Managing projects today means balancing multiple moving parts, tight deadlines, remote teams, stakeholder demands, and evolving risks. Without the right tools, even well-planned initiatives can drift off course. That’s why Microsoft Project has remained a cornerstone of project management for decades, helping professionals bring order, structure, and clarity to complex workflows.
The need is real: the Project Management Institute (PMI) notes that poor scheduling and unclear objectives consistently rank among the top causes of project failure, issues Microsoft Project is specifically designed to solve.
In this guide, we’ll explore what Microsoft Project is, its key features, benefits, use cases, and how it continues to evolve in 2025.
Table Of Contents
- What is Microsoft Project?
- History of Microsoft Project
- Key Features of Microsoft Project
- Benefits of Using Microsoft Project
- How Does Microsoft Project Work?
- Common Use Cases for Microsoft Project
- Conclusion
What is Microsoft Project?
Microsoft (MS) Project is a project management software developed and sold by Microsoft. It is designed to assist project managers in developing plans, assigning resources to tasks, tracking progress, managing budgets, and analyzing workloads. Although the first version of MS Project was released in 1984, it has evolved into a comprehensive project management tool that organizations of all sizes widely use.
Microsoft Project provides a wide range of features, including Gantt charts, which are used to visualize and schedule projects; resource management tools that help project managers to assign tasks and manage resources; and budget management tools that help track project costs and expenses. And reporting features that enable project managers to analyze and communicate project status to stakeholders.
Over the years, MS Project has undergone several upgrades, adding new features and improving existing ones.
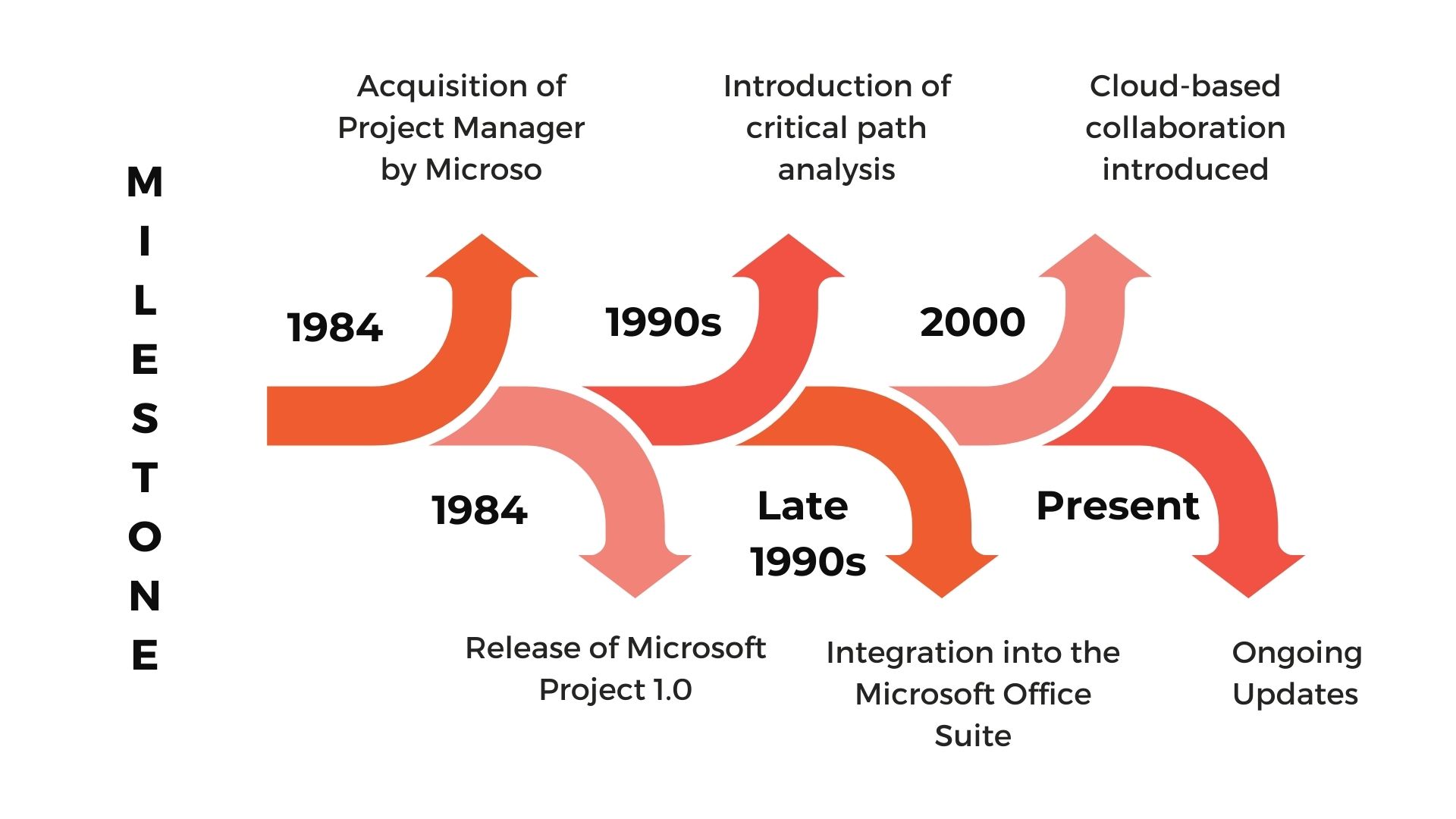
History of Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project is a powerful project management software developed by Microsoft Corporation. It has a long and influential history in project management, pivotal in helping individuals and organizations plan, track, and manage projects efficiently. Let’s take a journey through its development and evolution.
Early Beginnings
The roots of Microsoft Project can be traced back to the early 1980s when it was initially developed as a DOS-based software called “Project Manager.” Created by a small company named SuperProject Inc., this early version laid the foundation for what would eventually become Microsoft Project.
In 1984, Microsoft acquired SuperProject Inc., and with this acquisition, they gained access to the technology and expertise behind Project Manager. This marked the first step in Microsoft’s foray into the project management software market.
Microsoft Project 1.0
The first official version of Microsoft Project, “Microsoft Project 1.0,” was released in 1984. This version was compatible with the Windows operating system and brought a user-friendly graphical interface, making it easier for project managers to visualize and manage their projects. Microsoft Project 1.0 was well-received, and its success encouraged Microsoft to continue investing in its development.
Constant Improvements and Upgrades
Over the years, Microsoft continued to enhance and upgrade Projects, incorporating user feedback and adapting to changing project management needs. With each iteration, new features and capabilities were added, solidifying its position as one of the leading project management tools in the industry.
Notable milestones in the history of Microsoft Project include introducing critical path analysis, resource management, and advanced scheduling features. These additions improved the software’s ability to handle complex projects and efficiently align resources.
Integration with Microsoft Office Suite
In the late 1990s, Microsoft Project underwent significant changes with its integration into the Microsoft Office Suite. This integration allowed users to seamlessly collaborate with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Excel, Word, and Outlook, facilitating the exchange of project data and enhancing overall productivity.
Cloud-Based Collaboration
With the advent of cloud computing and the increasing demand for remote work capabilities, Microsoft introduced cloud-based versions of Project, enabling teams to collaborate in real-time, regardless of their physical locations. This move made project management more accessible and convenient for users worldwide.
Present and Future
Today, Microsoft Project continues to evolve and remains a popular choice for project managers across various industries. It has expanded its reach to support diverse project types, from small-scale initiatives to large enterprise-level endeavors.
With regular updates and ongoing improvements, Microsoft Project remains a vital tool for professionals seeking efficient project planning, tracking, and execution.
Table: Key Milestones in the History of Microsoft Project
|
Year |
Milestone |
| 1984 | Acquisition of Project Manager by Microsoft. |
| 1984 | Release of Microsoft Project 1.0. |
| 1990s | Introduction of critical path analysis, resource management, and advanced scheduling features. |
| Late 1990s | Integration into the Microsoft Office Suite. |
| 2000s | Cloud-based collaboration introduced. |
| Present | Ongoing updates and continuous development. |
Maximize productivity with Invensis Learning’s Microsoft Project training! Try it today to seamlessly handle the project.
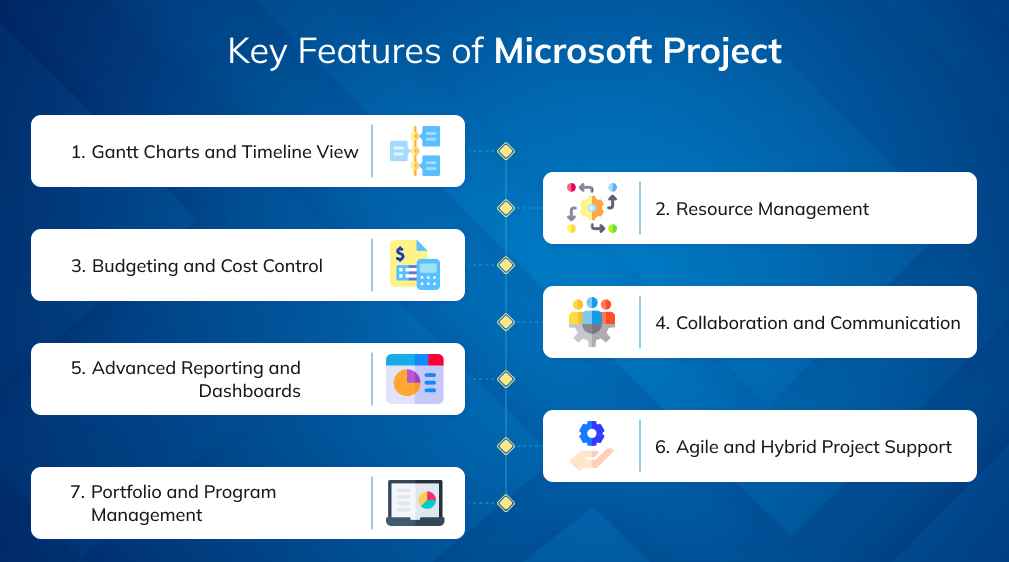
Key Features of Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project has earned its place as one of the most trusted project management solutions by combining powerful planning tools with enterprise-level control and integration. Here’s a closer look at the features that make it indispensable:
Let us now take a detailed look at Microsoft Project features:
1. Gantt Charts and Timeline View
Microsoft Project is best known for its Gantt charts, which provide a clear visual timeline of tasks, dependencies, and milestones. This helps project managers anticipate bottlenecks and communicate timelines effectively with stakeholders.
- Drag-and-drop scheduling makes adjustments simple.
- Dependencies ensure tasks automatically realign when timelines shift.
2. Resource Management
Efficient use of people, equipment, and materials can make or break a project. Microsoft Project’s resource allocation and workload balancing tools help managers prevent overbooking and underutilization.
- View resource capacity across multiple projects.
- Optimize workloads to prevent burnout or idle time.
| PMI’s Pulse of the Profession notes that 23% of projects fail due to poor resource allocation, highlighting the importance of tools like this. |
3. Budgeting and Cost Control
Project overruns are one of the most common pain points for organizations. Microsoft Project allows for detailed budget forecasting, cost tracking, and variance analysis, enabling leaders to maintain financial discipline.
- Compare planned vs. actual spend in real time.
- Forecast costs across multiple scenarios.
4. Collaboration and Communication
In today’s hybrid work environment, collaboration is non-negotiable. Microsoft Project integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Teams, Outlook, and SharePoint, allowing stakeholders to access schedules, provide updates, and share documents without switching platforms.
- Real-time task updates within Teams.
- Centralized communication tied to project milestones.
5. Advanced Reporting and Dashboards
One of Microsoft Project’s strengths is its ability to generate customized reports and interactive dashboards. By integrating with Power BI, teams can create data-rich visuals that highlight progress, risks, and ROI.
- Build stakeholder-specific dashboards.
- Export and share reports directly with executives.
6. Agile and Hybrid Project Support
While originally designed for Waterfall methodologies, Microsoft Project now supports Agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban. This flexibility makes it ideal for organizations running hybrid approaches.
- Manage sprints, backlogs, and boards.
- Switch between Agile and traditional views as needed.
7. Portfolio and Program Management
For enterprises, Microsoft Project extends beyond individual projects into portfolio management. This enables executives to prioritize initiatives, balance investments, and align projects with business strategy.
- Evaluate portfolio performance in real time.
- Optimize project selection against resource availability.
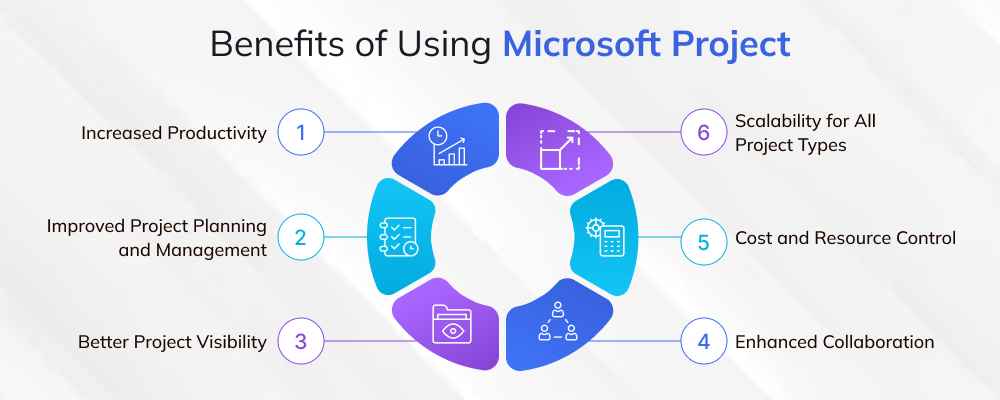
Benefits of Using Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project provides a wide range of benefits that make it one of the most trusted project management tools across industries. From productivity gains to organizational visibility, its impact is measurable.
1. Increased Productivity
MS Project automates routine project management tasks such as scheduling, task tracking, and reporting, allowing teams to focus on higher-value work.
- Customizing Microsoft Project to match project management processes has been shown to boost efficiency, as features grouped by phases reduce navigation time. (MPUG)
- This streamlined approach helps managers spend less time switching between views and more time managing project execution.
2. Improved Project Planning and Management
Features such as Gantt charts, critical path analysis, and workload balancing provide project managers with a clear view of dependencies and timelines, ensuring projects stay on track.
- In a large ERP rollout, Microsoft Project Portfolio Management (PPM) ensured clarity of scope, balanced reporting, and structured communication with executives, which reduced misalignment and improved delivery consistency.
3. Better Project Visibility
Real-time dashboards and reporting tools give project managers and stakeholders up-to-date insights into project progress and costs.
- At Microsoft’s EMEA Customer Support PMO, a reporting system built on Microsoft Project provided visibility into ~180 active projects within six months, significantly improving governance and decision-making.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Integration with Microsoft Teams, SharePoint, and Office 365 makes it easy for distributed teams to collaborate.
- The EMEA PMO case study showed how moving from fragmented tracking to a centralized Microsoft Project dashboard enabled standardized reporting and faster stakeholder alignment across countries.
5. Cost and Resource Control
Microsoft Project includes robust tools for resource allocation and cost monitoring. Managers can compare planned vs. actual costs, identify resource conflicts, and forecast requirements.
- Microsoft Project Server has been shown to improve enterprise-wide consistency in resource management, reducing overcommitments and allowing better cost forecasting. (PMI).
6. Scalability for All Project Types
From small team initiatives to enterprise programs, Microsoft Project adapts to different scales and industries.
- Its flexibility has been demonstrated in industries as varied as IT, healthcare, construction, and government, where it supports both traditional Waterfall and Agile approaches.
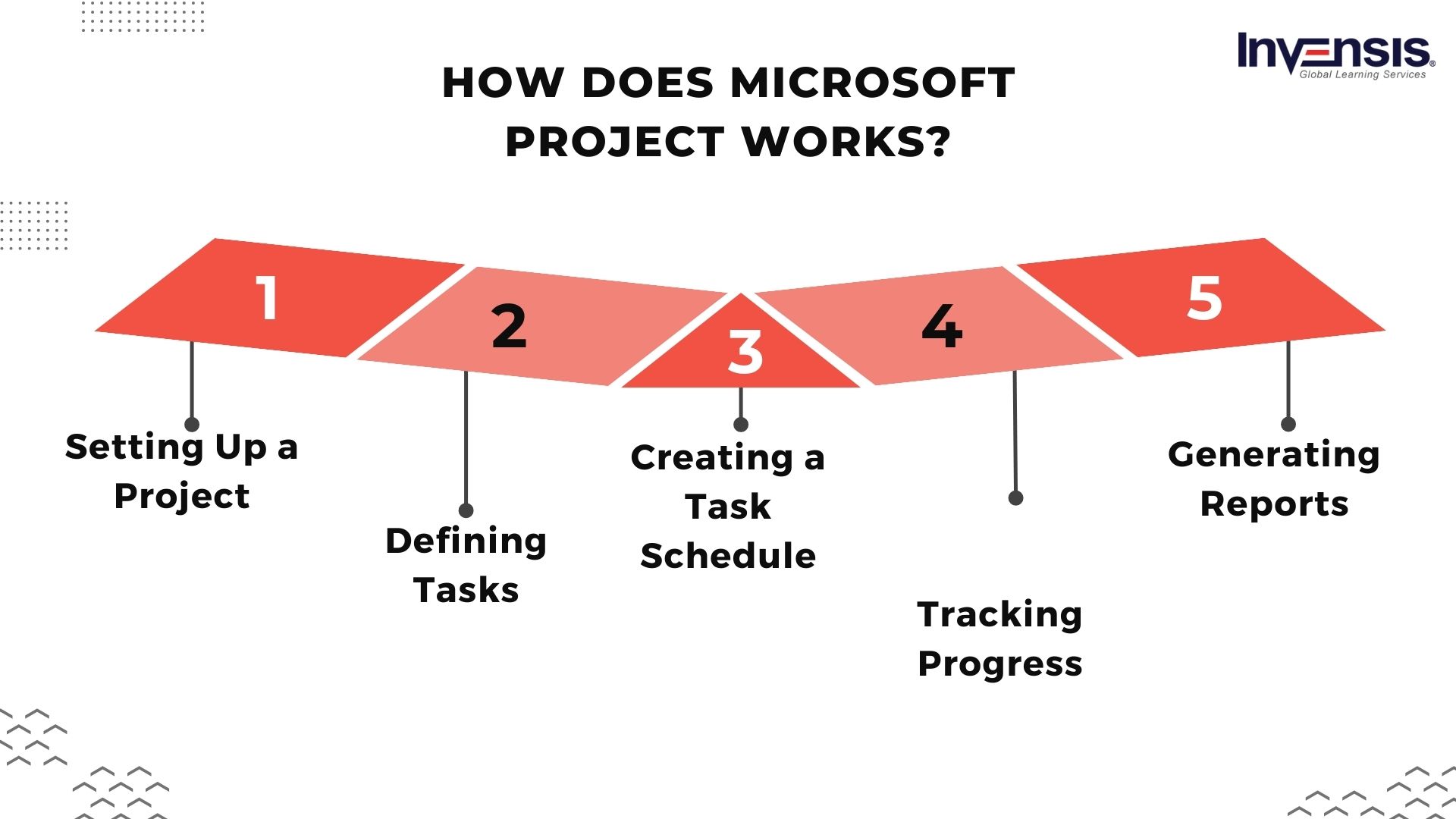
How Does Microsoft Project Work?
Microsoft Project is a project management software that helps individuals and teams plan, execute, and manage projects effectively. It can be used for various projects, including software development, construction, and event planning. Here is a basic overview of the steps involved in using MS Project:
Setting Up a Project
Before you start using Microsoft Projects, you need to set up the basic information for your project. This includes defining the project start date, end date, work hours, and calendar. You can also set up a project summary task to help you keep track of the overall progress of your project.
Defining Tasks
Once you have set up the basic information for your project, the next step is to define the tasks that need to be completed. You can add tasks, set task durations, and specify task dependencies. You can assign resources to tasks, such as people, equipment, or materials.
Creating a Task Schedule
After you have defined your tasks, you can use Microsoft Project to create a task schedule. The software will automatically calculate each task’s start and end dates based on your defined task durations and dependencies. You can also use the software to create a Gantt chart, a visual representation of the task schedule.
Tracking Progress
You can use MS Projects to track your progress as you work on your project. For example, you can update the status of tasks, including the percentage of work completed, and see the impact of any changes on the overall project schedule. You can also track resource utilization, such as the number of hours each person works on the project.
MS Project also provides tools for managing resources, such as people and equipment.
For example:
You can assign resources to tasks, view resource utilization, and resolve conflicts.
You can also use the software to track the cost of the project, including labor costs and material costs.
Generating Reports
Finally, you can use Microsoft Project to generate reports that help you communicate the status of your project to stakeholders.
For example:
You can create reports that show the overall project schedule, task status, resource utilization, and project costs. You can also export data from Microsoft Projects to other software programs, such as Microsoft Excel, for further analysis.
This is a basic overview of the steps involved in using Microsoft Project. However, the software is a powerful project management tool, and many features and functions go beyond what is covered here.
Common Use Cases for Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project is a popular project management tool that can be used in a variety of industries. Some common use cases for Microsoft Project include:
Case Study 1: South Gloucestershire Council – Transforming Portfolio Visibility
South Gloucestershire Council in the UK managed hundreds of projects using spreadsheets and fragmented tools, making it difficult to maintain visibility and align initiatives with strategic priorities. To address this, the Council adopted Microsoft Project Online as its central project and portfolio management platform.
- Challenge: Lack of visibility across ongoing projects, delays in resolving issues, and difficulty aligning resources with critical initiatives.
- Solution: Implementing Project Online provided a standardized platform for scheduling, reporting, and issue tracking.
- Outcome:
- Achieved complete visibility of project portfolios, improving decision-making at the executive level.
- Reduced the time spent on issue resolution by providing real-time dashboards.
- Improved accountability and transparency across departments.
Source: Tech Associates Case Study – South Gloucestershire Council
Case Study 2: The Go-Ahead Group – Building a Next-Gen PMO
The Go-Ahead Group, one of the UK’s largest public transport operators, needed a modern project management framework to handle its diverse and growing set of business initiatives. They implemented Microsoft Project Online to establish a next-generation Project Management Office (PMO).
- Challenge: Siloed reporting systems and inconsistent project governance across multiple subsidiaries.
- Solution: Using Microsoft Project Online, the company introduced standardized governance, portfolio reporting, and centralized budget tracking.
- Outcome:
- Gained enterprise-wide portfolio visibility to track project status in real time.
- Improved resource management across departments, resulting in reduced duplication of effort.
- Enhanced budget oversight and financial accountability.
Source: Tech Associates Case Study – The Go-Ahead Group
Conclusion
Microsoft Project is a powerful project management tool that enables individuals and teams to plan, track, and execute projects efficiently and effectively. With its wide range of features, including task scheduling, resource allocation, and progress tracking, Microsoft Project is an essential tool for project managers, team leaders, and other professionals involved in project management.
Whether managing a small personal project or a large-scale corporate initiative, Microsoft Project can help you stay on top of your tasks and keep your project on track. Want to get a deeper understanding of Microsoft Projects? Take Invensis Learning’s Microsoft Project Certification Training to enhance your knowledge in project management.