Table of Contents:
-
- Quality Analyst Job Role Description
- Importance of QA for an Organization
- Responsibilities of a Quality Analyst
- Quality Analyst Educational Requirements and Experience
- Emerging Skills of a QA Professional
- Quality Analyst Salary Trends
- Conclusion
In a software organization, the role of a quality analyst plays a vital role from initiation to the completion phase. Quality Analyst job description includes accomplishing manual testing and then move towards the automation part. They need to ensure that all the testing functionalities are working correctly.
A quality analyst supports planning, designing, and executing a project, i.e. it involves simple to complex responsibilities. They work with the development team in the organization and validate the test cases considering system requirements.
A quality analyst is held responsible for implementing quality assurance principles and practices throughout the SDLC.
Quality Analyst Job Role Description
To come up with a quality analyst job description, you need to understand the purpose of this role. The main purpose of this role is to test all the aspects of software, both technically and functionally, which is essential to delivering a quality product. They closely work with the IT department and identify software defects.
An efficient quality analyst should possess strong attention to detail and problem-solving ability. They must be able to implement quality assurance standards and provide accurate feedback to relevant teams. The role of a quality analyst is integral to delivering high-quality products that meet customer expectations and industry standards. By employing testing methods, effective communication, and continuous improvement practices, QAs help ensure that products are reliable, functional, and user-friendly.
Importance of QA for an Organization
In the software development world, the quality of the product is what actually counts. The design and concept can’t identify flaws that could have been easily avoided. Hiring a Quality Analyst is an effective way to ensure that the processes work as planned. A quality analyst is responsible from planning to the implementation phase and ensures that the product is delivered adhering to deadlines. It is essential for an organization to satisfy its clients by providing high-quality products that meet all their requirements.
Quality analysts are important in ensuring an organization’s overall performance and sustainability. Their work testing, identifying defects, and ensuring compliance contributes significantly to product quality, cost efficiency, customer satisfaction, and risk mitigation. In a competitive market, the role of a quality analyst is critical to preserving an organization’s reputation, operational efficiency, and customer trust.
Responsibilities of a Quality Analyst
Quality Analyst professionals have gained significance across various domains such as software development, customer service, manufacturing, and yet more.
A quality analyst possesses ample responsibilities, regardless of the domain they choose to pursue. Here is a compilation of it.
Responsibilities of a Quality Analyst
- A quality analyst should focus on designing/creating plans and ensure whether the quality requirements adhere to the organization’s policies
- A quality analyst is held responsible for implementing a plan with errors being fixed
- They are responsible to ensure whether the plan is apt considering its performance, reliability, functionality, and compatibility
- They should possess knowledge of quality assurance testing tools
- They collect all the essential statistics required and identify the root cause analysis method to identify the defect
- Reduction in employee attrition rates
- Provide knowledge/ Knowledge transfer to new joiners
- Develops a good rapport between the management and the employees
- Handling various resources at the workplace
- Providing efficient solutions for various types of issues
The responsibilities of a QA can be specific based on the organization and the domain you choose. However, a quality analyst’s education and skills remain constant.
Also read out to explore the roles and responsibilities of Quality Control Inspector!
Quality Analyst Educational Requirements and Experience
Now that you are aware of the responsibilities of a quality analyst, let’s take a look at the educational qualification to become one.
The educational requirements and experience of a quality analyst are crucial for developing the skills necessary to ensure product quality and reliability. A solid educational background in a relevant field, combined with practical experience in various testing methodologies and tools, prepares QAs to handle the complexities of their role. Continuous learning and professional development, including certifications and advanced degrees, further enhance a QA’s ability to contribute effectively to their organization’s success.
- Thorough knowledge of JavaScript, HTML, Python, Scrum, project management, Java, and SQL
- 2-4 years of proven experience in the software testing domain
- Bachelor’s degree in computer science, management information, or any other related field
- 3 years of quality analyst technical experience
- Comprehensive knowledge of tools, concepts, and associated methodologies of QA
- Proven skills in QA applications, databases, and Microsoft Office
- Certification like Quality Engineer, Quality Auditor, Six Sigma, and Quality Improvement associate
Emerging Skills of a QA Professional
With recent developments in the technological domain, the software testing industry has seen a huge rise. Thus, the demand for quality analysts has also increased in delivering efficient products to clients and customers.
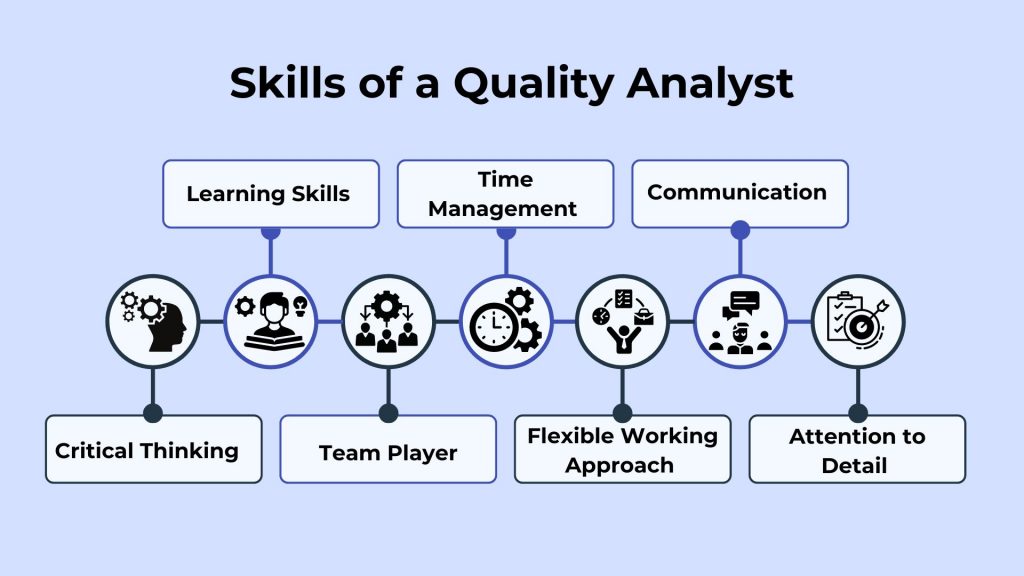
Here is a list of a few essential skills that help quality analysts to have a progressive career:
-
Critical Thinking
Having critical thinking ability helps in resolving the issues irrespective of the situation. It is a known fact that the product developed should adhere to organization norms and customer requirements. They must be capable of delivering more reliable and efficient software. They must be determined to dig out the bugs within the software and fix them at the earliest.
-
Learning Skills
To pursue a progressive career as a quality analyst it’s mandatory to have astounding learning skills. A quality analyst should possess ample knowledge of tools and technologies that are trending in their respective domain.
-
Team Player
With more companies incorporating Agile methodology, quality analysts are expected to work in coordination with various teams such as programmers, executives, developers, and testers in order to ensure successful product releases.
-
Time Management
A quality analyst should be well aware of how and when to deliver the product adhering to deadlines. Following time management best practices will help one become more efficient in their QA role.
-
Flexible Working Approach
A quality analyst should be flexible enough to take on added responsibilities for the successful accomplishment of the project. The term flexibility is related to various aspects such as skills, bandwidth, and duration.
-
Communication
Having clear and crisp communication skills is of utmost essential for a quality analyst role to effectively communicate with clients, stakeholders, and key users. They must be proficient enough in documenting the defects and reporting them. Other than bug reporting, the QA should also be able to provide appropriate solutions to those defects and this provides an edge to the overall process.
A quality analyst should be well-versed in both formal and informal communication. Information communication includes an oral conversation with the developer or other team members regarding the product. On the other hand, formal communication includes conveying the message through writing bug sheets, test cases, and other related documents.
-
Attention to Detail
Giving attention to minute details ensures that all the tasks are accomplished within the given time. It also prevents major intricacies hindering the supply chain and the need to redo the task to meet customer requirements at later stages.
Being a quality analyst, if you master the above set of skills, then absolutely you are bound to have a progressive career.
Quality Analyst Salary Trends
Quality Analyst salary trends are influenced by industry, geographic location, experience level, and specific skill sets. In the IT and software development sectors, QA professionals typically earn higher salaries due to the demand for software quality assurance. Geographic location also plays a significant role, with higher salaries in tech hubs like the United States, Europe, the UK, and India. The average QA analyst salary in the United States is $85,010 per year. Entry-level positions begin at $67,649 per year, while most experienced individuals earn up to $115,103 annually.
The rise of automation and remote work is further shaping salary trends, with a growing emphasis on advanced skills in automation tools and continuous learning. QA professionals who stay current with the latest testing tools and techniques are likely to see better salary growth, reflecting the increasing value of their expertise in ensuring quality and efficiency in product development.
Conclusion
There is fierce competition in the IT world, and hiring a quality analyst is not only advisable but also foreseeable. Now that you are aware of what Quality analysts do, their responsibilities, and the skills required, it is time to decide whether this career path is apt for you. They play a great role in delivering great software to the market. They are also accountable for identifying and fixing the bugs in the software. Nevertheless, their responsibilities involve testing to provide/ facilitate total quality management. They not only ensure an error-free product is released to the market, but they also ensure user satisfaction levels.
In the current scenario, quality analyst professionals should focus on improving their skills to overcome complex challenges by upgrading their knowledge through industry-recognized Quality Management and Six Sigma Certification Courses.