The PRINCE2 methodology stands out in project management for its essential framework and comprehensive guidance, ensuring projects are executed efficiently and effectively. A crucial component of the PRINCE2 business case is a dynamic document that justifies the project’s initiation, continuation, and final delivery. By emphasizing the alignment of project goals with strategic business objectives, the business case serves as a foundation for decision-making, risk management, and stakeholder engagement.
Table Of Contents
- What is a PRINCE2 Business Case?
- Importance of Business Case in Prince2 Approach
- How to Create a Business Case with PRINCE2? With Examples
- Element of a Business Case?
- Prince2 Business Case Template
- Conclusion
This blog explores the benefits of using business case examples and templates within the PRINCE2 methodology. It showcases how they enhance project success, provide clear investment justification, and maintain a focus on delivering actual business value.
What is a PRINCE2 Business Case?
A PRINCE2 business case is a document that justifies the initiation, continuation, or completion of a project. It outlines the reasons for the project, the benefits to be gained, the costs involved, and the potential risks.
The PRINCE2 business case serves as a critical tool for decision-making, ensuring that the project aligns with organizational goals and delivers tangible value. It includes key components such as the project objectives, expected benefits, options considered, financial appraisal, and risk analysis.
A PRINCE2 business case presents a clear and structured argument that helps stakeholders understand the project’s value and supports informed decision-making throughout the project’s lifecycle.
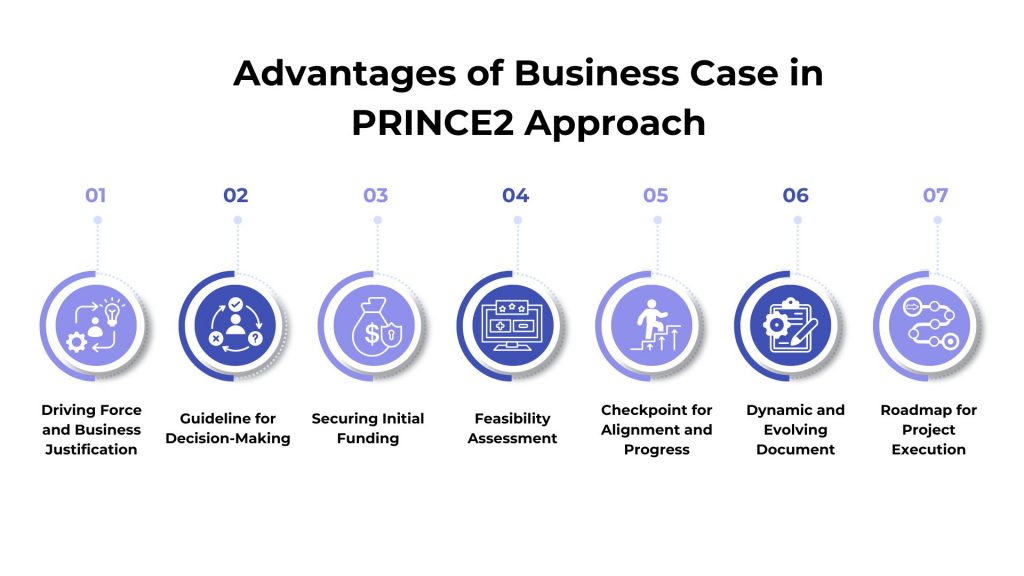
Importance of Business Case in PRINCE2 Approach
The importance of a business case in the PRINCE2 approach lies in its role as a central document that guides decision-making and ensures project alignment with organizational goals.
Here are the key reasons why a business case is crucial in the PRINCE2 methodology:
-
Driving Force and Business Justification
The business case is the project’s core driving force, providing the essential business reason for its initiation and continuation. It ensures that the project is justified and its objectives align with the business needs and strategic goals.
-
Guideline for Decision-Making
Project objectives are directly linked to the needs outlined in the business case, serving as a guideline for all decision-making processes. This alignment ensures that every decision supports the project’s goals and strategic direction.
-
Securing Initial Funding
The business case theme in PRINCE2 is crucial for securing the project’s initial funding. It justifies the investment and convinces stakeholders of the project’s viability and potential benefits.
-
Feasibility Assessment
Developing the business case involves a thorough feasibility assessment of the project. This allows the project board to make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project based on a detailed analysis of its potential success and alignment with business objectives.
-
Checkpoint for Alignment and Progress
The business case is a checkpoint throughout the project lifecycle to ensure the project remains aligned with its intended objectives. It helps maintain focus on the project’s goals and ensures that procedures stay on track.
-
Dynamic and Evolving Document
The business case is not a one-time document but a dynamic and evolving one. As the project progresses, it can be elaborated upon and updated to reflect new information, changes in scope, or business priorities, ensuring continuous alignment and relevance.
-
Roadmap for Project Execution
By outlining key aspects such as timeframe, cost, and major risks, the business case sets a clear roadmap for the project team. It ensures everyone understands the project’s critical features and works towards a common goal, contributing to a well-structured and goal-oriented project management approach.
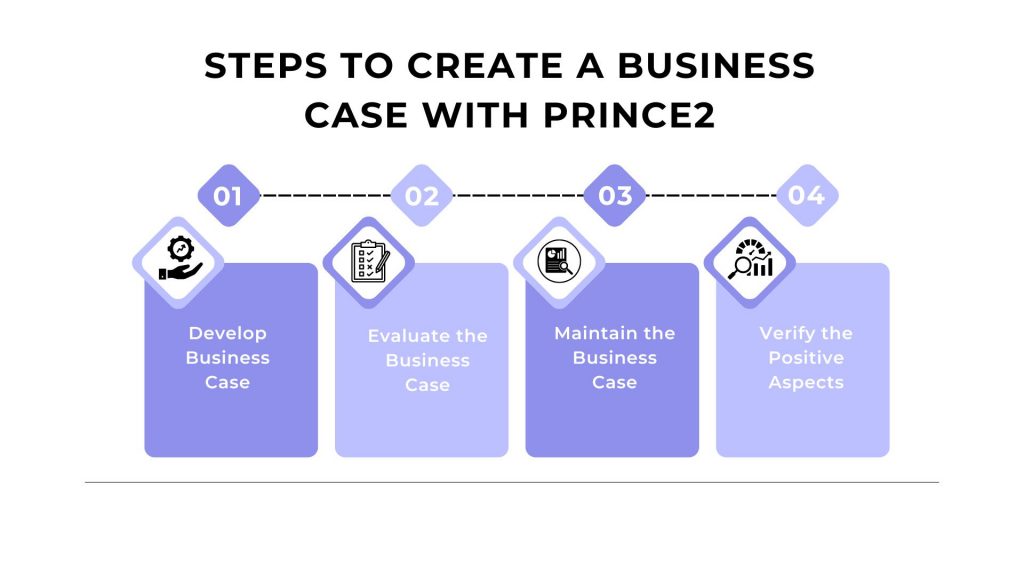
How to Create a PRINCE2 Business Case?
Creating a business case using the PRINCE2 methodology involves specific steps, each with concrete elements and examples to illustrate the process. Here is how you can develop a business case using PRINCE2, along with examples:
Develop Business Case
Creating the business case in PRINCE2 involves gathering comprehensive information to define and document the project’s justification. Start by understanding the problem or opportunity, often through stakeholder interviews and data analysis. Use the project mandate to outline the initial business need, and then develop a detailed business case. This document includes an executive summary, reasons for the project, options considered, expected benefits, estimated costs and timescales, identified risks with mitigation strategies, and an investment appraisal using financial metrics such as ROI and NPV.
For example, in a project to implement a new CRM system, the business case would justify the need for improved customer service and sales efficiency, outline the costs, and detail the expected 20% increase in sales.
Evaluate the Business Case
Verification ensures the business case is strong, realistic, and aligned with organizational goals before project initiation. This involves an internal review where the project board and key stakeholders evaluate the business case to confirm its alignment with strategic objectives and validate assumptions, benefits, and risks. Quality assurance steps, such as expert verification and scenario analysis, ensure the business case’s accuracy and completeness.
For example, the project board would review a CRM project’s business case to ensure it supports the company’s strategic aim of enhancing customer service, with departments like sales and customer service validating the system’s proposed benefits.
Maintain the Business Case
Maintaining the business case involves regularly updating it throughout the project lifecycle to reflect any changes and ensure it remains valid. This requires periodic reviews at the end of each project stage and in response to any significant deviations from the original plan. Continuous monitoring includes tracking project progress against business case projections and updating risk management plans as needed.
Verify the Positive Aspects
Confirming the benefits involves ensuring the project delivers the expected outcomes and value outlined in the business case. Develop a benefits realization plan that specifies how and when the benefits will be measured, defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. After project completion, conduct a post-project review to measure actual benefits against projections, document the findings, and identify lessons learned.
For example, six months after implementing the new CRM system, a review would measure a 15% increase in sales efficiency and a 10% improvement in customer satisfaction, compare these results to the projected benefits, and document insights for future projects.
Elements of a PRINCE2 Business Case
A business case is a comprehensive document or presentation that outlines the justification for initiating a project or task. It is used to convince stakeholders of the merits of the proposed initiative. Here are the key elements of a business case:
-
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a concise overview of the entire business case for quick reference by decision-makers. It briefly states why the project is being proposed, summarizes the most important aspects (including the problem, proposed solution, benefits, costs, and timelines), and highlights the preferred course of action along with its rationale.
-
Project Definition
The project definition clearly outlines the project’s scope, objectives, and deliverables. It defines what the project aims to achieve in measurable terms, describes the project’s boundaries (including what is in scope and what is out of scope), lists the tangible outputs or products that the project will produce, and lists any assumptions made during the project planning.
-
Business Options
The business options section presents different approaches to solving the identified problem or seizing the opportunity. It describes the implications of not proceeding with the project (highlighting potential risks and missed opportunities), outlines a basic, low-cost approach to address the problem or opportunity as a baseline comparison, and details the preferred solution along with any alternative viable options, including their benefits, costs, and risks.
-
Problem Statement / Definition
The problem statement articulates the specific problem or opportunity the project intends to address. It clearly describes the problem or opportunity in detail, explains its impact on the organization (including any quantitative and qualitative effects), and justifies why action is necessary now, emphasizing urgency or strategic importance.
-
Problem Analysis
The problem analysis section analyzes the underlying causes of the problem and understands its context and implications. It identifies the root causes of the problem using techniques such as the 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram, gathers relevant data and evidence to support the analysis, assesses the broader impact of the problem on the organization, stakeholders, and external environment, and examines trends related to the problem, including historical data and future projections.
-
Discuss all the Possible Options
Once you identify the problem statement, come up with all the possible solutions to address the issues. For each option/solution you come up with, discuss the time scale, benefits, cost, and risks associated.
- Expected Advantages: Outline each anticipated benefit, including how and when it will be measured. Detail the positive outcomes and performance indicators to track the benefits over time
- Expected Disadvantages: According to PRINCE2, dis-benefits are outcomes viewed negatively by one or more stakeholders. These may also be termed negative impacts
- Timelines: Specify the project’s start and end dates and the timeline for when the benefits will be realized. Clearly define the milestones and key delivery dates
- Costs: Include the total project costs and estimate the ongoing maintenance expenses post-completion. Provide a comprehensive financial overview encompassing both initial and recurring costs
- Investment Appraisal: Present a detailed Return on Investment (ROI) analysis, comparing costs versus benefits. Include calculations and data to demonstrate the project’s financial viability and expected return
- Major Vulnerabilities: Summarize the primary risks associated with the project, as identified in the Risk Register. Provide an overview of potential vulnerabilities and their possible impacts on the project
Prince2 Business Case Template
The purpose of using a PRINCE2 business case template is to provide a structured framework and standardized format for developing and documenting the Business Case within the PRINCE2 project management methodology. It facilitates efficient creation by providing a standardized format that aligns with PRINCE2 principles, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions and approvals. The template supports effective project governance, monitoring progress against objectives, and adapting to changes throughout the project lifecycle.
Here, you can access a straightforward PRINCE2 business case template available in PDF format. This user-friendly resource is designed to help you easily create a comprehensive and structured business case. Download it now to streamline your project planning and proposal process.
Conclusion
Utilizing PRINCE2 business case can significantly streamline the process of justifying and planning projects. These resources provide a structured framework that ensures all critical aspects, from financial justification to risk assessment, are comprehensively addressed. By adopting PRINCE2 methodologies, organizations can enhance their project management practices, leading to more successful outcomes and better alignment with business objectives.
Need help to write winning business cases and ensure project success? Explore Invensis PRINCE2 certification courses, which effectively help craft and manage business cases, a key project management skill. Enroll today!