Choosing a career path is a significant decision that can shape your professional future. Two fields that have gained prominence in recent years are project management and data analytics. Both offer exciting opportunities for growth and development, but they differ in many aspects.
In this blog, we will compare project management and data analytics, exploring their roles, skills required, career prospects, and more to help you determine which path may be better for you.
Table of Contents
- What is Project Management?
- What is Data Analytics?
- Data Analytics Vs. Project Management
- Data Analytics vs. Project Management: Career Prospect
- Conclusion
What is Project Management?
Project management is a systematic approach to planning, organizing, executing, and closing projects efficiently and effectively. It encompasses defining project objectives, creating schedules, allocating resources, and managing budgets to ensure successful project completion within the constraints of time, cost, and scope.
Project management is a critical discipline that transcends industries, ensuring that projects are delivered successfully. By employing best practices in project management, organizations can enhance their ability to adapt to change, mitigate risks, and maximize resources.
Effective project management leads to increased efficiency, improved project outcomes, and higher project stakeholder satisfaction, positioning organizations for long-term success and growth.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is a systematic process that explores data to extract valuable insights, inform decision-making, and enhance organizational performance. It encompasses various processes, including data collection, cleaning, analysis, and interpretation, often employing advanced statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization tools.
By analyzing historical data, data analytics enables businesses to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that can uncover valuable insights into customer behavior, market dynamics, operational performance, and more.
Moreover, predictive analytics techniques allow organizations to forecast future trends and outcomes, empowering them to anticipate changes and proactively address challenges or capitalize on opportunities.
Data analytics is crucial in helping organizations gain a competitive edge and achieve strategic objectives. By leveraging the power of data, businesses can make more informed decisions, optimize processes, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Data Analytics Vs. Project Management
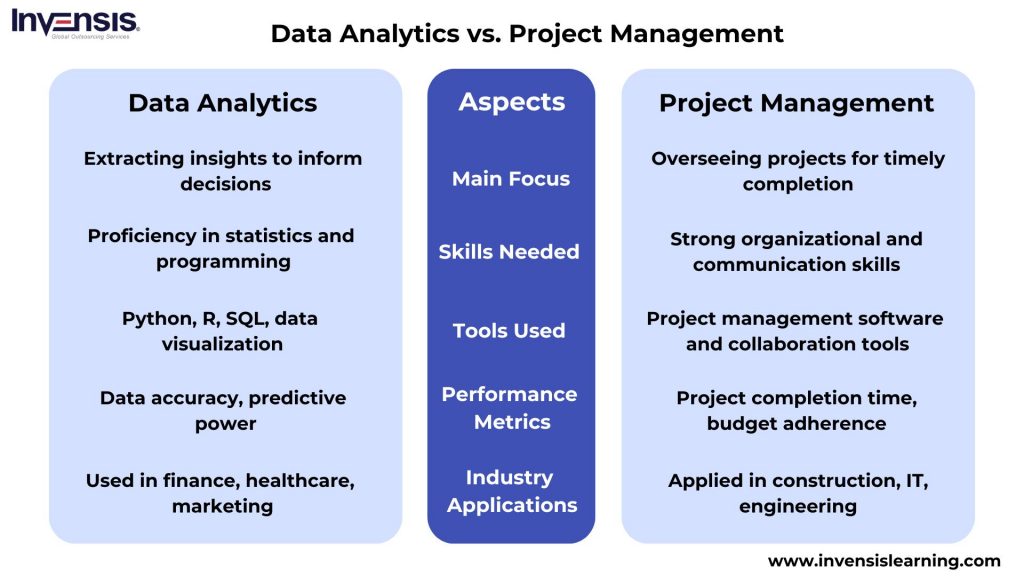
Data analytics and project management are crucial for success in today’s business environment. Data analytics extracts insights from data, informing decisions, while project management ensures projects are completed effectively.
Comparing their focus, skills, tools, education, and experience provides valuable insights.
Main Focus
Data Analytics:
- Focuses on extracting insights from large datasets using statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization techniques.
- Primarily concerned with uncovering patterns, trends, and correlations within data to inform decision-making and drive business strategy.
Project Management:
- Involves overseeing projects from start to completion, ensuring that they are delivered on time, within budget, and according to specifications.
- The primary focus is managing project timelines, resources, and deliverables to achieve project objectives and meet stakeholder expectations.
Skills Needed
Data Analytics:
- Proficiency in statistical analysis, data manipulation, and programming languages such as Python or R.
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills and the ability to communicate complex findings effectively to non-technical stakeholders.
Project Management:
- Excellent organizational and time management skills, with the ability to prioritize tasks and manage multiple projects simultaneously.
- Effective communication and leadership abilities to coordinate teams, resolve conflicts, and drive project success.
Tools Used
Data Analytics:
- Tools such as Python, R, SQL, and data visualization libraries like Matplotlib or Tableau.
- Data analytics platforms such as Google Analytics, SAS, or IBM SPSS for advanced analytics and predictive modeling.
Project Management:
- Project management software such as Microsoft Project, Asana, or Trello for task management and project tracking.
- Collaboration tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for communication and document sharing among project team members.
Performance Metrics
Data Analytics:
- Data analytics performance metrics include data accuracy, model accuracy, predictive power, and ROI on analytics investments.
- Key indicators also include data quality, processing speed, and the efficiency of data pipelines.
Project Management:
- Performance metrics in project management encompass factors like project completion time, budget adherence, stakeholder satisfaction, and adherence to project scope.
- Other metrics include resource utilization, risk mitigation effectiveness, and the achievement of project milestones.
Education
Data Analytics:
- Typically requires a statistics, mathematics, computer science, or data science background.
- Advanced degrees such as a Master’s in Data Analytics or a related field may be preferred for senior-level positions.
Project Management:
- Degrees in project management, business administration, or related fields are common but not always required.
- Project management certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or PRINCE2 Foundation and Practitioner certification training can enhance career prospects and demonstrate proficiency in project management principles and practices.
Experience
Data Analytics:
- Experience with data analysis, statistical modeling, and machine learning techniques.
- Practical experience working with large datasets and applying analytical methodologies to solve real-world business problems.
Project Management:
- Experience leading and managing projects, including developing project plans, allocating resources, and monitoring progress.
- Strong track record of successful project delivery and stakeholder management.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Data Analytics:
- Collaboration in data analytics involves multidisciplinary teams comprising data scientists, analysts, domain experts, and IT professionals.
- Team dynamics focus on sharing insights, collaborating on data projects, and leveraging diverse expertise to solve complex problems.
Project Management:
- Project management relies on cross-functional teams consisting of project managers, team members, stakeholders, and subject matter experts.
- Effective collaboration entails clear communication, task delegation, conflict resolution, and fostering a positive team environment to achieve project goals.
Innovation and Problem-Solving
Data Analytics:
- Data analytics drives innovation by uncovering insights, identifying trends, and discovering new opportunities within datasets.
- Problem-solving in data analytics involves applying analytical techniques to address business challenges, optimize processes, and drive continuous improvement.
Project Management:
- Project management brings innovation by facilitating the execution of new initiatives, product development, and process improvements.
- Problem-solving in project management entails identifying risks, implementing mitigation strategies, and resolving issues to ensure project success.
Industry Applications
Data Analytics:
- Industry applications of data analytics span across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, marketing, and retail.
- Data analytics is used for customer segmentation, market analysis, risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized marketing campaigns.
Project Management:
- Project management finds applications in construction, IT, engineering, and event planning industries.
- It manages construction projects, software development, product launches, and organizational change initiatives.
Data Analytics vs. Project Management: Career Prospect
Data analytics and project management offer promising career paths. This comparison examines career opportunities, salary potential, and growth prospects. Both fields provide diverse career options, from data analysts driving innovation to project managers ensuring success.
| Aspect | Data Analytics | Project Management |
| Career Opportunities | Data analysts and data scientists are in high demand across industries such as finance, healthcare, and technology, and there are opportunities for growth from entry-level to managerial roles. | Project management roles offer diverse opportunities in various sectors, and there is a demand for skilled professionals to drive project success and oversee complex projects. |
| Salary
Potential |
Data analytics roles often come with competitive salaries and room for growth, especially for those with specialized skills and experience in advanced analytics techniques. | Project management professionals can command competitive salaries, with potential for salary increases and bonuses as they progress into senior management roles and oversee larger projects. |
| Growth Opportunities | Professionals in data analytics have a range of career paths to explore, from data analyst to data scientist, with opportunities for advancement into managerial and leadership positions as organizations prioritize data-driven decision-making. | Project managers can advance their careers through experience and certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional), with opportunities to lead larger and more complex projects and teams. Certification benefits can also enhance career prospects and open doors to new opportunities. |
| Industry
Demand |
With the increasing importance of data-driven decision-making, the demand for skilled data analysts and data scientists continues to grow across industries. Data analytics is an essential function for driving business performance and innovation. | Project management is essential for ensuring project success across industries, with businesses relying on skilled project managers to oversee timelines, budgets, and resources while aligning project objectives with organizational goals. As organizations undertake more complex projects to innovate and grow, the demand for project management professionals remains strong. |
Conclusion
Both project management and data analytics are integral to the success of projects and businesses in different ways. Project managers are essential for organizing and overseeing projects, ensuring they are completed on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of stakeholders.
On the other hand, data analysts play a crucial role in extracting insights from data, informing decision-making, and driving business strategy.
The choice between project management and data analytics depends on individual interests, skills, and career goals. Those inclined towards leadership, organization, and overseeing projects may find project management more suitable.
Conversely, individuals with a passion for data, analysis, and deriving insights may prefer a career in data analytics. Ultimately, both fields offer rewarding career paths with opportunities for growth and advancement.
For individuals interested in pursuing a career in Project Management, enroll in Invensis Learning’s Project Management Courses to enhance your skills and knowledge in this field.