Ensuring the highest quality of products and services is crucial for business success. This is where the role of a Quality Control Inspector becomes essential. These professionals are responsible for examining products and processes to meet specified standards and regulations. Their meticulous attention to detail helps identify defects, prevent errors, and maintain consistent quality throughout production.
This blog explores the key roles and responsibilities of a Quality Control Inspector, highlighting how their work contributes to organizational efficiency and success. Whether you’re considering a career in quality control or looking to understand its importance for your business, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the critical functions these professionals perform and their impact on overall business performance.
Table of Contents:
- Who is a Quality Control Inspector?
- Quality Control Inspector Responsibilities and Duties
- Quality Control Inspector Requirements
- Quality Control Inspector – Work Environment
- Job Outlook of a Quality Control Inspector
- Salary Outlook
- Conclusion

Who is a Quality Control Inspector?
A “Quality Control Inspector” monitors the quality aspects of incoming raw materials to the organization and the products that are ready to be shipped. They ensure that manufactured products meet the specified quality standards set by the organization before being sent to customers.
The quality control inspector’s job role involves analyzing the measurements, conducting tests, and monitoring the production phase. They are engaged in various domains, from food to electronics to automobiles to clothing. They sort out the items that fail to meet the quality standards and enhance the production process to reduce the chances of failure.
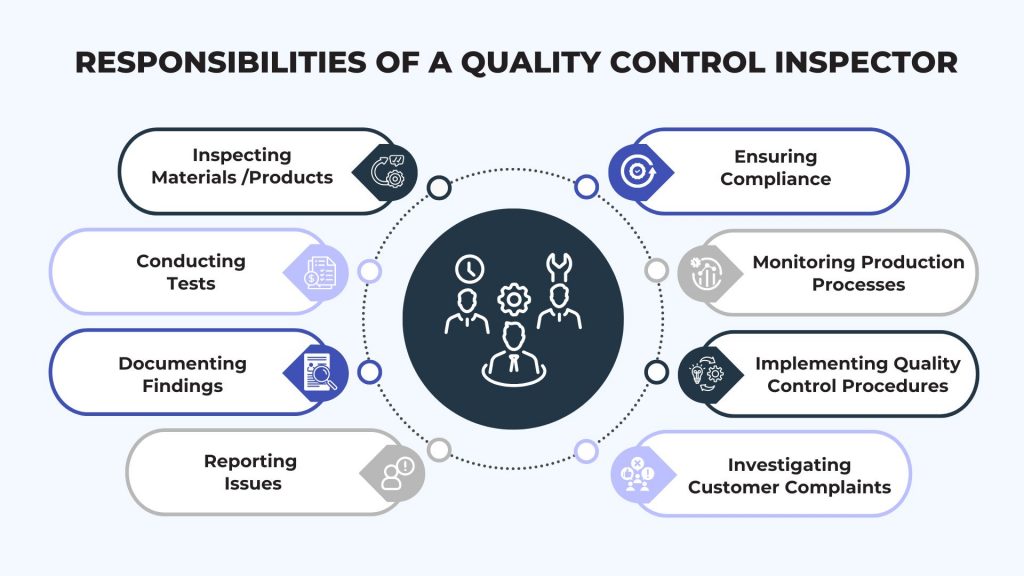
Quality Control Inspector Responsibilities and Duties
The responsibilities of a quality control inspector vary from one industry to another, but there are a few common responsibilities irrespective of the domain. Let’s take a look at them:
- Ensure raw materials and finished products meet specifications through meticulous examination and precise measurement tools
- Perform durability, functionality, and safety tests to validate product quality and performance using standardized methods
- Maintain detailed records of inspections, noting deviations or defects found to ensure traceability and quality control
- Communicate identified defects promptly to supervisors and collaborate on corrective actions for timely resolution
- Verify products meet industry standards, company policies, and regulatory requirements by staying updated on quality regulations
- Oversee production stages to uphold consistent quality standards and identify areas for improvement in machinery and workflows
- Develop and enforce effective protocols to optimize inspection processes and enhance product quality assurance
- Analyze quality-related customer concerns, identify root causes, and collaborate on solutions to prevent recurrence
- Ensure adherence to safety protocols during inspections and production activities to promote a secure workplace for all personnel
Quality Control Inspector Requirements
Quality Control Inspectors play a key role in ensuring that products and services meet the required standards and specifications. To excel in this role, individuals must meet several key requirements:
Education
Educational requirements for the quality control inspector job role depend on the industry you are working. Here is a list of educational requirements that one must possess to get into this role:
- They must have a high school diploma or any equivalent education
- Having a bachelor’s degree can expand your job horizons and earning potentiality as well
- Real-time experience in the same domain is preferred
- Excellent documentation and presentation skills
- Excellent knowledge of Microsoft Office
- Profound knowledge of quality control standards
Certification
The role of a Quality Control Inspector does not require certification for career advancement. However, obtaining certification can greatly enhance your professionalism and demonstrate your expertise in the field. Employers increasingly seek candidates with proven skills and knowledge in today’s competitive job market. Certifications, such as those offered by the International Association of Six Sigma Certification (IASSC), can set you apart.
The IASSC provides globally recognized Lean Six Sigma certifications, including Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt, Lean Six Sigma Green Belt, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. These certifications can be earned through computer-based exams at recognized exam centres, and they signal to employers that you have a solid understanding of quality control principles and methodologies, making you a valuable asset to any organization.
Skills
Quality Control Inspectors require diverse skills to ensure that products and processes meet established standards effectively. To successfully pursue a career as a quality control inspector, one needs a combination of soft skills, technical skills, and certain qualities. Here are some essential skills for a quality control inspector:
- Attention to Detail: Precision is key in quality control. Inspectors must meticulously examine products and processes to identify any deviations from specifications
- Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze data, understand quality metrics, and interpret technical documents, blueprints, and specifications is vital for identifying issues and making informed decisions
- Problem-Solving Skills: Inspectors are not just observers; they are problem-solvers. They must be able to think critically and propose effective solutions when defects or quality issues are identified. This includes understanding root causes and implementing corrective actions
- Technical skills: The quality control inspectors should possess strong knowledge of the type of equipment and computer programs used, adhering to the organization’s safety guidelines. They must also know technical documents, manuals, and blueprints to ensure products meet quality standards
- Communication Skills: Inspectors are not just silent observers but good communicators. Clear and effective communication is essential for documenting findings and reporting issues to production teams, supervisors, and clients. Inspectors should be able to articulate problems and suggest solutions
- Organizational Skills: Strong organizational abilities are required for managing multiple inspections and maintaining detailed records. Inspectors must prioritize tasks and keep track of various quality control activities
Quality Control Inspector – Work Environment
The job roles of a quality control inspector entirely depend on the industry and organization size. The work routine/work environment of a quality control inspector has various aspects in common; some might work regular hours, and others might work extra hours as per the production deadline concerned.
List of industries providing quality control inspector job roles:
- Food production
- Chemical and apparel industries
- Furniture manufacturer
- Appliance manufacturer
- Electronic manufacturing industry
- Pharmaceutical company
Job Outlook of a Quality Control Inspector
The job outlook for quality control inspectors is stable, with steady demand driven by the need for high-quality products and regulatory compliance across various industries. Those continuously developing their skills and adapting to technological advancements will likely find ample opportunities in this field.
There will still be a need for quality control inspectors. The BLS projects around 64,300 job openings annually from 2022 to 2032. These openings will primarily be due to the need to replace workers who retire or leave the profession for other reasons. As manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, automotive, aerospace, and other industries prioritize quality to meet regulatory standards and customer expectations, the demand for skilled quality control inspectors remains high.
The table below shows the largest employers of quality control:
|
Manufacturing |
62% |
|
Administrative and support services |
10% |
|
Professional, scientific, and technical services |
9% |
|
Wholesale trade |
6% |
Salary Outlook
The salary outlook for quality control inspectors varies based on factors such as industry, location, level of experience, and education. The average salary of a quality control inspector in the United States is $89,982, but the range typically falls between $39,282 and $140,683.
Source: Salary.com
Conclusion
Quality Control Inspectors play an essential role in ensuring that products and processes meet established quality standards. Their responsibilities include examining products, using various inspection tools, analyzing data, and collaborating with other departments to resolve quality issues. By maintaining high standards and ensuring compliance with regulations, quality control inspectors help businesses improve product quality, enhance customer satisfaction, and stay competitive in the market.
Interested in mastering quality management and enhancing your career as a quality control inspector? Explore our comprehensive Quality Management and Six Sigma Certification Courses and gain the skills to excel in quality assurance and contribute to organizational success. Enroll today and take your career to the next level!