Quality Assurance (QA) ensures products or services meet the highest standards before reaching customers. It’s a way for businesses to check their work, fix problems early, and deliver something they can be proud of. QA is not just a task; it’s a promise to customers that they will receive something reliable, safe, and worth their trust.
In this blog, we’ll break down what QA means, why it matters, and how it helps businesses succeed. QA is key to creating better products and services, from saving costs to building customer loyalty. If you’re curious about how companies maintain quality and improve their processes, keep reading to uncover the basics of Quality Assurance!
Table of Contents
- What is Quality Assurance?
- Importance of Quality Assurance
- Methods Used in Quality Assurance
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
- QA Standards
- QA in Software
- QA Team
- QA vs Testing
- Use of QA in Industry
- Example of Quality Assurance
- Conclusion
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance (QA) is like the foundation of a business’s efforts to maintain product quality and meet industry standards. It involves a series of organized steps to ensure products consistently meet certain quality standards.
Essentially, QA is about always finding ways to improve products. By implementing QA processes, businesses can detect problems early on, saving time and resources while maintaining a strong reputation for quality and reliability.
For many businesses, QA is more than just a checklist of tasks; It’s a commitment to their team and customers. It’s a promise to deliver excellent products that meet expectations and create a great experience for users.
When companies make QA a priority, they show they’re serious about providing top-notch quality and are dedicated to always improving their products and services.
Businesses must understand that QA isn’t a one-time task but an ongoing process deeply ingrained in their operations. By embracing QA as a fundamental aspect of their business strategy, companies can bring a culture of quality consciousness and continuous improvement.
Companies can build strong brand loyalty and differentiate themselves from competitors by consistently delivering superior products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
QA isn’t just about meeting standards; It’s about exceeding them and setting new benchmarks for quality and innovation in the industry.
Importance of Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) is immensely important across industries for several reasons. First, it ensures that products or services meet predefined quality standards, thus enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
By consistently delivering high-quality products, businesses can build trust with their customers and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Moreover, QA helps minimize risks and costs associated with defects or errors in products or processes. By identifying and addressing issues early on, companies can avoid costly recalls, rework, and customer complaints, significantly saving time and resources.
Additionally, QA promotes continuous improvement within organizations. By establishing systematic procedures for monitoring and evaluating quality, businesses can identify areas for enhancement and implement corrective actions to optimize their processes and enhance overall efficiency.
Overall, quality assurance is essential for ensuring product integrity, maintaining customer trust, reducing costs, and driving continuous improvement, making it a successful business operation.
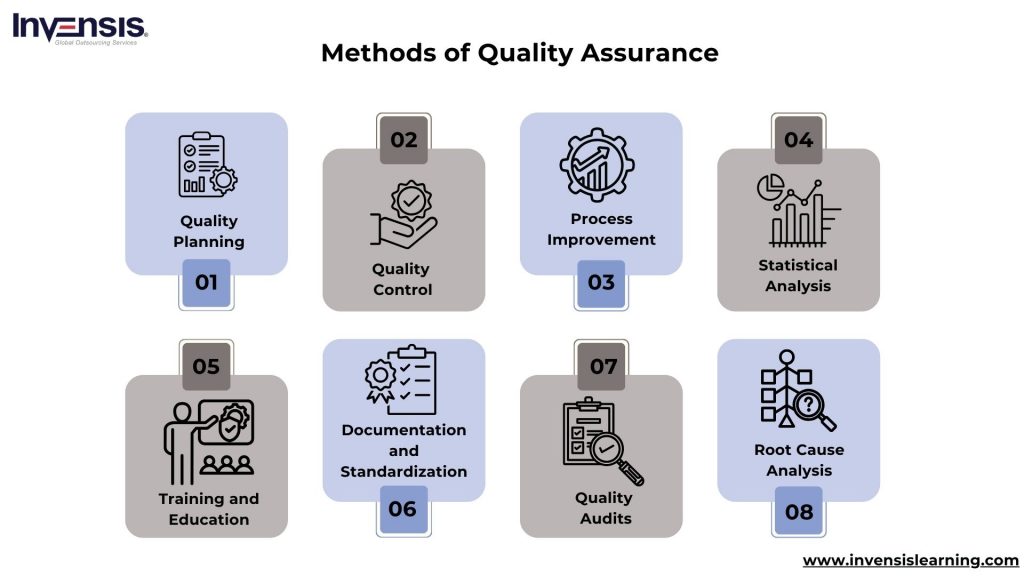
Methods Used in Quality Assurance
Software Development Methodologies Waterfall, Agile, and Scrum offer insight into three prominent approaches to software development. Each methodology offers different frameworks and strategies for managing the software development process.
Through concise analysis, this exploration provides a comprehensive understanding of these methodologies and their implications for modern software development projects.
- Quality Planning: Involves defining quality objectives, processes, and criteria necessary to meet customer requirements. It includes creating quality plans, establishing quality metrics, and setting targets for performance and reliability
- Quality Control (QC): QC involves executing planned activities to verify that products or services meet quality requirements. This may include inspections, testing, and sampling to identify defects or deviations from specifications
- Process Improvement: Continuous process improvement methodologies such as Lean, Six Sigma, and Total Quality Management (TQM) are often used in QA to identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and enhance overall quality and productivity
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical methods such as statistical process control (SPC), hypothesis testing, and regression analysis are employed to analyze data and monitor process performance over time, helping to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA): Root Cause Analysis is a systematic approach to identify the underlying causes of problems or defects and develop corrective actions to prevent recurrence. Techniques such as Fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys, and Pareto analysis are commonly used in RCA
- Quality Audits: Regular audits assess compliance with quality standards, procedures, and regulations. Audits may be internal or external and help identify non-conformities and opportunities for improvement
- Documentation and Standardization: Proper documentation of processes, procedures, and standards ensures consistency and transparency in quality assurance activities. Standardization helps streamline operations and facilitates continuous improvement efforts
- Training and Education: Providing employees with training and education on quality principles, procedures, and tools is essential for building a culture of quality and ensuring that everyone understands their role in maintaining product integrity and customer satisfaction
Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
The Quality Control team conducts tests post-product development to identify errors and bugs before the product reaches customers, focusing on rectifying issues.
Conversely, the Quality Assurance team is actively involved throughout the development process, ensuring that every part of the product aligns with quality standards and striving to deliver a satisfactory customer experience.
By working collaboratively, both teams contribute to ensuring that the end product meets or exceeds customer expectations in terms of quality and functionality.
| Aspect | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
| Objective | Ensure products or services made through processes meet quality standards | Check products or services to fix any problems and ensure they’re good enough |
| Focus | Preventing mistakes | Fixing mistakes |
| Approach | Being proactive, like planning ahead to avoid problems | Reacting to problems as they happen |
| Activities | Setting standards, making sure everyone follows them, checking how things are going | Checking products or services for problems, fixing them if needed |
| Time of Execution | All the time, from the start of making something to the end | While making something, or before it’s given to customers |
Quality Assurance Standards
QA methodologies have evolved to adapt to changing businesses as with QA standards. The most recent iteration, ISO 9001:2015, reflects a heightened emphasis on customer-centric approaches, top management’s pivotal role in organizational transformation, and the integration of continuous improvement practices.
In addition to enhancing the overall framework of ISO 9001, the 2015 version introduces structural refinements.
It provides comprehensive guidelines for risk-based decision-making, ensuring that companies remain agile and responsive to evolving market dynamics.
Quality Assurance in Software
Software Quality Assurance (SQA) aims to systematically identify patterns and necessary actions to enhance development cycles in software projects. Addressing coding errors can sometimes lead to unintended consequences, potentially breaking other features or functionalities in the process.
As developers increasingly prioritize proactively avoiding errors, SQA has become crucial, saving time and expenses in the development process. Despite the implementation of SQA processes, software updates can still introduce defects, commonly called bugs.
Various strategies exist within the domain of SQA. For instance, the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) focuses on performance improvement by assessing maturity levels across organizational areas and suggesting enhancements, ranging from disorganization to optimal efficiency.
Software development methodologies, including Waterfall, Agile, and Scrum, have evolved to incorporate SQA practices.
- Waterfall follows a linear progression from requirements gathering to release, often criticized for its perceived slowness, prompting the emergence of alternative methodologies
- Agile, a team-centric approach, treats each step as a sprint, offering adaptability but reduced predictability due to potential changes in project scope
- Scrum combines aspects of both methodologies, dividing developers into teams for specific tasks, with each task segmented into multiple sprints
To implement an effective QA system, it is essential to establish standardized goals, considering the benefits and drawbacks of each approach, such as maximizing efficiency, reducing costs, or minimizing errors.
Management commitment to process changes and collaborative efforts to support and uphold quality standards are essential to successful QA implementation.
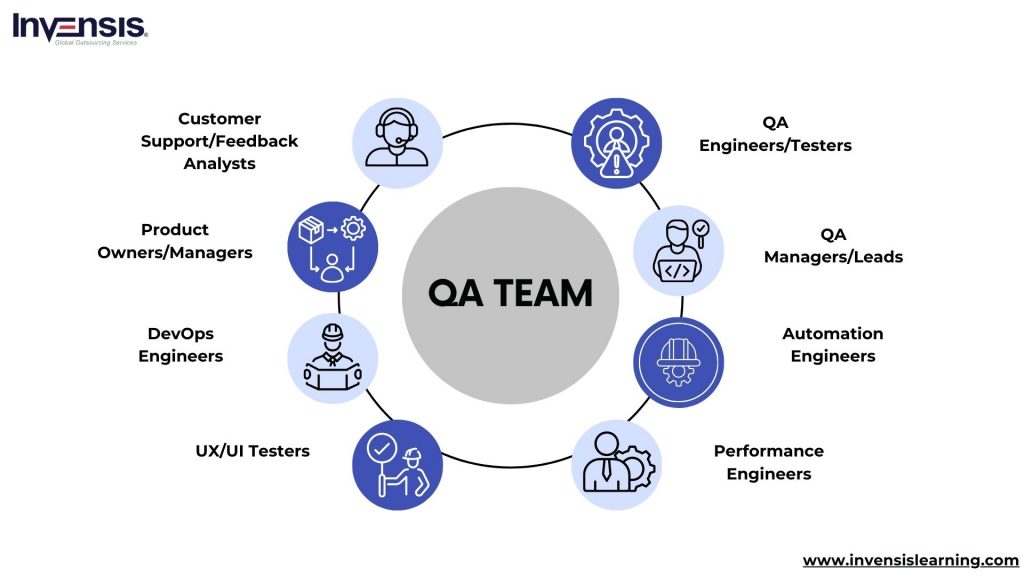
QA Team
Quality involves a collaborative effort by various professionals who play distinct yet interrelated roles within the quality assurance and testing stream. Let’s take a closer look at the key individuals involved in this process and their unique contributions to ensure the delivery of high-quality software products.
Here are some key roles commonly found in a QA team!
- QA Engineers/Testers: They execute test cases, identify defects, and ensure the software meets quality standards
- QA Managers/Leads: They oversee the QA process, coordinate testing activities, and ensure testing objectives are met. QA Managers may also create test plans and manage the QA team
- Automation Engineers: They develop and maintain automated testing scripts to streamline the testing process and improve efficiency
- Performance Engineers: They focus on testing the performance, scalability, and reliability of software applications under different conditions, such as heavy loads or high traffic
- UX/UI Testers: They evaluate the software’s user experience and interface design to ensure that it is user-friendly and meets user expectations
- DevOps Engineers: DevOps Engineers collaborate with developers and QA team members to integrate testing into the software development lifecycle and automate deployment processes
- Product Owners/Managers: Product Owners provide input on quality requirements, prioritize features, and collaborate with the QA team to ensure the software meets user needs and business objectives
- Customer Support/Feedback Analysts: They gather feedback from customers and end-users, identify issues or areas for improvement, and communicate these findings to the QA team for further investigation and resolution
QA Vs. Software Testing
Quality Assurance and Software Testing are crucial for delivering high-quality products in software development. QA focuses on establishing standards and processes to optimize development, while Testing evaluates functionality to identify defects. Understanding their distinctions is key to implementing effective quality strategies.
Quality Assurance (QA)
- QA is a comprehensive process that ensures the software development process is efficient and effective in delivering a high-quality product
- It involves defining and implementing processes, standards, and methodologies to ensure that the software development life cycle is well-managed and that quality is built into the product
- QA encompasses establishing quality standards, defining processes, conducting audits, and ensuring compliance with standards and best practices
- It is a proactive approach aimed at preventing defects and ensuring that the development process itself can produce high-quality software
Software Testing
- Software testing is a subset of QA that verifies the software behaves as expected and meets the defined requirements
- Testing involves executing the software with the intent of finding defects or errors. This includes validating functionality, performance, security, usability, and other quality attributes
- Testing can be manual or automated and involves techniques such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing, and regression testing
- While QA concerns the entire software development process, testing is primarily concerned with evaluating the product itself to identify and address defects
Use of QA in Industry
Quality assurance is a cornerstone across diverse industries, ensuring products and services meet strict standards and regulations. From manufacturing to healthcare, software development to construction, QA processes safeguard quality, reliability, and compliance, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and industry reputation.
- Manufacturing: QA ensures that products meet quality standards throughout production, reducing defects and enhancing reliability
- Healthcare: QA processes ensure compliance with regulations, accuracy in diagnosis, and safety in patient care, ultimately improving healthcare outcomes
- Software Development: QA verifies that software meets requirements, functions correctly, and is user-friendly, enhancing user satisfaction and reducing errors
- Construction: QA ensures adherence to building codes and standards, resulting in safe and durable structures
- Food Industry: QA ensures food safety, hygiene standards, and compliance with regulations, safeguarding consumer health
- Automotive Industry: QA verifies the safety, performance, and reliability of vehicles, enhancing customer satisfaction and brand reputation
Example of Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance demonstrates the multifaceted role of quality assurance across industries, highlighting its key function in ensuring product and service excellence. A quality assurance examples can be seen in monitoring manufacturing processes to optimize customer service and regulatory compliance; QA is critical in identifying and rectifying issues before they escalate.
Through collaborative efforts and proactive measures, QA teams uphold standards, enhance operational efficiency, and bring trust among stakeholders, ultimately contributing to organizational success and customer satisfaction.
Customer Service Enhancement
In businesses providing customer service, quality assurance ensures customer interactions meet high standards and resolve issues effectively.
For instance, if a telecommunications company notices a rise in customer complaints about billing errors, the quality assurance team will investigate the root cause. Upon finding that a recent software update led to billing contrasts, they would collaborate with the IT department to rectify the issue promptly.
Additionally, they recommend implementing new training protocols for customer service representatives to handle billing inquiries better, ensuring a smoother customer experience and preventing further complaints.
Product Development Optimization
Quality assurance extends to product development processes to ensure that products meet customer needs and expectations. Consider a software development company releasing a new mobile application.
If user feedback indicates frequent crashes and performance issues, the quality assurance team would analyze user reports and conduct descriptive testing to identify bugs and usability issues.
Subsequently, they would collaborate with developers to prioritize and address these issues, ensuring that subsequent updates enhance the application’s functionality and user experience.
Through continuous monitoring and improvement, the quality assurance team helps optimize product development processes and deliver superior products.
Regulatory Compliance Assurance
In industries subject to strict regulations, such as finance or healthcare, quality assurance is crucial in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
For example, a pharmaceutical company receiving reports of adverse effects from a newly launched medication would prompt the quality assurance team to investigate.
Upon discovering discrepancies in manufacturing processes leading to dosage variations, they would initiate corrective actions to rectify the issue and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Additionally, they would implement enhanced monitoring procedures to prevent similar deviations in the future, safeguarding both patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Data Integrity and Privacy Protection
Maintaining data integrity and protecting user privacy are paramount concerns for businesses in the digital age. Quality assurance teams collaborate closely with IT departments to safeguard data against breaches and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Suppose an e-commerce platform detects unauthorized access to customer payment information. In that case, the quality assurance team would promptly investigate the security breach, assess the extent of the damage, and implement measures to enhance cybersecurity protocols.
By conducting thorough audits and implementing encryption technologies, they mitigate risks and reinforce data integrity, fostering customer trust and preserving the company’s reputation.
Conclusion
Understanding what quality assurance is essential for businesses striving to deliver exceptional products and services. Through meticulous planning, implementation of standards, and continuous improvement, It ensures that organizations meet customer expectations, comply with regulations, and maintain competitive advantages in their respective industries.
By recognizing the importance of quality assurance, embracing appropriate methods and standards, and distinguishing it from quality control, businesses can foster a culture of quality excellence. From software development to manufacturing, quality assurance in every aspect of the industry, safeguarding reputation and driving success.
Take your understanding of Quality Management Courses to the next level by enrolling in quality management certification courses offered by Invensis Learning. Gain valuable insights, enhance your skills, and become a certified quality management professional to lead your organization towards excellence in quality assurance. Join us today to embark on your journey towards mastering quality management principles and practices.