Organizations are grappling with escalating costs, staffing challenges, and stringent regulations in today’s healthcare landscape. These factors pose significant obstacles to their sustainability and growth. As a result, healthcare teams are under immense pressure to optimize resources, trim overhead, and embrace effective project management practices. Effective project management in healthcare is not just a matter of chance; it’s a critical necessity in healthcare.
It directly influences an organization’s reputation, financial health, and employee morale. Moreover, in healthcare, the stakes are even higher, as projects and initiatives directly impact patient care.
To excel in healthcare project management, you need a clear understanding of your objectives, a well-defined execution framework, and the right tools to succeed. This blog will show you how to kickstart your journey towards achieving excellence in healthcare project management.
What is Project Management in Healthcare?
Project Management in Healthcare serves as a catalyst for innovation and progress within the industry. With the rapid advancement of medical technologies and treatment modalities, healthcare organizations must remain at the forefront of innovation to provide the best care possible.
Project management ensures the successful implementation of new medical technologies and fosters an environment of continuous improvement.
It encourages healthcare teams to explore innovative solutions, whether adopting cutting-edge treatments, enhancing patient engagement through digital platforms, or reimagining healthcare delivery models.
By systematically planning and executing projects, healthcare organizations can seize opportunities to pioneer new methods, improve existing processes, and elevate the standard of care they offer patients.
In this way, Project Management in Healthcare responds to the evolving landscape and actively drives positive change and progress in the industry.
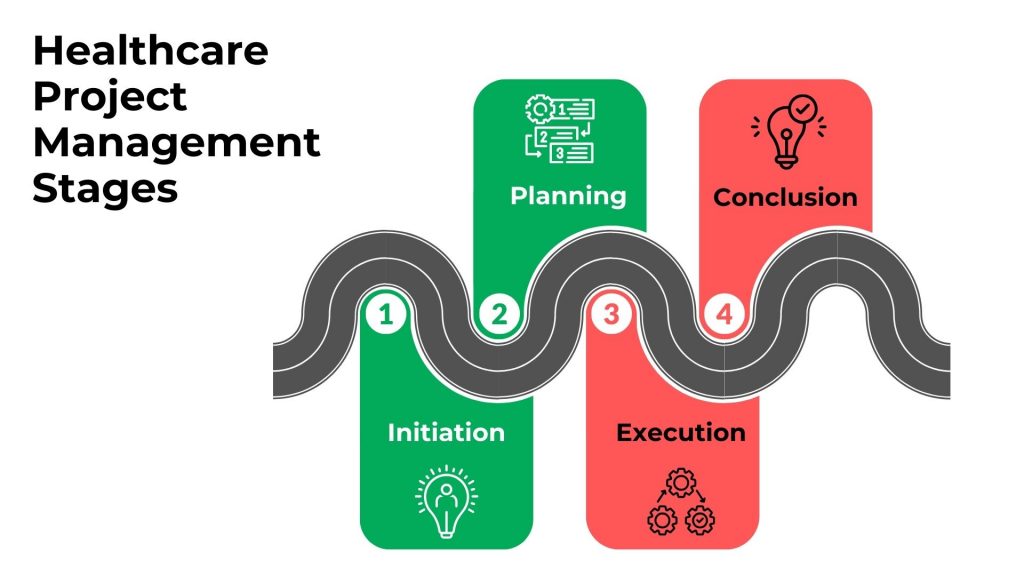
What are the stages in Healthcare Project Management?
The stages of project management represent a systematic approach to executing projects successfully. These stages typically include initiation, planning, execution, and conclusion. Each stage is crucial in guiding projects to completion efficiently and effectively.
The four key phases of healthcare project management are as follows:
Stage 1 – Initiation
In this initial phase, stakeholders assess potential projects, evaluating their objectives, resources, and expected outcomes. This evaluation determines which projects receive approval and which ones are deferred. This stage is particularly crucial for healthcare organizations, which often operate with limited resources and must prioritize projects with the greatest potential impact.
For instance, large hospitals might consider new facility construction based on changes in patient demographics or advancements in medical technology, while fitness studios may assess equipment procurement or staffing needs.
Stage 2 – Planning
After a project receives approval, it advances to the planning phase. Here, the project manager develops a comprehensive project plan that outlines key details such as the schedule, tasks, budget, team members, and their responsibilities.
Potential challenges and the criteria for measuring project success are also identified at this stage. The goal is to secure all the necessary approvals and decisions to proceed to the execution phase, which may involve conducting facility assessments with hospital leadership or determining the total costs of gym equipment.
Stage 3 – Execution
The execution phase is where the project’s actual work takes place. Project contributors carry out their assigned tasks and work towards project completion. Effective progress tracking, measurement, and communication are critical during this phase.
This allows the project manager to identify and address obstacles, reallocate resources, and make necessary adjustments to ensure the project stays on course.
For example, it involves submitting hospital wing construction documents for regulatory permits or placing orders for gym equipment.
Stage 4 – Conclusion
Once the project is finished, the conclusion phase comes into play. Here, the healthcare project manager provides stakeholders with a summary of the project’s performance, highlighting key deliverables and outcomes. It is also an opportunity for reflection on successes, areas for improvement in future projects, and an assessment of each contributor’s performance.
In the case of hospital construction, this phase includes final inspections and gathering feedback from patients and staff who will use the new facility and equipment.
Each project management stage is interconnected and vital to overall project success. By giving attention to all four stages rather than focusing on just a couple, healthcare organizations can increase the likelihood of achieving favorable project outcomes.
Useful Methodologies for Project Management Healthcare
Several project management methodologies can be useful in healthcare settings, helping organizations plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively. Here are some methodologies commonly employed in healthcare project management:
Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall approach is a traditional, sequential project management method well-suited for healthcare projects with well-defined requirements. It involves a linear and structured process where each phase must be completed before the next begins. This methodology is often used for projects like implementing an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system.
Agile Methodology
Agile is a flexible and iterative approach that is increasingly popular in healthcare. It is valuable for projects where requirements may evolve or are not fully known upfront, such as software development for healthcare applications. Agile promotes collaboration, adaptability, and regular feedback from end-users.
Also check the role of agile in healthace and medical research and its impact in the domain!
Scrum
A subset of Agile, Scrum is particularly useful in healthcare IT projects. It organizes work into short, time-boxed iterations and sprints, allowing teams to prioritize and deliver features incrementally. This approach facilitates quick responses to changing requirements and provides transparency into project progress.
Lean Healthcare
Lean principles, derived from manufacturing, focus on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. In healthcare, Lean methodologies can streamline processes, reduce wait times, and enhance the overall patient experience. Lean Six Sigma is a variant of this methodology that combines Lean principles with data-driven analytics to identify and address issues.
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 is a process-driven project management framework emphasizing organization, control, and effective communication. It suits complex healthcare projects requiring strict governance and risk management.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM is a mathematical approach to project management that is useful for healthcare projects with well-defined tasks and dependencies. It helps identify the critical path—the sequence of activities that determines the project’s overall duration. This is beneficial for projects like hospital construction or facility expansion.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma methodologies aim to reduce process defects and errors. Healthcare organizations often use Six Sigma to improve patient safety, reduce medical errors, and enhance the quality of care.
Master Project Management mehtodologies with Invesis Learning’s industry aligned top project management courses!
Key Challenges in Healthcare Project Management
Healthcare project management presents a unique set of challenges that require careful consideration and proactive strategies. These challenges often include navigating complex regulatory requirements, managing limited resources effectively, ensuring seamless communication among diverse stakeholders, adapting to rapidly evolving technology and treatment methods, and maintaining a strong focus on patient care and safety throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Additionally, healthcare project managers must address budget constraints, staff shortages, and the need to keep projects aligned with the organization’s mission and goals. Successfully overcoming these challenges is essential for healthcare organizations to deliver high-quality care, implement crucial initiatives, and drive positive outcomes in the dynamic healthcare landscape.
Now, let us discuss a few of these challenges:
Escalating Costs
The current landscape sees a record number of insured Americans, intensifying the demand for healthcare services. This surge in demand and continuously increasing costs exert tremendous pressure on the industry to deliver cost-effective yet high-quality care. Striking the delicate balance between efficiency and excellence underscores the critical importance of improved project management.
Stringent Regulatory Environment
The healthcare sector is burdened with many regulations, including the stringent patient privacy laws mandated by HIPAA. The imperative to safeguard sensitive information has led to the introduction of multiple layers of approvals for projects. Often, projects necessitate endorsement from the hospital’s local and national governmental bodies, resulting in heightened project complexity and more rigorous project management prerequisites.
Ever-Evolving Industry Dynamics
Healthcare is predominantly service-driven, heavily reliant on highly skilled professionals whose roles cannot be easily automated. Despite an increasing demand for healthcare services, there remains a need for more healthcare practitioners, negatively affecting productivity. Effective project management is vital to bridge this gap by optimizing processes and resource allocation.
Heightened Risk
Project management’s inherent strength lies in its ability to mitigate risks, a particularly valuable trait in the healthcare industry, which is prone to litigation. Establishing streamlined and efficient processes is the primary way project management reduces or eliminates potential risks.
For example, a hospital undertaking a project to define the optimal pre-surgery process can significantly reduce errors made during surgical procedures.
Diverse Array of Stakeholders
Many of these challenges, ranging from stringent regulations to heightened litigation risks, translate into the involvement of numerous stakeholders. Managing healthcare projects often entails navigating a complex web of diverse interests.
Some projects necessitate approval from various quarters, including hospital boards, healthcare providers, patients, and state and national governing bodies. Effective project management is essential in coordinating these multifaceted interactions and ensuring successful project outcomes.
Benefits of Effective Project Management in Healthcare
When executed effectively, project management becomes an indispensable asset for healthcare providers, facilitating improvements and enhancing operational efficiency across various domains.
Streamlined Processes
Among the most significant advantages of implementing project management in hospital settings is its ability to mitigate the ever-present litigation risks that hover over healthcare organizations. The establishment of meticulously defined, step-by-step processes serves to minimize unfavorable outcomes.
Consider, for instance, the various tasks a surgical team must undertake before a procedure, encompassing room setup, surgeon hand sterilization, and dosage verification by the anesthesiologist.
In this context, a well-defined process significantly enhances positive patient outcomes by leaving nothing to chance or memory.
Strategic Organizational Planning
Achieving excellence in project management necessitates a pronounced emphasis on meticulous planning. Project contributors, managers, and stakeholders must cultivate a forward-thinking mindset, becoming proficient in methodically charting the course of a project step by step.
This commitment to planning extends its influence throughout the organization, impacting areas such as scheduling and procuring vital medical supplies, ultimately enhancing the quality of care.
Financial Alignment
Project management harmonizes financial resources with project activities, ensuring fiscal accountability and transparency. It acts as a diligent steward, validating the availability of funds at each project stage.
For instance, it offers insights into whether the budget is sufficient to initiate a project and provides a mechanism to recalibrate and reprioritize in the event of unexpected expenditures.
Nurturing Stakeholder Relationships
Organizations can foster robust relationships with their board of directors, volunteers, and donors by involving them in the project approval phase and maintaining regular communication regarding project progress and milestones.
Furthermore, a systematic approach to tracking project completion and assessing success enables the quantification of the impact of organizational improvements, thereby demonstrating value effectively.
Enhanced Communication
Distinguishing project management in healthcare from other industries is the intricate network of individuals involved in patient care, underscoring the critical importance of clear and effective communication. Staff turnover ranks among the foremost causes of errors in healthcare settings.
For example, a departing physician’s ability to communicate a patient’s current status to the incoming physician significantly influences patient outcomes, highlighting the need for seamless and unambiguous communication practices.
Best Practices for Healthcare Project Management
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to healthcare project management. How you approach project management can vary based on your organization’s structure, your preferred methodology, the type of projects you manage, and other factors.
With that being said, there are a few simple steps you can take to improve project management within your healthcare practice. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to healthcare project management. How you approach project management can vary based on your organization’s structure, your preferred methodology, the type of projects you manage, and other factors.
With that being said, there are a few simple steps you can take to improve project management within your healthcare practice.
Foster Transparent Communication within the Organization
Establish a standardized and open planning approach that encourages participation from various departments across the organization. Create an environment where team members feel valued and are motivated to voice potential concerns or obstacles.
Prioritize Thorough Planning
Inadequate planning significantly contributes to project failures. Before diving into specific tasks, invest time in crafting a comprehensive project charter. This document should outline the project’s objectives, required resources, key deliverables, and success metrics.
For example, if you’re upgrading cardio equipment at your fitness center, clarify the project’s significance, define the involved parties, and set expectations regarding deadlines and communication. This charter is vital to ensuring alignment among the entire team and stakeholders concerning project goals and logistics.
Simplify Your Processes
Once you’ve defined your project management processes, streamline their implementation and execution. Utilize tools that facilitate planning for the next steps and monitoring progress, including strategy management software capable of automating various process aspects.
Facilitate Cross-Department Collaboration
Many healthcare facility projects necessitate collaboration among multiple departments. Effective collaboration is paramount; siloed information within departments can lead to project delays. Leverage your project management tools to simplify collaboration, enabling all teams to work seamlessly, regardless of their department.
Document Results for Continuous Improvement
Document key project aspects, including challenges and their solutions, outcomes, lessons learned, unexpected occurrences, and best practices. This documentation is a valuable resource for enhancing your project management processes and provides an opportunity to celebrate achievements.
Conclusion
Having an effective healthcare project management is not a luxury but a necessity. By implementing the right project management approaches and tools, healthcare organizations can not only save lives but also improve daily processes and outcomes for all healthcare providers.
Invensis Learning’s PMP certification equips healthcare professionals with the skills needed to navigate the complexities of healthcare projects, ultimately leading to enhanced patient care and streamlined operations.