Risk management is a crucial factor in successful project management. It ensures that potential threats are identified, assessed, and mitigated to keep projects on track. Understanding and implementing effective risk management strategies can mean the difference between a project’s success and failure in a complex business environment. By proactively managing risks, project managers can avoid or minimize potential negative impacts, leading to smoother project execution and improved outcomes.
The demand for risk management in project management is rising due to the complexity and unpredictability of modern projects. Factors such as technological advancements, market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and global competition introduce new risks that can derail projects if not properly managed. Organizations are recognizing that effective risk management is essential for maintaining a competitive benefit and ensuring long-term sustainability.
This blog will explore the fundamentals of risk management in project management, delving into its importance, key processes, and best practices to help you navigate and minimize risks in your projects.
What is Risk Management in Project Management?
Risk management in project management is the systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to potential risks that could affect the success of a project. It involves the identification of risks, assessment of their impact and possibility, development of strategies to mitigate or manage these risks, and continuous monitoring and review throughout the project lifecycle.
As per Robert S. Kaplan and Anette Mikes
“Managing risk is very different from managing strategy. Risk management focuses on the negative—threats and failures rather than opportunities and successes.”
Effective risk management is crucial in project management as it helps prevent potential problems from becoming significant issues that can delay a project. By systematically managing risks, project managers can enhance the chances of project success, improve decision-making, optimize resource allocation, and increase stakeholder confidence. Risk management ensures that projects are more resilient, adaptable, and better positioned to achieve their goals.
What are the Types of Project Risk?
Project risks can be categorized into several types, each presenting unique challenges and potential impacts on project outcomes. Here are the common types of project risks:
- Scope Creep: This risk occurs when the project’s scope gradually expands beyond its original definition. Feature creep, requirement changes, and miscommunication can all contribute to scope creep, leading to increased costs, schedule delays, and resource constraints.
- Schedule Risk: Will you meet your deadlines? Schedule risk encompasses anything that could threaten your project’s timeline. Unrealistic estimates, resource limitations, and unforeseen dependencies can contribute to schedule risk.
- Cost Risk: Budget blowouts are a project manager’s nightmare. Cost risk refers to the possibility that project expenses will exceed the allocated budget. Inaccurate estimates, unforeseen changes, and poor cost control can all contribute to cost risk.
- Performance Risk: Will your project deliver the expected results? Performance risk refers to the possibility that the project may not meet its performance objectives in terms of quality, functionality, or user satisfaction. Inadequate planning, poor quality control, and a lack of stakeholder alignment can all contribute to performance risk.
- Resource Risk: Having the right people and tools in place is crucial. Resource risk refers to the possibility that essential resources, such as personnel, equipment, or materials, may not be available when needed or may not possess the necessary skills or capabilities.
- External Risks: Not everything is within your control. External risks encompass events outside the project team’s influence, such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or changes in regulations. While some external risks may be unavoidable, proactive planning can help mitigate their impact.
External Risks: Not everything is within your control. External risks encompass events outside the project team’s influence, such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or changes in regulations. While some external risks may be unavoidable, proactive planning can help mitigate their impact.
Why is Project Risk Management Important?
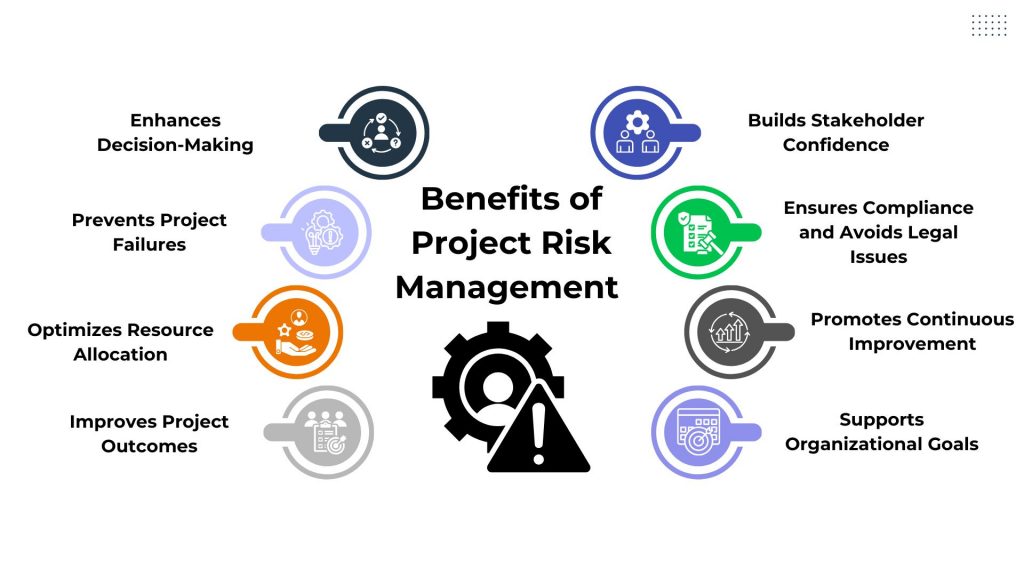
Risk management in project management is crucial for several reasons, all of which contribute to the successful completion of projects and the overall health of the organization. Here are the key reasons why risk management in projects is important:
- Enhances Decision-Making: By identifying and analyzing risks early, project managers make informed decisions, ensuring actions are proactive and aligned with project goals
- Prevents Project Failures: Proactive risk management prevents issues from escalating, minimizing delays, cost overruns, and other disruptions that could impact project success
- Optimizes Resource Allocation: Understanding project risks helps allocate resources effectively, focusing efforts where they are most needed to mitigate potential impacts
- Improves Project Outcomes: Effective risk management leads to smoother project execution, ensuring projects are completed on time, within budget, and meeting quality standards
- Builds Stakeholder Confidence: Stakeholders trust projects managed with clear risk strategies, increasing support and investment in project success
- Ensures Compliance and Avoids Legal Issues: Compliance with regulations and proper risk management reduces the risk of legal challenges and ensures project adherence to necessary standards
- Promotes Continuous Improvement: Ongoing risk monitoring and adaptation improve risk management strategies over time, fostering organizational resilience and learning
- Supports Organizational Goals: Projects managed with effective risk strategies contribute to broader organizational objectives, aligning project outcomes with strategic goals
What is the Risk Management Process?
The Risk management process is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and managing potential risks that could affect the achievement of objectives within an organization or a specific project. It’s like a roadmap that helps you navigate the unpredictable terrain of business and increase your chances of success. This structured process aims to enhance decision-making by systematically addressing uncertainties, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate risks and optimize the chances of success.
The risk management process in project management is dynamic, iterative, and adaptable, ensuring that risk management strategies evolve in response to changing circumstances and new insights. By following a systematic risk management process, project managers can proactively identify and address potential issues before they impact the project, thereby increasing the chances of successful project delivery within scope, time, and budget constraints.
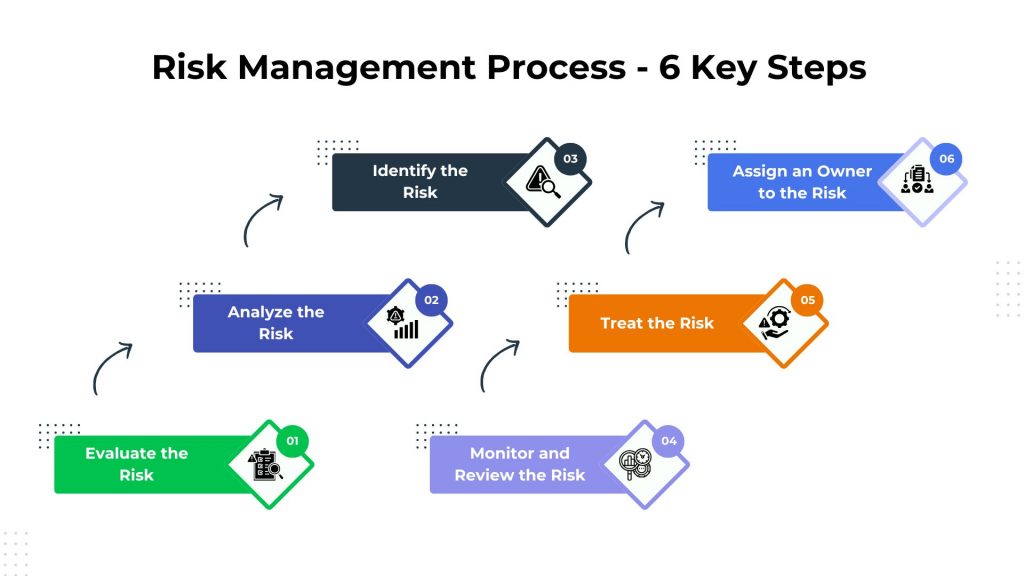
6 Steps in the Risk Management Process
The Risk Management Process is a systematic approach to handling uncertainties in a structured manner. These steps create a cyclical and adaptive process, allowing organizations to navigate uncertainties effectively and make informed decisions to enhance the likelihood of successful project outcomes. Let’s break down each step of the risk management process in project management:
Step 1: Identify the Risk
The first step in a successful risk management process is to identify the type of risk the organization is currently dealing with or could deal with in the future. It is not merely a one-time activity but a continuous process that requires a thorough understanding of the project or organizational landscape. This step involves engaging key stakeholders, conducting risk workshops, and employing various tools to systematically identify potential risks.
Risks can manifest in various forms, including external factors like economic shifts, internal factors like resource constraints, or project-specific risks such as technology failures or scope changes. Some of the different types of risks include:
- Strategic Risk: Associated with potential strategy failures, often due to external factors like market shifts or internal issues like poor decision-making
- Compliance Risk: Relates to potential violations of laws, regulations, or ethical standards, leading to legal actions, financial penalties, and reputational damage
- Market Risk: Arises from uncertainties in the market environment impacting financial performance, including changes in interest rates, currency fluctuations, or demand shifts
- Regulatory Risk: Involves potential negative impacts from changes in laws and regulations governing industry operations
- Operational Risk: Originates from internal processes, systems, people, or external events disrupting normal organizational functioning
It is important to identify all the different potential types of risks that the organization can face. These risks can be noted manually, but if a risk management platform is implemented in the organization, the risk identification process becomes much simpler. The gathered information is directly inserted into the system. Access to this data also becomes a lot simpler because the project managers and other team members do not have to request an email for this information. They can directly log in to the risk management system and see all the identified risks.
Step 2: Analyze the Risk
All the possible risks for the organization have been identified in the previous step, which will lead the teams to analyze these risks. Once risks are identified, a detailed analysis is crucial for informed decision-making. The risk analysis should answer the following questions:
- What is the likelihood of these risks occurring?
- What will be the consequences of these risks to the organization?
During the risk analysis process, teams estimate the probability of each risk occurring and its fallout to prioritize the identified risks. The factors that companies consider when prioritizing the risks include:
- Potential financial loss
- Time lost
- The severity of the impact
- Availability of resources to manage the risk
Risk analysis helps companies create their response to these risks depending on their severity. It also helps in understanding the link between the risk and the number of aspects of the business it will affect. To put it simply, the more business aspects at risk, the higher the risk to an organization.
If companies use a manual risk management process, then this risk analysis takes place manually. Suppose a risk management solution is deployed across the organization. In that case, different documents, policies, processes, and procedures are analyzed by the solution to map the risk and create a framework for the next step, which is risk evaluation.
Ready to take your project management skills to the next level? Enroll in our PMP Certification Training today and learn how to expertly analyze project risks.
Step 3: Evaluate the Risk
Risk prioritization is a critical aspect of effective risk management. It involves categorizing and ranking risks based on their severity. Many risk management solutions feature various risk categories, each assigned a rating corresponding to the potential harm they pose. Risks causing minor inconveniences receive lower ratings, while those with the potential for catastrophic loss are rated the highest.
Prioritizing risks is essential as it provides the organization with a comprehensive overview of its overall risk exposure. While the business may face numerous low-level risks that don’t necessitate upper management intervention, a single high-rated risk can demand immediate attention.
There are two primary types of risk assessments: Qualitative Risk Assessment and Quantitative Risk Assessment.
1. Qualitative Risk Assessment
A qualitative risk assessment involves a comprehensive analysis of an event’s criticality by evaluating its probability of occurrence and its potential impact on the organization. This method delves into the qualitative aspects of risks, seeking to understand the nature and severity of the event rather than assigning specific numerical values.
A qualitative risk assessment provides a nuanced understanding of the risk landscape by examining factors such as the likelihood of the event happening and the magnitude of its consequences. It uses expert judgment, historical data, and contextual information to categorize risks into qualitative levels, such as low, medium, or high, allowing for a subjective yet informed prioritization.
2. Quantitative Risk Assessment
Quantitative risk assessment focuses on assigning numerical values to various aspects of the risk, primarily honing in on the financial impact or benefit associated with the event. This method seeks to quantify the potential monetary consequences of the risk, providing a precise and measurable representation.
Through statistical models, data analysis, and mathematical calculations, a quantitative risk assessment enables organizations to not only prioritize risks based on their financial implications but also to make data-driven decisions. This approach is particularly beneficial when precise numerical data can be obtained, allowing for a more objective and quantitative evaluation of the risk event.
Step 4: Assign an Owner to the Risk
If you don’t designate someone to manage the risk, all of your effort in identifying and evaluating it will be in vain. In fact, you should do this when outlining the hazards. Who is in charge of that risk, determining when and if it might arise and then directing the effort to address it?
You have the decision as to what to do. For example, a team member with more expertise or experience in the risk may be present. Then, that person should take the initiative to fix it. Or it can be a random decision. Of course, delegating the duty to the appropriate individual is ideal, but ensuring every risk has a point of contact is crucial.
If you don’t assign someone to each risk who is responsible for monitoring it and resolving it when the time comes, you risk taking on more risks. Identifying risk is one thing, but it won’t protect the project if you don’t manage it.
Step 5: Treat the Risk
Once the risks have been analyzed and prioritized, it is time to take action. Every risk to the organization or the project must either be eliminated or contained. If the risk treatment is done manually, team members must contact each stakeholder to discuss the issues. Usually, these discussions get spread out over email chains, various documents, and many phone calls, making the entire process longer and more difficult.
When companies employ a risk management solution, the stakeholders are immediately notified by the application, and all the key decisions are made in one go. This way it becomes easy to monitor the progress of the solution.
One aspect of effectively treating the risk is using resources without losing the progress made in the active projects. Over time, organizations can create a log of all the projects, the risks faced, and the mitigation process. This will help anticipate future risks so that the team members can be proactive in their risk management strategy. Depending on the nature of the risk, a response strategy is defined for the project. The following seven strategies are possible:
- Accept: Refrain from taking any proactive measures and instead maintain vigilant monitoring.
- Mitigate/Enhance: Decrease (for a risk) or increase (for an opportunity) the likelihood of occurrence and the magnitude of impact
- Transfer/Share: Shift the responsibility for a risk to a third party, which would assume the consequences of the issue (or share the benefits of a seized opportunity)
- Avoid/Exploit: Eliminate uncertainty or capitalize on the opportunity
Step 6: Monitor and Review the Risk
Organizations will notice over time that there will be some risks that cannot be eliminated and will be omnipresent. These continuous risks can include external risks such as market risks and environmental risks. They need to be continuously monitored to make the mitigation process more effective.
When companies employ risk management solutions, the system becomes responsible for monitoring the organization’s complete risk framework. If there is any change, all relevant parties get notified immediately. This also ensures continuity. When employees are properly trained in the processes, they can use the system efficiently.
5 Tips to Reduce and Manage Risk Management
Even the most meticulously planned projects can encounter unexpected challenges. But fear not! By implementing a proactive approach to risk management, you can significantly increase your chances of success. Here are five powerful tips to get you started:
1. Develop a Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
Begin by creating a detailed risk management plan that outlines how risks will be identified, assessed, prioritized, and mitigated throughout the project lifecycle. This plan should include clear roles and responsibilities for managing risks, communication protocols, and strategies for monitoring and controlling risks.
2. Ensure Your Risk Register Remains Updated
Maintain an up-to-date risk register that documents all identified risks, their potential impacts, and their current status. Review and update the risk register regularly as new risks emerge or existing risks evolve. This ensures that all stakeholders are aware of potential threats and that appropriate actions are taken in a timely manner.
3. Gain a Clear Understanding of Potential Risk Events
It’s essential to thoroughly understand each identified risk event, including its causes, potential consequences, and likelihood of occurrence. This understanding allows project teams to prioritize risks effectively and develop targeted mitigation strategies that address the root causes of potential issues.
4. Take Proactive Measures Rather Than Reacting
Take a proactive approach to risk management by anticipating potential challenges and implementing preventive measures to mitigate risks before they impact the project. This proactive stance helps minimize disruptions, reduces the need for reactive firefighting, and enhances overall project stability.
5. Enhance Your Project Management Expertise
Continuously develop and refine your project management skills, including risk management competencies. This includes staying updated on best practices, learning from past projects, and seeking opportunities for professional development. Strong project management skills enable more effective risk identification, analysis, and response planning, contributing to project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
Conclusion
Don’t let project uncertainty hold you back! Equip yourself with the power of risk management. This blog has provided the roadmap – now it’s your turn to take charge. By proactively identifying and mitigating risks, you’ll transform them from roadblocks into opportunities. Adopt risk management as a strategic tool to navigate challenges effectively. By understanding potential pitfalls early on and developing robust mitigation strategies, you pave the way for smoother project execution and better outcomes.
Understanding risk management is crucial, but mastering it takes dedication and practice. If you’re looking to take your project management expertise to the next level, consider enrolling in a Project Management Certification Courses. Don’t wait to start mastering risk management and advance your career with us!