COBIT 5 framework or Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies 5 framework was developed to guide IT governance and management. The COBIT 5 framework was first released by ISACA in April 2012 and is essential to developing, controlling, and maintaining risk and security for organizations worldwide.
IT Governance frameworks help align IT Strategy and Business Strategy to ensure that IT investments support business objectives. By following a framework, companies can produce measurable results towards achieving their strategies and goals. A formal program also considers the stakeholders’ interests as well as the needs of staff and the processes they follow.
Who Needs IT Governance?
Any organization that needs to comply with regulations related to financial and technological accountability. Implementing an IT governance program requires a lot of time and effort. Some companies may only practice essential IT governance methods, but larger and more regulated organizations have a full-fledged IT governance program.
The easiest way to implement an IT governance program is to start with a pre-designed framework. Many frameworks include guides to help organizations phase in an IT governance program with fewer issues. The most used frameworks are COBIT, ITIL, CMMI, and FAIR.
How to Select an IT Framework?
IT governance frameworks are designed to determine how your IT department is functioning overall, the key metrics management needs, and what IT is giving back to the business from its investments. When reviewing frameworks, it has to be checked if a particular framework or model seems natural for the organization. And does it resonate with the stakeholders? If yes, then that framework is probably the best choice. Some companies also include multiple frameworks together.
For example, COBIT and ITIL can be implemented together in an organization, or COBIT along with COSO (for managing information security) can be implemented along with ISO 270001.
How do you Ensure a Smooth Implementation?
To gain executive buy-in, you need to view that team as you would your buyers. It starts with understanding the problems they see in the business and focusing your efforts on solving them. One has to speak to the high-level benefits of the framework and how it addresses those problems.
For this to happen, a risk management committee with an executive sponsor and representation from the business must be formed. One should always keep the communication lines open for various parties, measure and monitor the progress, and seek outside help if necessary.
COBIT 5 Framework
COBIT links IT STRATEGY and BUSINESS STRATEGY. It creates a process that can help bridge a gap between IT and other departments. COBIT, when compared to other frameworks, emphasizes risk management, security, and information governance.
The COBIT processes include governance objectives and management objectives.
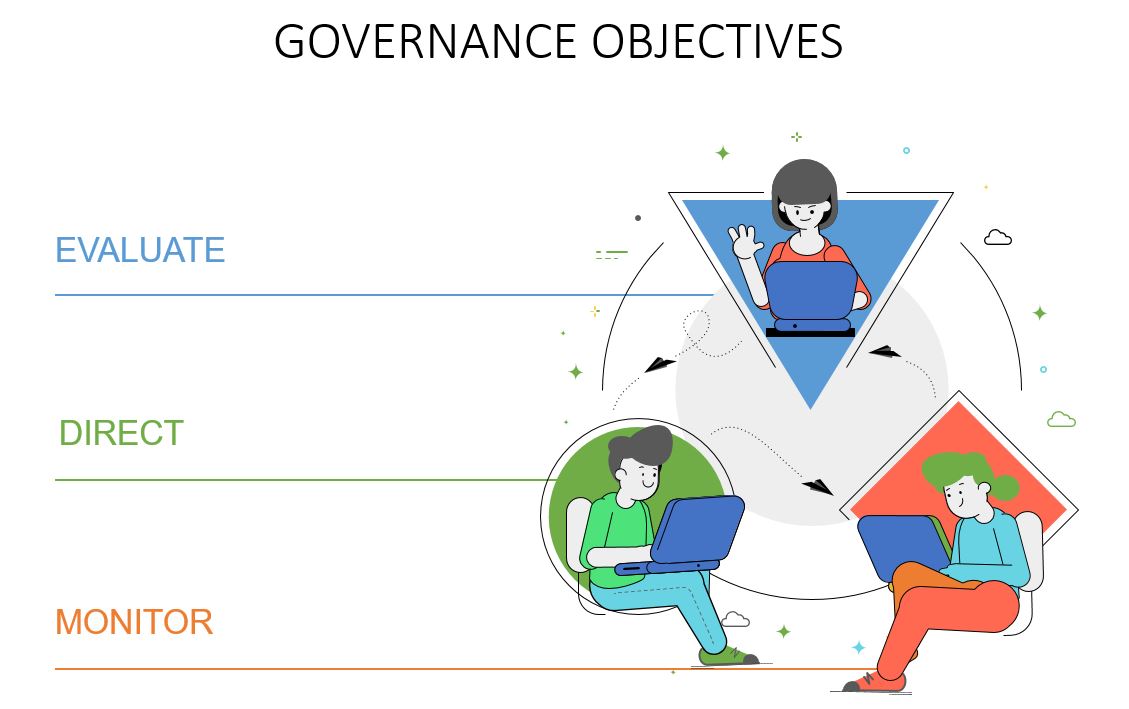
Governance Objectives
Governance objectives are Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor (EDM)
- Evaluate-It involves agreeing and identifying objectives that need to be achieved
- Direct- This includes decision-making and prioritization
- Monitor- Compliance, and performance against objectives
In short, governance objectives evaluate strategic options, direct the chosen options and monitor strategy achievement.
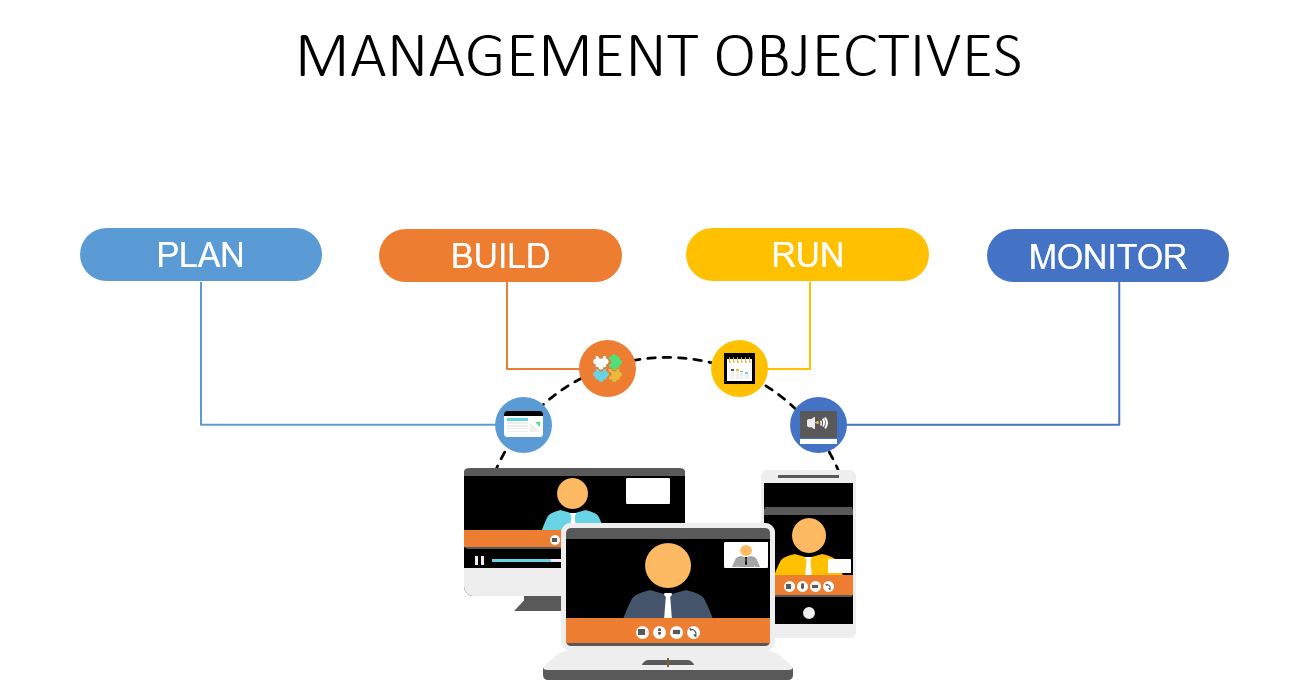
Management Objectives
Management objectives are Plan, Build, Run, and Monitor (PBRM)
The management objectives further include:
- APO (Align, Plan, and Organize) – This involves organization, strategy, and supporting activities for IT
- BAI (Build, Acquire, and Implement) – This involves the definition, acquisition, and implementation of IT solutions
- DSS (Deliver, Service, and Support) – It is the operational delivery and support of IT services
- MEA (Monitor, Evaluate and Assess) – The most important part which involves performance and conformance monitoring of IT.
In short, the management objectives are activities that are undertaken and monitored to align with the governance function’s direction.
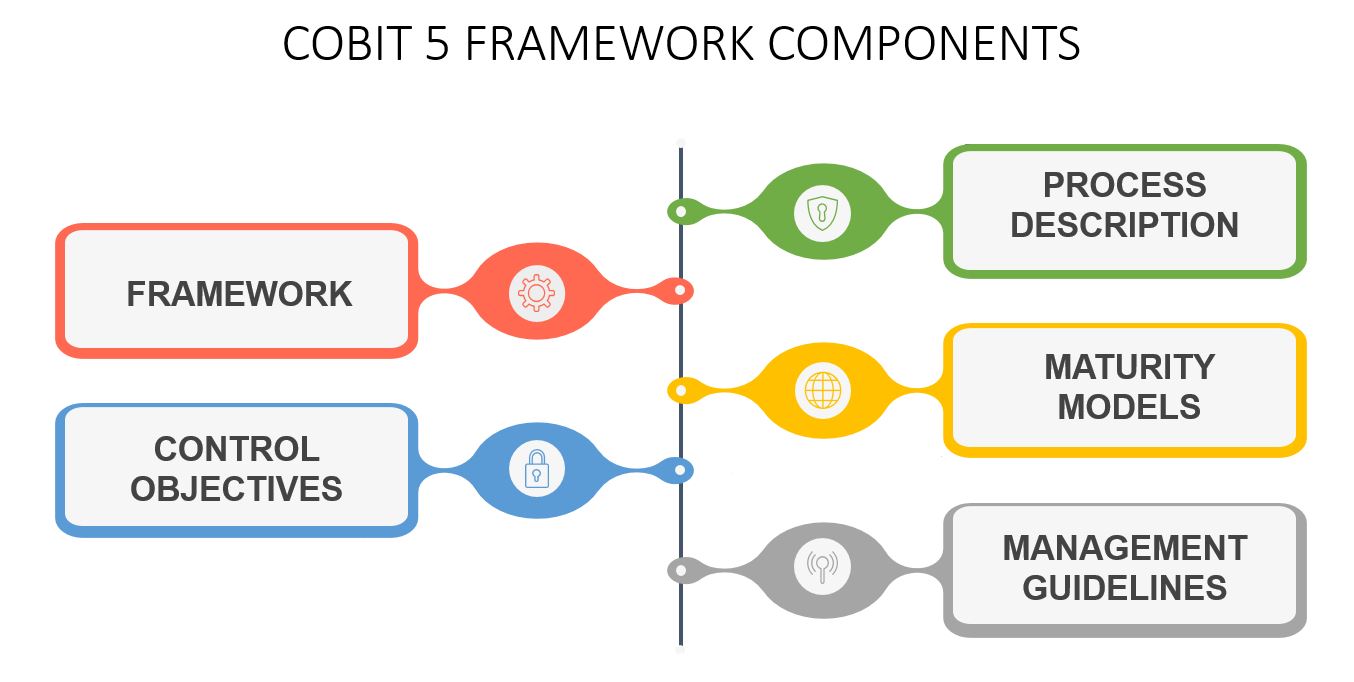
Components of COBIT 5 Framework
Adopting the COBIT framework will help enterprises to improvise and maintain important information related to business decisions. This helps organizations realize the value of
their investments in IT and achieve compliance with laws, regulations, and contractual agreements. The major components of the COBIT 5 framework are shown in the schematic below.
Framework – It organizes IT governance objectives and links them to business requirements by ensuring good practices of IT domains and processes are implemented simultaneously.
Process Description – A reference process model that is followed during the implementation, which is available for everyone working in the enterprise. It maps the responsibility areas of Plan, Build, Run, and Monitor (PBRM).
Control Objectives – Provide a complete set of high-level requirements to be considered by the management for effective control of each IT process.
Management Guidelines – These help to assign responsibility to agree on objectives and measure performance to illustrate the relationship between each individual process.
Maturity Models – Access maturity and capability for each process and help to address gaps in the implementation of the processes.
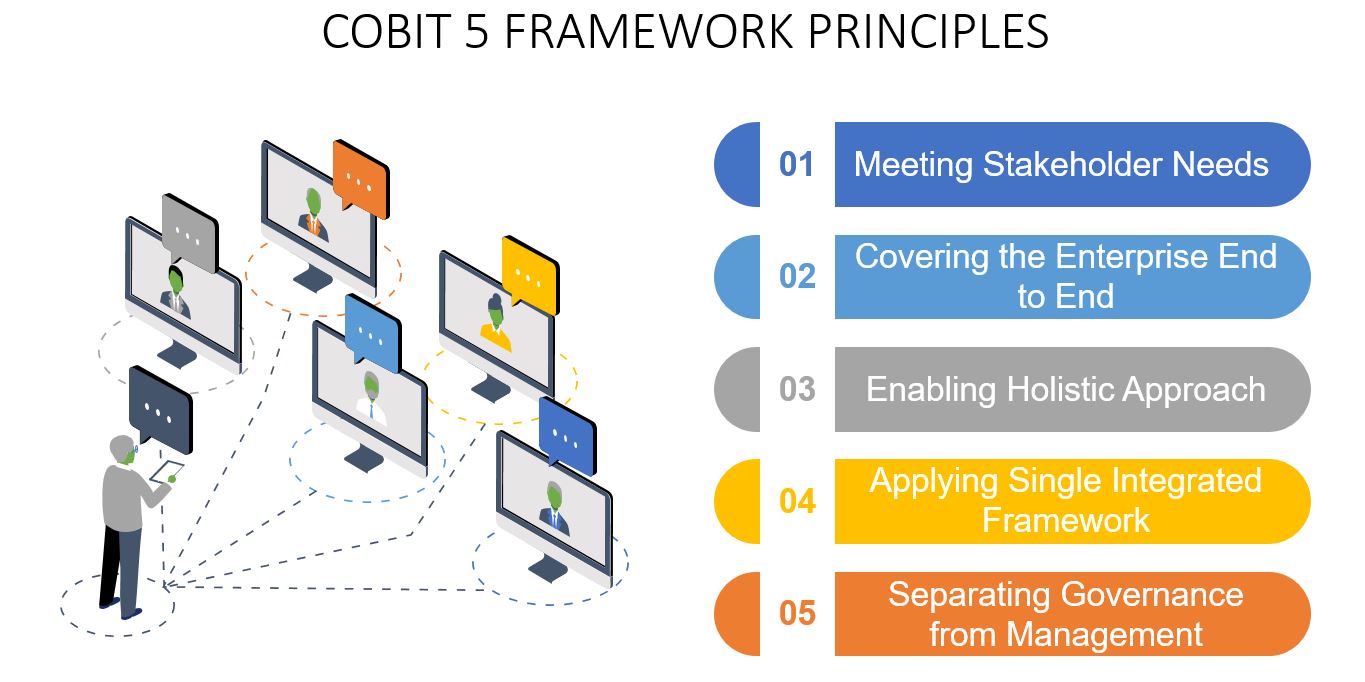
COBIT 5 Framework Principles
Adopting the COBIT framework will help enterprises to improvise and maintain important information related to business decisions. This helps organizations realize the value of
their investments in IT and achieve compliance with laws, regulations, and contractual agreements.
The five main principles of COBIT are primarily focused on meeting the needs of all stakeholders while handling governance, using a single integrated network with a holistic approach. These principles are listed below:
Meeting Stakeholder Needs
It provides all required processes and other enablers to support business value creation through the use of IT. An enterprise can customize COBIT 5 framework to suit its own context through goals cascade and translate high-level enterprise goals into manageable specific IT-related goals and map these to specific processes and practices.
For example, the business’s owners expect profits while government agencies expect the organization to obey the rules and pay its taxes on or before time. Each stakeholder’s role in the business determines the degree to which the company attempts to take in the stakeholder in planning its actions.
Covering the Enterprise End to End
Integrate governance of enterprise IT into enterprise governance. It includes all functions and processes within the enterprise. It considers all IT-related governance and management enablers to be enterprise-wide and end to end.
For example, in the IT industry, end-to-end solutions comply with a philosophy that removes as many steps as possible, which improves the efficiency and performance of a business.
Applying a Single Integrated Framework
COBIT 5 framework is a single integrated framework and it aligns with other relevant laws and regulations standards and frameworks. This permits the enterprise to use COBIT 5 framework as the overarching governance and management framework integrator.
For example, an individual from the management may be a novice when it comes to IT technology. This single integration gives a common interface for both of them to work together
Enabling a Holistic Approach
COBIT 5 framework defines a set of enablers to support the implementations of comprehensive governance along with the management system for enterprise IT that requires a holistic approach taking into account several interacting components.
For example, enablers guide as a checklist to ensure that the directives are implemented in accordance with the framework.
Separating Governance from Management
The COBIT 5 framework makes a clear distinction between governance and management. These two encompass different types of activities. Both require different organizational structure which serves different purposes.
For example, various mnemonics such as EDM(Evaluate, Direct, and Monitor) for Governance activities and PBRM(Plan, Build, Run, and Monitor) for Management activities are used to separate both from each other.
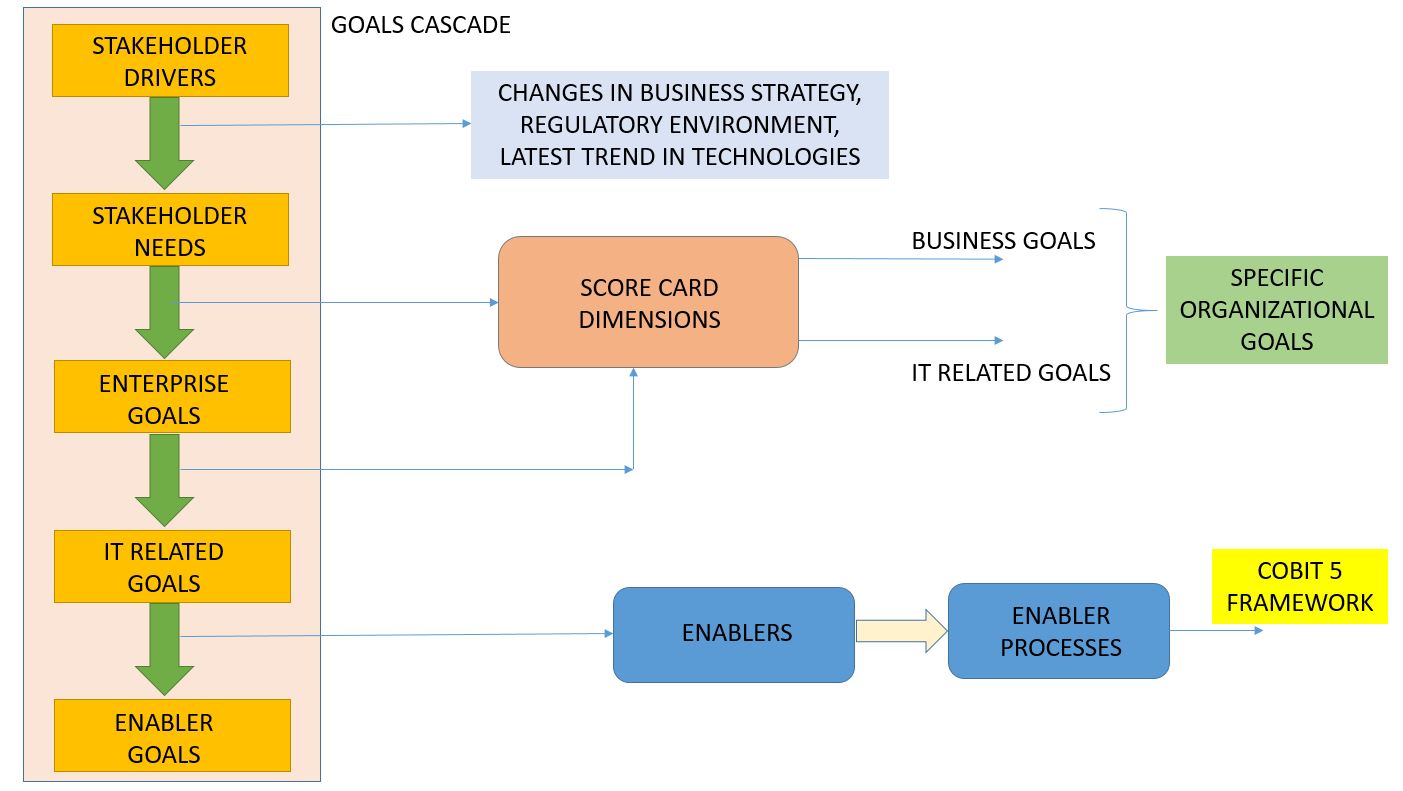
COBIT 5 Framework Goals Cascade
COBIT 5 framework defines required processes and enablers to support value creation through the use of IT. This permits transforming stakeholder needs into an actionable strategy. The COBIT 5 goals cascade is the procedure used to translate stakeholder needs into enabler goals, customized enterprise goals, and IT-related goals. This alignment of needs to goals is an essential step towards achieving an enterprise’s needs, and with the right IT solutions and services, these can be applied at different levels.
The goals cascade works through the following steps:
Step 1. The stakeholders’ needs are influenced by various factors such as changes in strategy, the latest trend in technologies, and the business environment.
Step 2. Stakeholder needs can be seen from a set of enterprise goals. The COBIT5 goals cascade organizes these into the four balanced scorecard dimensions, with 17 generic goals that can also be easily linked to specific organizational goals.
Step 3. Generally, enterprise goals can only be achieved if the IT-related goals are met. In the goals cascade, each of the 17 enterprise goals is linked to many relevant IT-related goals. There are 17 IT-related goals, and they are also organized into the four balanced scorecard dimensions.
Step 4. To achieve IT-related goals, a set of enablers must be applied successfully. One of these enablers is processed. Similar to earlier steps, each IT-related goal is then mapped to one or more processes. The COBIT 5 framework has, however, a total of 37 processes.
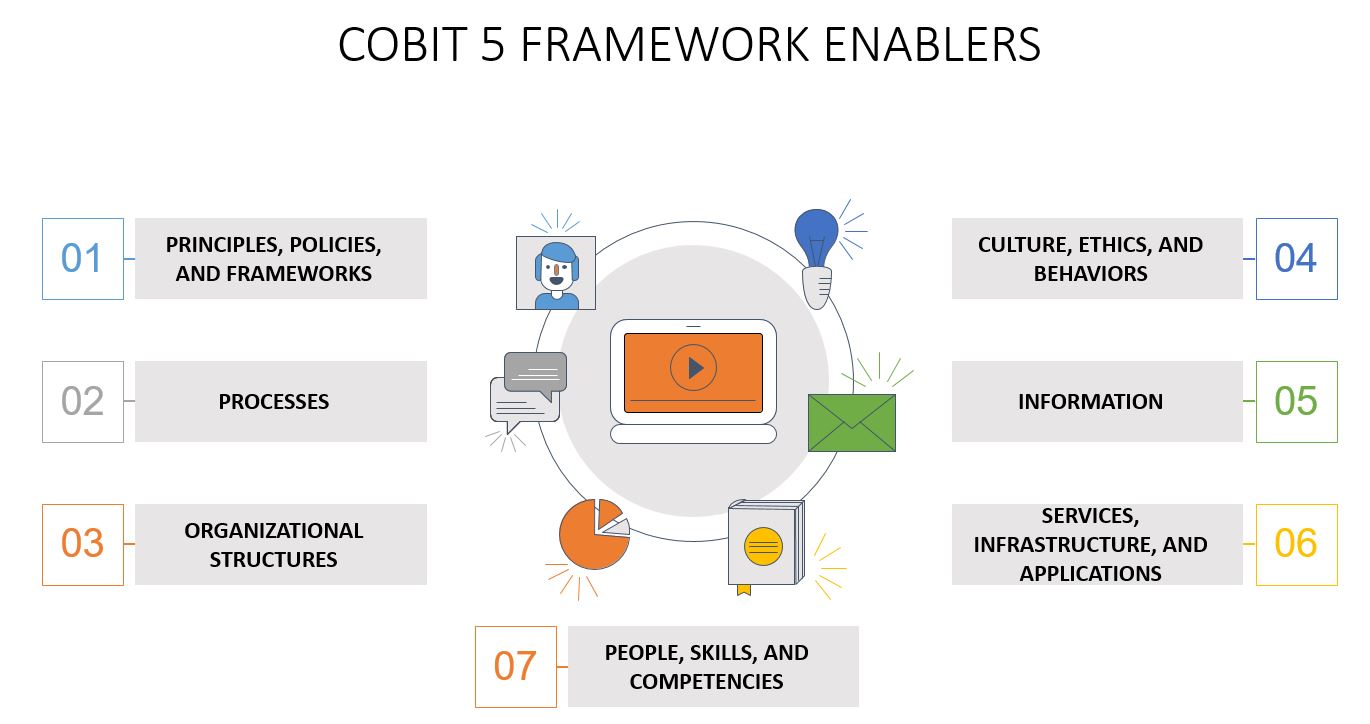
Seven Enablers of COBIT 5 Framework
COBIT 5 framework consists of seven enablers. These enablers determine if the management and governance of enterprise IT will work. The goals cascade drives the enablers, where the IT-related goals define the objectives of each enabler.
Some of these are pre-defined within the framework, while the remaining need to be designed by the organization itself based on their organizational structure, managerial context, and size of the enterprise.
1. Principles, Policies, and Frameworks: These are essential and practical guidelines that are necessary to reach the desired result within the organization for the day-to-day management
2. Processes: COBIT 5 framework describes processes as a set of practices designed to bring about a specific output in support of organizational IT targets and achieve certain objectives
3. Organizational Structures: The critical decision-making elements in an organization are the executive board or the IT Steering committee
4. Culture, Ethics, and Behaviors: Having a culture that supports the organizational goal, backed up by the right behaviors and attitudes, is a crucial factor in the implementation process of COBIT in achieving the desired outcome
5. Information: Information is essential to the organization, but having the right information to concede for good governance, management, and use of that information is also crucial
6. Services, Infrastructure, and Applications: The infrastructure, technology, and applications that are needed to convey the information to the organization. These play a key role given the integration of IT and management
7. People, Skills, and Competencies: Having competent people in the right areas, making decisions, and executing processes to deliver organizational objectives and goals is the key
Enablers are a significant part of implementing a COBIT 5 framework approach. Using the list of enablers as a checklist to ensure that they are delivered in place is vital in bringing out the most of the guidance.
KMP Provided by COBIT 5 Framework IT Compliance
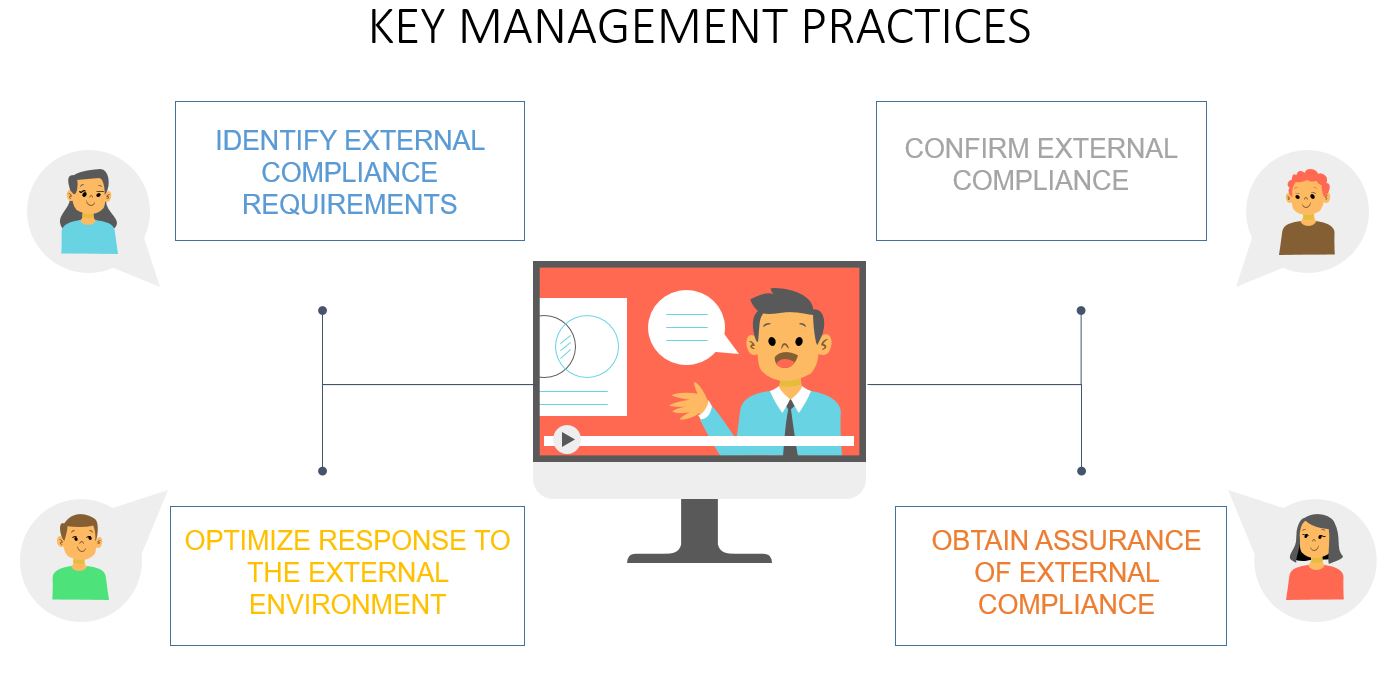
COBIT 5 framework provides Key Management Practices or KMP for ensuring IT compliance with external compliance as relevant to the enterprise. These include the following:
- Identify External Compliance Requirements: On a regular basis, diagnose and check for changes in international and local laws, regulations, and other external requirements that must be complied with from an IT perspective
- Optimize Response to the External Requirement: Here we have to analyze and adjust policies, procedures, principles, standards, and methodologies to ensure that legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements are addressed and communicated. We have to consider here the industry standards, codes of good practices, and best practice guidance for adoption and adaptation to any enterprise
- Confirm External Compliance: Here we have to confirm with policies, principles, standards, procedures, and methodologies with legal, regulatory and contractual requirements
- Obtain Assurance of External Compliance: To obtain and report assurance of compliance and adherence with policies, principles, standards, procedures, and methodologies to confirm that corrective actions to address compliance gaps are closed in a timely manner
Key Metrics for Assessing Compliance in COBIT 5 Framework
- Compliance with External Laws and Regulations
Compliance with external laws and regulations can be monitored from (a)Cost of IT non-compliance including settlements and fines. (b)The number of IT-related non-compliance issues reported to the board or causing public comment or embarrassment. (c) The number of non-compliance issues relating to a contractual agreement with IT service providers. (d) Coverage of compliance assessments.
- IT Compliance with Internal Policies
For compliance with internal policies, we need to check (a) the number of incidents related to non-compliance policy. (b) Percentage of stakeholders who understand policies. (c) Percentage of policies supported by effective standards and working practices. (d) Frequency of policies reviewed and updated.
KMP to be Implemented in COBIT 5 Framework for IT Derived Business Evaluation
- Evaluate Value Optimization: Continuously assess IT-related investments and services and assets to understand the likelihood of achieving the objectives and delivering value at a reasonable cost. Identify and decide on any amendments that are to be made and inform the management to improve and add value
- Direct Value Optimization: Direct value management involves principles and practices to enable optimal value realization from IT-enabled investments throughout the business life cycle
- Monitor Value Optimization: Monitor the key goals and metrics to understand the extent to which any business is generating the desired value and benefits the enterprise from IT-enabled investments and services. After monitoring, we have to identify significant issues and consider corrective actions
Case Study
ENTSO-E was established in 2008 and given legal mandates in 2009 by the European Union’s 3rd Legislative Package for the Internal Energy Market to achieve liberalizing gas and electricity markets in the EU. This required closer cooperation among Europe’s TSOs to support the implementation of the EU energy policy. To achieve Europe’s energy and climate policy objectives, there was a dire need to implement a framework that would make this possible.
The IT director of ENTSO-E or the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity decided to implement COBIT 5 framework at the organization beginning in 2014. After two years, with a successful collaboration between the internal IT department, the business organization, and the external consultants COBIT 5 framework came into action.
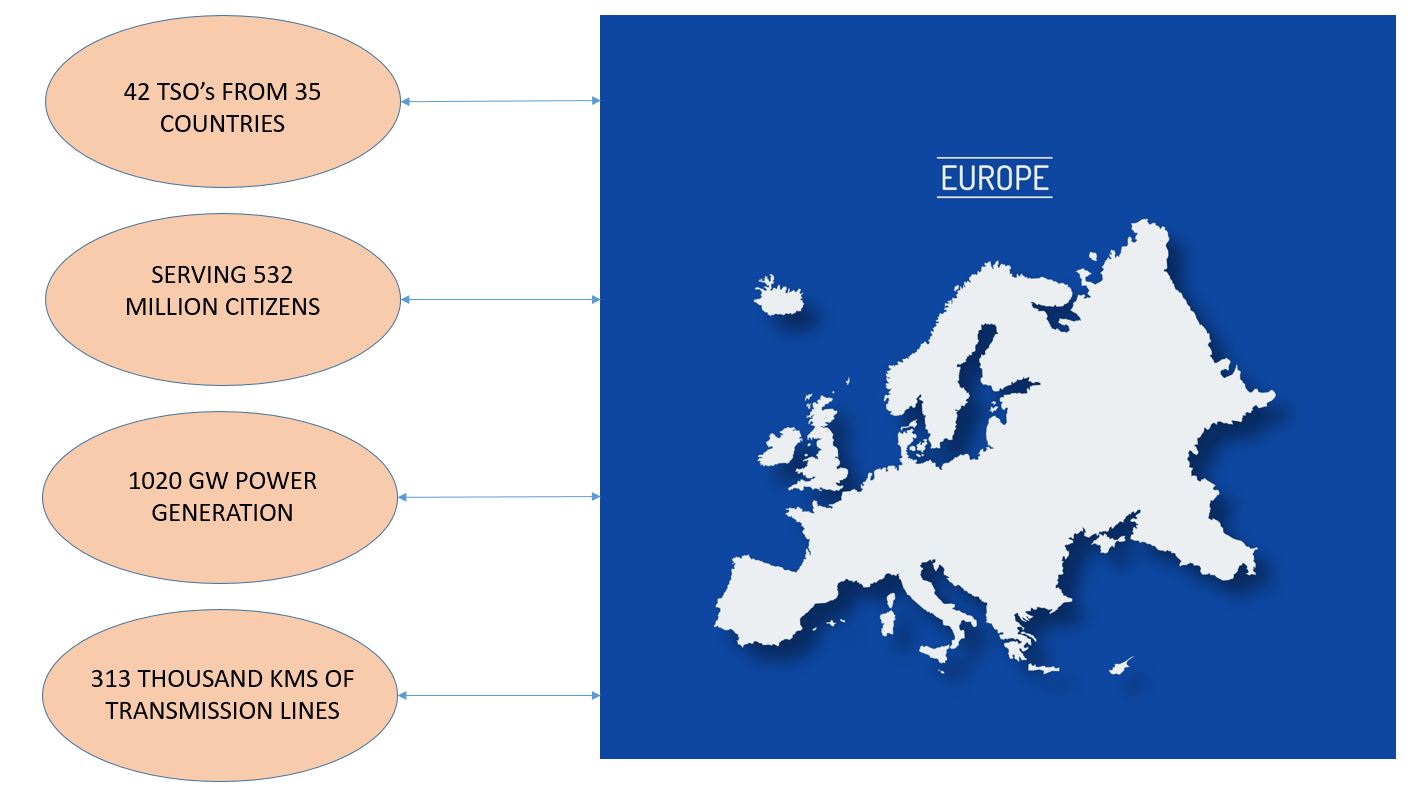
Taking a practical approach towards implementing a program for enterprise IT governance (GEIT) based on COBIT 5, ENTSO-E focused on prioritizing the processes, developing these processes, and overcoming practical issues during the implementation of the COBIT 5 framework. There are 42 electricity transmission system operators, also called TSO’s from 35 countries across Europe.
This is a six-step procedure:
- Step 1—Establish business drivers relevant to the IT processes
- Step 2—Set up the IT processes in the enterprise
- Step 3—Perform a prior selection of target processes based on the above selection
- Step 4—Confirm the prior selection of target processes with the project sponsor and key stakeholders
- Step 5—Finalize the list of processes
- Step 6—Document the scoping methodology in the IT strategy document
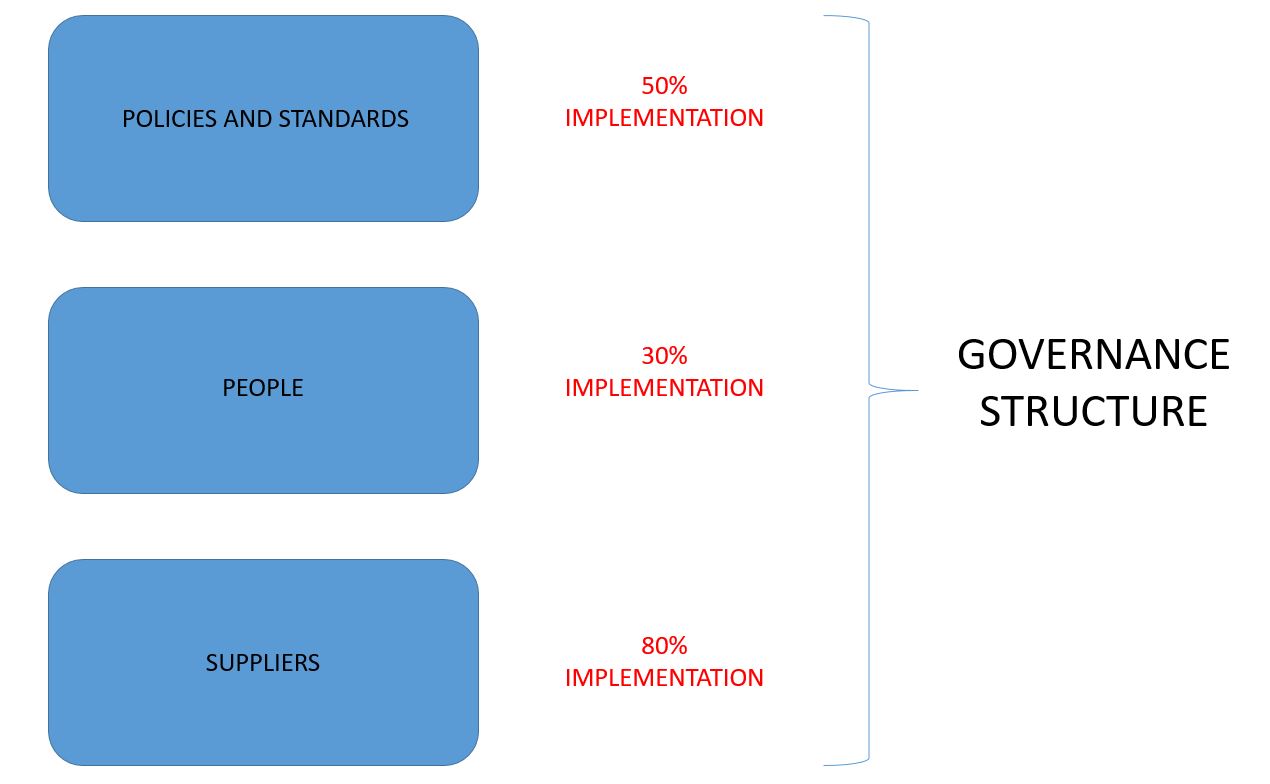
After implementation, the results were evaluated. This is done by going back to the original governance structure put in place.
The review was completed considering all major IT suppliers:
- All data center activities moved to a single permanent supplier
- All application operations moved to two or more permanent suppliers
- Supporting the TSO members in the best possible way by the IT organization
- Maintain the size of the IT department: the number of employees, the ratio of internal versus external employees, and a revived focus on activities related to data management development
- A final review to check if the enterprise goals are being achieved. The percentage of goals achieved for each of the 37 COBIT processes was done, and another calculation was performed through the IT-related goals to arrive at the achievement of all 17 generic enterprise goals
This report shows where development has been made after two years with respect to the business goals. Here the business department is quite satisfied with the overall result, as the development in the organization was startling.
Benefits of COBIT 5 Framework
Listed below are the key benefits of implementing the COBIT 5 framework:
- It is a comprehensive framework that enables enterprises to achieve their objectives for the governance and management of enterprise IT
- It creates optimal value for IT by maintaining a balance between realizing benefits and optimizing risk levels and resource use
- Helps to govern and manage IT in a holistic manner for the entire enterprise by taking into account the full end-to-end business and functional areas considering internal and external stakeholders
Conclusion
Implementing COBIT 5 framework is costly and extremely complicated. Analysts need meticulous planning and expertise to implement it in an enterprise. There are many advantages of COBIT, but there is still a lot of scopes to make it cost-effective and simplify its implementation process. Now that more and more organizations are looking to implement IT in their portfolio, factors like these play a major role in the coming future.