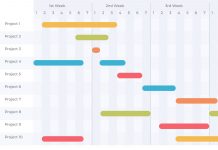
According to various project management approaches, stakeholder engagement is a critical aspect of a project lifecycle. A project performance report plays a significant role in determining the end results of a project. Whether or not a project met the desired objectives is determined by looking at the project performance report. When a project ends, a few basic questions needs to be answered by stakeholders such as, ‘Is the project successful?’, ‘What could have been better?’, ‘Is the team efficient enough? ‘Is the cost justified?’ In order to have answers to the above questions, you should have appropriate data to back up the story you want stakeholders to know. Therefore, it is necessary to have a mechanism in place to measure the success or failure of a project.
A project report is an approved performance communication plan outlining the key project information which concerns project costs, quality, profit, risks, and areas of improvement.
Benefits of Having a Project Performance Report
There are a few distinct benefits of having a performance report.
- The report will provide a clear picture of the pain points, and risks within the project. These will enable you to prepare well for your future projects in terms of what to expect, what not to expect, and how to eradicate risks, and improve the areas of pain points.
- You can identify whether the service level agreements have been met.
- Your work can be justified through a performance report and you can ask for more resources for future prospective projects.
- A performance report provides a picture of the project performance against the decided baselines. In case, it is seen that the project did not progress as per plan, corrective actions may be undertaken by stakeholders by adding funds, and resources, or extending the timeline of the project.
Content of a Performance Report
A performance report mainly consists of the amount of work completed during a certain period, amount of the work remaining to be completed, amount of money spent till date, amount of money remaining from the set budget, the balance time available, key risks occurred during the project development, the risks that could have occurred, performance indexes like cost performance index and schedule performance index, additional fund forecasted to complete the remaining tasks in the project, forecasted time (additional time to what was decided) time to complete the project, and a summary of the key change requests approved during the tenure of the project. Below are a few key elements of a project report.
Key Elements of a Project Report
1. Budget:
This includes the amount set aside to be used for the project, the percentage used up, and the percentage remaining. The project report, having detailed data regarding the percentage of budget used up, and the percentage remaining, provides a clear picture regarding where the project stands in terms of money and resources. Depending on the report budget can be increased or decreased.
2. Resource:
A project report gives a clear picture of where the project stands in terms of resource utilization. In case additional resources are needed to complete the assigned tasks within scheduled date, the same is arranged after taking approval from project board or stakeholders.
3. Risks:
A project report highlights the main risks faced. This enables the project board and stakeholders to decide on changes so that the factors leading to risks can be removed. The report also tries to find out the adverse circumstances that could have occurred. Precautions are taken so that such circumstances can be prevented from occurring in the future.
4. Time:
A project report gives a picture of where the project stands in terms of on-time completion. In case, the report shows that the amount of tasks remaining to be completed is a lot compared to the time left, stakeholders may consider putting in more resources or extending the time limit.
5. Change Requests:
Before a project initiates, you have a plan chalked out according to which the project is expected to initiate and progress. However, there may occur unforeseen circumstances for which changing the plan becomes necessary. The change can be in the form of adding or eliminating resources and finance etc. However, every change request needs to have a justification on the basis of which it will be approved by stakeholders. The performance report will have a summary of all the requests raised, approved, and unapproved. This will give you a snapshot of deviations in plans that had happened to date, hence helping you forecast the changes that may happen in the future.
A project board performs a few critical functions listed below.
Functions of a Project Board
1. Distributing Information:
A project report provides a synopsis of a project, its progress till date, the goals it is trying to achieve, and where it stands against its goals. With actual data in hand, which the report provides, it is convenient to distribute information within the organization. Everyone associated or not associated with the project can catch a glimpse of all aspects of the project through its performance report.
2. Managing Communication:
Putting across your own views about the risks and benefits, good and bad aspects of a project are not easy when you do not have data to support your view. A project report is also one of the best mediums to put across important communications within the team and across the organization. Once the report is ready, the project team can sit and discuss good and bad aspects, the risks and benefits, and put across their opinions against the data presented by the report.
Performance Reporting Method – PEMARI
When preparing your project performance report, you can take recourse to the PEMARI method. It stands for measurement plan; establish measures, measure performance, analyze data, performance reporting, and continuous improvement.
1. Measurement Planning:
This step includes identifying the performance measuring team, the project areas that need to be measured, and the associated tools to include.
2. Establishing Measures:
This step includes developing the measures to be undertaken, planning data collection, communicating the data source, collecting data, and ensuring the data quality.
3. Measuring Performance:
In this step, you identify the data source, plan for data collection and communicate to the source regarding what is expected out of the data.
4. Analyzing Data:
This step – perhaps the most crucial step, involves analyzing data, calculating metric values, validating results and conducting a benchmarking and a comparative analysis.
5. Performance Reporting:
In this step, you need to develop a performance communication plan which may include the events that have occurred, the target audience, the message you want to convey, the key objectives that need to be accomplished, and impacts and comments if any. The report once ready, can be shared with stakeholders.
6. Continuous Improvement:
In this step, you need to review the target metric value, learn your lessons from feedback, formally collect and document the lessons learned, and set the target action items to achieve goals.
A project performance report is simply a method of communication that enables anyone within your organization to understand what is happening in your project. Having full proof data, planning and analysis, enables you to explain or justify any questions or doubts raised across your organization.