsible for making a project’s vision a reality. They plan, coordinate, and oversee the entire lifecycle of a project – from initiation to delivery, ensuring that objectives are achieved on time, within scope, and on budget.
The role of a project manager is not limited to one industry. Whether in IT, construction, manufacturing, or healthcare, project managers translate strategic goals into actionable plans and guide teams through complex challenges.
The project manager role is unique because it blends technical expertise, leadership, and communication. They align diverse teams, manage risks, balance competing priorities, and ensure everyone, from executives to team members, understands what success looks like.In short, project managers are the link between vision and execution, the people who ensure that great ideas don’t just stay on paper.
What Do Project Managers Do?
The project manager deals with the enterprise in a holistic manner on an everyday basis. They keep a track of the task for the benefit of the project board within the requirements and coordinate all through the venture with the project board and project assurance.
The project manager is responsible for pitching ideas for projects that are assigned, planning the budget, monitoring, and reporting on the project with Project Management tools. Project managers are the bridge between the management and the team entrusted with the execution of the project. They ensure that the scope of the project is comprehensive and regular reporting on the advancement of the task is updated and also provide that the project is right on schedule.
Responsible for all of the PRINCE2 processes except for the “Directing a Project” process, project managers need to plan the sequence of activities to achieve control over the track of implementing the right strategies and completing the project on time.
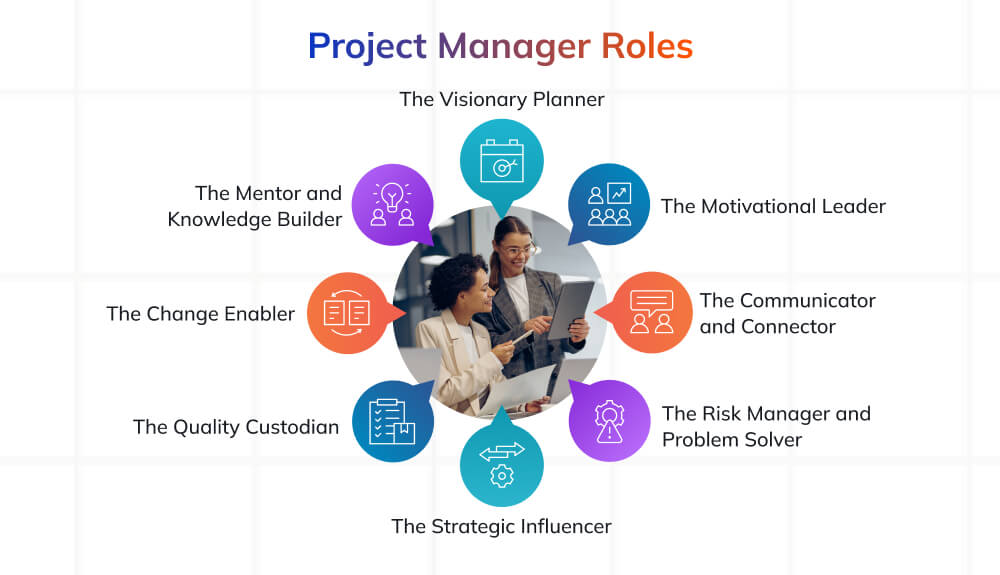
Core Roles of a Project Manager
A project manager wears many hats: strategist, leader, communicator, problem-solver, and coach. While the exact duties may vary across industries, the core roles of a project manager remain constant: ensuring alignment between vision, people, and performance.
Let’s explore these roles in detail.
1. The Visionary Planner
At the heart of every successful project lies a clear plan, and the project manager is the architect of that clarity. They define the project’s scope, set achievable goals, and design the roadmap that turns strategy into action.
A visionary planner doesn’t just outline tasks; they anticipate dependencies, align priorities, and help the team see how their daily work contributes to the bigger picture. This role demands foresight, analytical thinking, and adaptability, skills that allow project managers to make quick yet informed adjustments when timelines or budgets shift.
2. The Motivational Leader
Project management is as much about people as it is about processes. As leaders, project managers set the tone for collaboration and accountability. They understand team dynamics, mediate conflicts, and motivate people to deliver their best work, even under pressure.
Strong leadership in project management isn’t about control; it’s about creating psychological safety, an environment where individuals feel confident to share ideas, own mistakes, and take initiative.
In high-performing teams, this leadership role often makes the difference between a completed project and a truly successful one.
3. The Communicator and Connector
The project manager’s role as communicator is critical for keeping everyone on the same page. They act as a bridge between stakeholders, sponsors, and team members, ensuring that expectations, risks, and progress updates are shared transparently.
Clear communication helps prevent misunderstandings, builds trust, and keeps projects aligned with evolving business priorities. It also involves active listening, understanding concerns, translating complex information into actionable insights, and maintaining relationships beyond project completion.
4. The Risk Manager and Problem Solver
Every project faces surprises, scope changes, resource gaps, or unexpected delays. Here, the role of the project manager is to stay calm under pressure and lead with logic.
They proactively identify risks before they escalate, design contingency plans, and make informed trade-offs to protect project outcomes. Problem-solving in this context is not reactive; it’s anticipatory. The best project managers look ahead, not around.
5. The Strategic Influencer
Great project managers think beyond deliverables; they connect projects to the organization’s broader goals. As strategic influencers, they align each initiative with business priorities, ensuring that time and resources generate measurable value.
This role often involves engaging senior stakeholders, translating strategy into execution, and demonstrating ROI through data-driven reporting.
By bridging business strategy with operational execution, project managers elevate their impact from coordination to leadership.
6. The Quality Custodian
Projects succeed not only when delivered on time and within budget but when they meet quality expectations. The project manager defines measurable standards, establishes review mechanisms, and ensures that deliverables reflect both technical excellence and customer satisfaction. They also ensure that lessons learned are captured for continuous improvement, transforming each project into a foundation for the next.
7. The Change Enabler
Change is the only constant in modern projects.
A project manager’s role is to help people adapt by clarifying the reasons for change, managing resistance, and aligning new processes with existing workflows. They ensure transitions happen smoothly, minimizing disruption and maintaining morale. This requires empathy, emotional intelligence, and the ability to see the human side of transformation, not just the operational one.
8. The Mentor and Knowledge Builder
A project manager’s responsibilities span every stage of a project, from defining the vision to ensuring the final delivery meets expectations. These duties require a mix of strategy, coordination, communication, and leadership.
Here are the key roles and responsibilities of a project manager that define success across industries:
Key Roles & Responsibilities of a Project Manager
In order to become a project manager, it’s mandatory for them to possess various organizational strategies that could be used for various projects. These skills are considered to be important skills to have a booming career in Project Management.
1. Cost Estimation, and Quality Satisfaction
Any product or service innovation can be pursued to successful completion only with a precise cost estimation done using either a bottom-up or a top-down approach. The bottom-up approach allows a project manager to break the project down into units, and calculate the cost of a unit based on cycle time, resources used, cost per person, and other metrics. This is then applied to each unit to arrive at a project budget. The top-down estimation technique is more general in approach, taking into account major expenditure heads, recurring and non-recurring expenditure, and other parameters. Cost estimation is not complete unless there are optimistic, pessimistic, and realistic forecasts.
One of the primary project manager’s responsibilities is to consider cost-benefit trade-offs to meet quality requirements and ensure customer satisfaction. So the expense of quality management–which implies higher productivity at lower costs to fulfill stakeholder expectations– should not be neglected.
To achieve this balance, it is truly said that the role of a project manager is that of a juggler.
2. Managing Risks & Containing Issues
Any project manager worth his salt will know that a risk is anything that occurs during the lifecycle of a project that is “not as per plan.” This unforeseen development may either be a positive or a negative for the success of the project. Being prepared to tackle it is what managing risk is all about.
Unless project manager responsibilities stress the need to list the risks as potentialities that could turn into realities, they will become major issues. If threats are not identified, categorized, prioritized, and planned for, the project will suffer from problems that cannot be addressed adequately. Obviously, the role of the project manager as a Problem Solver comes to the fore here.
3. Activity, and Resource Planning
A project manager not only outlines the structure of work but also provides a breakdown of tasks that go to make up activity in the project. It is considered part of the project manager’s responsibility to map the various activities of a project to the resources available.
When planning is done meticulously and the progress of groups of tasks is followed closely, a smart project manager can identify wastage of resources and redeploy them for better purposes or utilization. This applies to human, physical, technical, and natural resources. So the role of the project manager turns into that of a Tracker at some point in the project.
4. Scalability, Interoperability, and Portability
First, a project manager should be quick to identify if a system or process being deployed to execute a project is capable of being “sufficiently” scaled to meet customer demands.
Secondly, the project manager’s responsibilities include the ability to assess if the software and hardware components may be configured differently to enable different capabilities in an organization. Also important is to check if a program or process can be transferred to work on another operating system without significant reworking.
In other words, the role of the project manager as an Augmenter of capabilities is crucial.
5. Reporting and Documentation
With so many people working to make an idea come true, the only way to ensure order and a sense of single-minded purpose is to ensure there is a process to report each and every minute detail. Time records, schedules, correspondence, and photos are some components of documentation, all of which, when recorded, provide evidence, summarize efforts and showcase the project.
It is one of the project manager’s responsibilities to see that all tasks and everyone’s contributions are recorded for reference during and after the gestation of a project.
Thus, the role of the project manager as a Chronicler of a project lifecycle is clear.
6. Communication
It is not enough for a project manager to record and document project details, but it should be done in such a way that stakeholders and anyone interested in the project understand every nuance.
For effective communication, it is another of the project manager’s responsibilities to put in place a proper mode (telephone, fax, encrypted, messenger) multiple channels (emails, memos, reports, press releases), and message structure – five W’s, i.e, Why, What, Where, When, Who, and one How.
So steering all aspects of a project shapes the role of the project manager as a communicator.
7. Strategic Influence
The different project manager responsibilities extend the sphere of influence wielded by a project manager to stakeholders, suppliers, customers, end-users, sponsors, governing bodies, steering committees; project team members, resource managers, and industry peers.
Case Studies in the Roles and Responsibilities of Project Managers
Case Study 1: The Mars Pathfinder Mission, Leadership Under Constraints
Source: Mars Case Study
In the mid-1990s, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) launched the Mars Pathfinder mission, a groundbreaking project designed to demonstrate that complex space missions could be achieved faster, better, and cheaper. The mission’s goal was to deliver a robotic lander and rover, Sojourner, to Mars for scientific exploration at a fraction of the traditional cost and time.
The project manager’s role was central to the mission’s success. Operating under intense budgetary and timeline pressures, the PM had to integrate resource planning, risk mitigation, and cross-disciplinary communication across hundreds of scientists, engineers, and vendors.
Key leadership actions included:
- Comprehensive Planning: Breaking the mission into tightly controlled phases to ensure precision without over-engineering.
- Proactive Risk Management: Implementing redundancy in critical systems to minimize the chance of mission failure.
- Continuous Quality Monitoring: Introducing iterative testing cycles that improved reliability while reducing cost.
- Team Motivation and Communication: Maintaining morale across distributed technical teams working on unprecedented challenges.
Despite a tight budget ($265 million versus the $1 billion average for comparable missions), the Mars Pathfinder launched flawlessly in 1996 and successfully landed on Mars in 1997. It became a textbook example of how strong planning, team coordination, and adaptive leadership can turn constraints into innovation opportunities.
Key Takeaway for Project Managers:
Great project managers transform limitations into levers of creativity. Through meticulous planning and proactive communication, even the most ambitious goals can be achieved within limited resources.
Case Study 2: The Channel Tunnel (“Chunnel”) – Lessons in Risk and Stakeholder Management
Source: PMI Case Study
The Channel Tunnel (or Chunnel) project, connecting the United Kingdom and France, stands as one of the most ambitious civil engineering projects of the 20th century. The 50-kilometer undersea tunnel was conceived to improve trade and travel between the two nations, but its success came at enormous cost and complexity.
The project managers on both sides faced the daunting task of coordinating thousands of
\workers, engineers, and government agencies across two countries with differing regulations, political expectations, and financial pressures.
Key project management lessons from this case include:
- Risk Identification and Mitigation: Early cost projections proved inaccurate, leading to significant overruns. The PM teams learned the importance of dynamic risk registers and continuous scenario planning.
- Stakeholder Communication: Balancing the interests of investors, governments, and the public required exceptional diplomatic and communication skills.
- Strategic Alignment: Maintaining clarity on the project’s shared vision helped both nations stay committed despite mounting costs.
- Change Management: Shifts in design and compliance standards during construction demanded rapid adaptation and cross-border collaboration.
Although the Chunnel was ultimately completed in 1994, well over budget but technically successful, it remains one of the best-documented examples of how large-scale stakeholder complexity and risk exposure can test every facet of a project manager’s responsibilities.
Key Takeaway for Project Managers:
Effective communication, transparent risk reporting, and cross-functional collaboration are non-negotiable when managing high-stakes, multi-partner projects.
7 Practical Tips to Become a Successful Project Manager
The project manager’s role is essential to the success of any project and it requires attention to minute details. Not every project manager knows how to handle hurdles that might come up during any project. Time and experience will always work in your favor and so will a few expert tips too.
There is no specific way to ensure the success of a project, but there are a few tips that help you come out with notable results.
So, let’s take a look at 7 practical tips for project managers to succeed. Let’s get started:
1. Find Yourself a Mentor
Look for a mentor who is a seasoned project manager. Just by watching them work, you will learn a lot. See how they tackle issues, how they interact with shareholders, and team members, and in all other aspects related to the project. On many occasions, companies do provide a mentor when you first start as a project manager, but if they do not, then your first step to success in becoming a better project manager lies in finding a good mentor and learning as much as possible.
2. Effective Use of Teamwork
Your project will be successful only if your team succeeds. A project manager’s job is not just to serve as a leader, but also to serve as an effective team player. Take some time and understand your team and its members, and know their strengths and skills. It is your job to get the team to work together and deliver the service or product which ultimately provides value to the customer.
3. Know Your Customer
It is better to know who your customers are as individuals and as an organization. Understand the customer’s goals, vision, and mission and identify what they really care about and how they are communicating the same. Learn how they deal with change and when there is confusion. If you can react to your customers during a change in an appropriate and meaningful manner, then there is a higher percentage of guarantee that your project will be a success.
4. Be Prepared for Change
Changes happen all the time in a project. Ask any experienced project manager out there, when a project has happened exactly as planned. 9 out of 10 will always say there were changes in the project as it progressed. So, do not fret when changes occur. The key is to have a change management plan in place which describes how a request for change is made and how you as a project manager manage the change request. If this plan is well documented and shared with all the stakeholders of the project, you will be able to manage change in project deliverables.
5. Ask for Help
Nobody expects you to know everything when you are new to the project manager’s role. Just because you asked for help, does not mean you are not a good project manager. If you are unsure of something, ask the proper questions to seek better guidance than taking decisions that set back the project.
6. Continuous Learning is Key to Success
Every day on a project will provide new learning. Be it with human resource management, technology, communication with stakeholders, quality management, or any other aspect. Keep learning on the job and ensure you incorporate what you learn in the next project assigned to you.
7. Become a Certified Professional
Certifications can be an asset to any individual’s career. Project Management Certification Courses like Project Management Fundamentals Course, PRINCE2 Training, CAPM Course, and PMP Exam Prep Training, are globally recognized credentials that impart knowledge of best practices in Project Management. With these skills, Project Management is streamlined, instead of being a practice area full of unknown variables.
Conclusion
Project management isn’t just about managing deadlines, budgets, or reports; it’s about managing people, possibilities, and progress. A great project manager brings order to uncertainty, keeps teams motivated when things get tough, and helps turn ideas into outcomes that truly make a difference.
The more you grow in this role, the more you realize that success doesn’t come from perfection; it comes from adaptability, empathy, and the willingness to keep learning. Every project teaches something new: how to listen better, plan smarter, and lead with balance.
So, if you’re just stepping into project management or have led dozens of initiatives already, remember this: every successful project starts with a leader who never stops improving.