Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- What is Lean Six Sigma
- What is Lean
- What is Six Sigma
- Integrating Lean and Six Sigma into Lean Six Sigma
- Benefits of Using Lean Six Sigma
- Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
- Popular Lean Six Sigma Tools
- Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma
- What are Different Belt Levels in Lean Six Sigma?
- Lean Six Sigma Use Case Examples
- Conclusion
Introduction
In a world where efficiency and quality become the benchmarks for success, the demand for methodologies that can deliver both has advanced. Lean Six Sigma, a blend of the Lean method’s speed and efficiency with Six Sigma’s focus on quality and precision, has emerged as a critical tool in modern businesses. This powerful approach is not just a trend but a fundamental shift in how companies optimize processes, reduce waste, and ensure the quality of their products and services.
As industries evolve and the pressure mounts to deliver flawless outcomes quickly and cost-effectively, Lean Six Sigma professionals are in high demand. From manufacturing industries to corporate sectors, the principles of Lean Six Sigma are being applied to transform business operations. This guide explores how Lean Six Sigma works, why it’s being adopted by top companies around the globe, and how it can be the key to your professional advancement and organizational success.

What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that integrates two distinct yet complementary approaches to process improvement: Lean and Six Sigma.
Lean focuses on efficiency and waste reduction. It identifies and eliminates non-value-adding activities within processes, streamlining operations to enhance productivity, quality, and resource optimization.
On the other hand, Six Sigma is a data-driven method for minimizing defects and process variations. It employs rigorous statistical analysis through phases of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC) to achieve consistent, reliable outcomes.
By combining these methodologies, Lean Six Sigma offers a comprehensive framework adaptable across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and services. Its application aims to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and elevate customer satisfaction through systematic process enhancement.
What is Lean
Lean refers to a systematic approach aimed at minimizing waste and maximizing value within processes. Originating from the Toyota Production System (TPS), Lean principles emphasize eliminating activities that do not add value to the end product or service.
Key concepts of Lean include continuous improvement (Kaizen), reducing lead times, optimizing workflows, and enhancing overall efficiency through the involvement of all employees in identifying and solving problems. Lean techniques are widely applied across manufacturing, healthcare, services, and other sectors to streamline operations and improve customer satisfaction.
What is Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a disciplined, data-driven methodology focused on improving processes by identifying and eliminating defects and variations. Originally developed by Motorola, Six Sigma aims to achieve near-perfect quality by reducing process variability and improving efficiency.
It follows a structured approach known as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), which involves defining the problem, measuring process performance, analyzing data to identify root causes, implementing improvements, and controlling the process to sustain improvements.
Six Sigma uses statistical tools and strict measurement to ensure processes deliver consistent and predictable results. It is a widely adopted approach in manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and services industries.
Six Sigma Institute states that Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve processes by identifying and eliminating defects or variations, ultimately striving for near-perfect quality with only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
Integrating Lean and Six Sigma into Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma represents a systematic approach, combining the strengths of Lean and Six Sigma methodologies to form a powerful framework for business process improvement. Lean focuses on streamlining operations by eliminating waste and enhancing process speed, while Six Sigma emphasizes accuracy, reducing defects through rigorous data analysis. This integration allows organizations to tackle inefficiencies and quality issues simultaneously, enhancing overall performance.
The integration process begins by aligning the principles of Lean with the structured methodology of Six Sigma’s DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) model. Organizations develop comprehensive training programs that equip employees with various tools and techniques from both disciplines. This fosters a more versatile skill set and promotes a culture of continuous improvement and precision.
Projects selected under Lean Six Sigma are typically those that promise significant impacts on reducing waste and improving quality, thereby aligning closely with strategic business objectives. The dual focus on efficiency and quality not only drives cost reduction but also boosts customer satisfaction through improved service delivery and product quality. This holistic approach ensures that companies are better equipped to adapt to market changes and operational demands, maintaining competitiveness and driving sustainable growth.
Benefits of Using Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a versatile methodology that drives significant enhancements across various sectors. When organizations integrate Lean Six Sigma principles into their routine operations, it creates substantial benefits for employees, the business itself, and its customers:
-
Lean Six Sigma Benefits for Businesses
One of the most compelling advantages for businesses implementing Lean Six Sigma is the substantial cost reduction. Businesses can build a more secure financial foundation, by refining process flows, minimizing waste, shortening cycle times, and standardizing operations. This systematic approach to process improvement also enhances operational agility and increases the ability to innovate, keeping businesses competitive in their markets.
Businesses can build a more secure financial foundation.
-
Lean Six Sigma Benefits for Customers
At its core, Lean Six Sigma focuses intensely on customer satisfaction and delivering superior-quality outcomes. This leads to improved customer service and product quality, boosting customer loyalty and retention. Customers benefit from higher-quality products and services and more reliable delivery, which significantly enhances their overall experience and satisfaction.
-
Lean Six Sigma Benefits for Employers
Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of active participation among employees in continual improvement, which enhances team collaboration and job satisfaction. It empowers employees to understand their critical role in achieving business goals, fostering a sense of accountability and respect across departments. This engagement boosts personal development and elevates overall organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
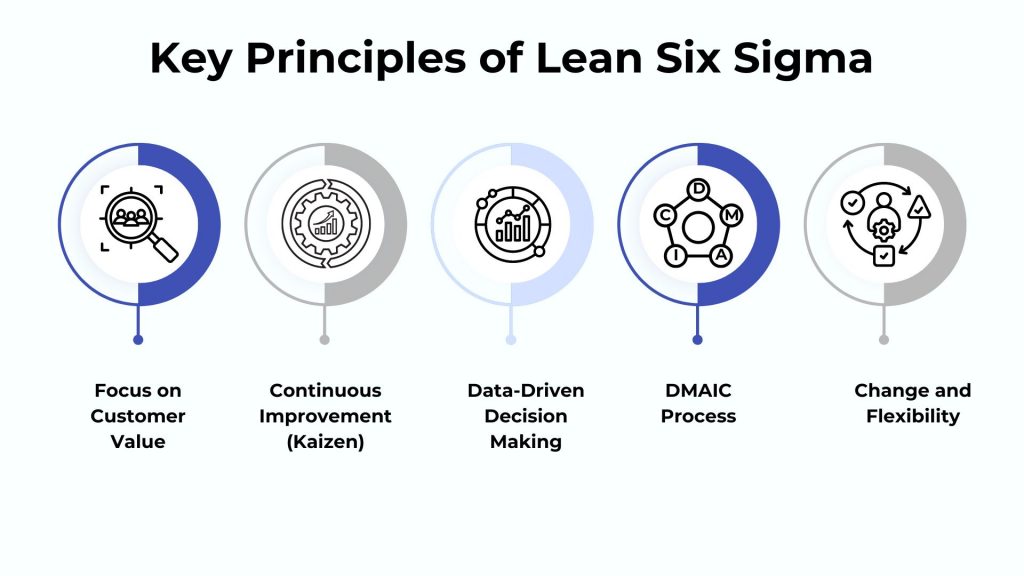
Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology combining Lean and Six Sigma principles to improve efficiency and quality in organizational processes. Understanding its key principles is crucial for driving customer satisfaction, reducing waste, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
1. Focus on Customer Value
Lean Six Sigma emphasizes understanding and prioritizing customer needs and expectations. By aligning processes with customer value, organizations ensure that every improvement directly enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. This focus ensures that resources are allocated efficiently to deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations, thereby driving competitiveness and growth in the market.
2. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Continuous Improvement, or Kaizen, is a core principle of Lean Six Sigma that encourages ongoing efforts to enhance processes incrementally. By fostering a culture where small improvements are made consistently over time, organizations can achieve significant efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction gains. Kaizen involves all employees in identifying opportunities for improvement, implementing solutions, and monitoring results to sustain continuous growth and adaptation to changing business environments.
3. Data-Driven Decision Making
Lean Six Sigma relies on data-driven decision-making to drive process improvements. This principle ensures that decisions are based on factual analysis rather than assumptions or intuition. By collecting and analyzing data, organizations gain insights into process performance, identify root causes of issues, and measure the impact of improvement initiatives. This systematic approach enables informed decision-making that leads to sustainable improvements in quality, efficiency, and overall business performance.
4. Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (DMAIC)
DMAIC is a structured methodology used in Lean Six Sigma projects to systematically improve processes. It begins with defining project goals and customer requirements and measuring current performance metrics. Data analysis then identifies factors contributing to issues or inefficiencies, leading to targeted improvements. Implementation of these improvements is followed by the establishment of controls to sustain the gains achieved.
DMAIC ensures a disciplined approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement, driving measurable results and enhancing organizational effectiveness.
5. Create a Culture of Change and Flexibility
Lean Six Sigma promotes a culture that embraces change and fosters organizational flexibility. Businesses can adapt more readily to evolving market demands and competitive pressures by encouraging openness to new ideas, methods, and technologies. This culture empowers employees at all levels to innovate, experiment with new approaches, and drive improvements in processes and performance. By cultivating an environment that values flexibility and agility, organizations can respond proactively to challenges and opportunities, ensuring long-term success and sustainability.
Popular Lean Six Sigma Tools
Lean Six Sigma offers tools designed to enhance operational efficiency and quality. Here’s an overview of some of the most popular Lean and Six Sigma tools used within this methodology, each tailored to specific improvement needs.
1. Value-Stream Mapping
This tool visualizes the materials and information needed to deliver a product or service to a customer. Employed mainly in lean manufacturing, value-stream mapping can be advantageous across various industries. It identifies critical elements like cycle times, wait times, and bottlenecks in the production process. The map comprises three components: the process map, the timeline, and the information flow, helping businesses streamline operations and reduce waste.
2. Cause-and-Effect Analysis
Also known as the fishbone diagram, this tool helps identify multiple causes of a problem through a structured brainstorming session. The process starts by defining the problem and placing it at the left of a diagram, extending a line across the page representing the “spine.” Branches off this spine represent major causes and potential sub-causes, facilitating a thorough analysis to pinpoint root causes that might require further investigation.
3. The 5 Whys
Originating from the Japanese industrial revolution, the 5 Whys is a simple but effective tool for recurring problems. By asking “why” five times, this method helps peel away the layers of symptoms to reach the core issue. It’s particularly useful for straightforward problems and works well with more complex analytical tools like the fishbone diagram.
4. Kanban System
Kanban is a supply chain management tool that enhances efficiency by implementing Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory principles. It minimizes waste by replenishing parts and materials only as needed, based on actual demand. The Kanban system streamlines production processes and can significantly reduce costs by eliminating excess inventory.
5. 5S Workplace Organization
The 5S system is a set of practices designed to organize and manage the workspace efficiently, enabling a more productive and safer environment. The steps include Seiri (sort), Seiton (set in order), Seiso (shine), Seiketsu (standardize), and Shitsuke (sustain). This method improves operational efficiency and instils a culture of continuous improvement within the team.
Six Sigma vs Lean Six Sigma
Understanding the distinctions between Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma is crucial when examining process improvement methodologies. While both aim to enhance organizational efficiency and quality, they employ different approaches and tools to achieve these goals. This comparison explores the key differences and applications of Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma, highlighting their unique strengths in optimizing processes across various industries.
| Aspect | Six Sigma | Lean Six Sigma |
| Focus | Reduces defects and variations in processes | Reduces defects, variations, and waste in processes |
| Methodology | DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) | DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) |
| Tools | Statistical tools (e.g., Control Charts, SPC) | Lean tools (e.g., Value Stream Mapping, 5S) |
| Objective | Achieve consistent process improvement | Enhance efficiency, reduce waste, improve quality |
| Applications | Manufacturing, service industries | Manufacturing, healthcare, finance, services |
| Benefits | Quality improvement, cost reduction | Faster processes, reduced waste, improved efficiency |
| Emphasis | Data-driven decision making | Waste reduction and efficiency alongside quality |
| Origins | Developed by Motorola | Evolved from Toyota Production System (Lean) |
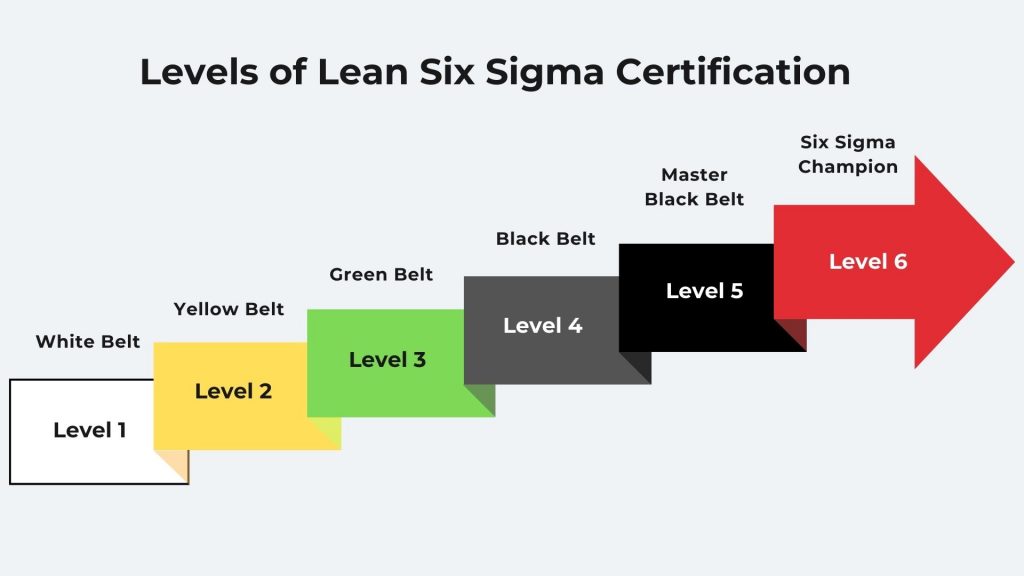
What are Different Belt Levels in Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is structured around a belt certification system that signifies varying degrees of knowledge and skills across its methodology. From White Belts, who are beginners, to Master Black Belts, who are experts in the field, each belt level represents a step higher in expertise and responsibility. Here, we explore these different belt levels and the roles they play in improving organizational processes.
- White Belt: Focuses on basic Lean Six Sigma concepts. White Belts assist with change management and can participate in problem-solving teams supporting projects
- Yellow Belt: Gains a deeper understanding of the process and supports projects. Yellow Belts help Green and Black Belts by taking on smaller responsibilities in Lean Six Sigma projects
- Green Belt: Has comprehensive training on Lean Six Sigma methodology. Green Belts lead smaller projects or assist Black Belts with managing larger projects, focusing on data collection and analysis
- Black Belt: Possesses expert knowledge of Lean Six Sigma and leads projects full-time. Black Belts focuses on project management, statistical analysis, and training team members
- Master Black Belt: Trains and coaches Black and Green Belts. Master Black Belts are highly experienced and focus on strategic implementation within an organization
- Six Sigma Champion: Typically, senior management ensures projects align with organizational goals. Champions support the Lean Six Sigma program within an organization and help to remove any roadblocks to project success
Lean Six Sigma Use Case Examples
Motorola, the company that originally developed Six Sigma in the 1980s, provides a rich backdrop of use case examples for successfully applying Lean Six Sigma methodologies. Here are two examples illustrating how Motorola has used Lean Six Sigma to achieve significant improvements in its operations:
Quality Improvement in Manufacturing:
- Challenge: Motorola faced significant issues with product defects that affected customer satisfaction and increased costs
- Solution: By implementing Six Sigma methodologies, Motorola rigorously analyzed its manufacturing processes to identify the root causes of defects. Using the DMAIC process, they implemented strategic changes to reduce variability in their manufacturing processes
- Outcome: The application of Six Sigma resulted in a dramatic reduction in defect rates, from hundreds of defects per million opportunities to fewer than six, leading to an estimated savings of over $16 billion during the first few years of implementation
Supply Chain Optimization:
- Challenge: Motorola’s complex supply chain led to delays and increased inventory costs
- Solution: Lean principles were applied to streamline supply chain processes, focusing on eliminating non-value-added steps and implementing a Just-In-Time inventory system
- Outcome: The optimization of the supply chain allowed Motorola to reduce inventory levels significantly, shorten delivery times, and improve overall supply chain responsiveness, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing costs
Conclusion
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that combines the efficiency-driven principles of Lean with the quality-focused strategies of Six Sigma. This fusion creates a comprehensive approach that significantly enhances an organization’s operations by minimizing waste and reducing variability. By understanding and applying Lean Six Sigma, businesses can achieve higher efficiency, improve quality, and deliver greater customer value, positioning themselves for sustained success in their respective industries.
To further your understanding of quality management and excel in Lean Six Sigma methodologies, enroll in Invensis Learning Quality Management Certification Courses. Begin your journey to becoming a certified expert.