Every organization purchases some quantity of goods and services from external suppliers. These supplies are essential for the smooth functioning of an organization. It is thus important that the organization engages properly with its suppliers, establishes a proper relationship, manages the requirements, and communicates properly about them to the suppliers. All these play a role in the success of the organization, which is why a comprehensive supplier management policy is required.
The main purpose of supplier management is to get adequate returns for the money spent on the suppliers and provide seamless quality of service to the business.
The Objective of Supplier Management
The objectives of supplier management are:
- Ensure that maximum value for money spent is obtained from all the suppliers and contracts
- Make sure that the underpinning contracts (UCs) and agreements with the suppliers are in line with the business needs and agreed on targets of the organization
- Manage the relationships with the various suppliers and monitor their performance by keeping accurate records
- Negotiate with the suppliers, finalize contracts, and manage them throughout their lifecycle
- Establish and maintain a policy regarding suppliers and also maintain a supporting Supplier Contract Management Information System
Scope of Supplier Management
The management of all the suppliers and contracts which are needed to support the IT services are included in supplier management. This process recognizes the value of the supplier’s contribution. It then builds and manages a relationship with the supplier to sustain that contribution.
The supplier management process is used to centrally review and manage the relationship with each supplier which is owned by an individual.
Value of Supplier Management
The following benefits are provided by supplier management:
- It provides value for money to all the parties involved
- Ensures that the targets in all the supplier agreements and contracts are aligned with the needs of the business and within the service level agreements
- It ensures the seamless delivery of quality IT services which are aligned with the expectation of the business
Principles and Basic Concepts
Contract
The ability of a service, component, or configuration item to perform its agreed function when required is called availability.
Supplier and Contract Management Information System (SCMIS)
A supplier and contract management information system should be established in order to achieve a degree of consistency and effectiveness while implementing the supplier policy.
The SCMIS should record the following:
- All the details about the suppliers and the contracts
- The different types of services or products which are provided by each supplier
- The relationships with the other configuration items
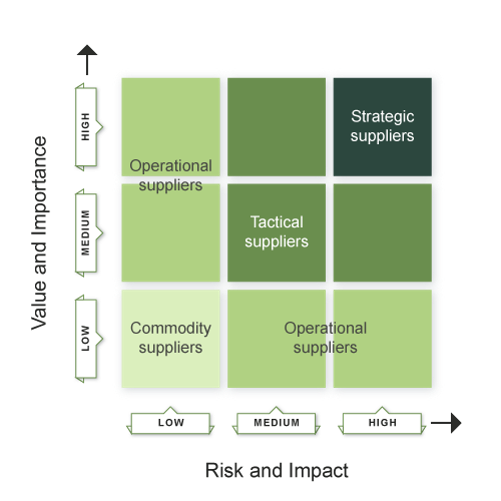
Supplier Categorization
More time and effort should be spent by the managers in order to manage important suppliers than the ones which are less important.
Suppliers can be classified on the basis of the following:
- Assessment of the risk and impact which is associated with using that particular supplier.
- The importance and value of the supplier and the service they provide to the business.
The suppliers are given the following classifications based on the roles they play:
- Strategic: They are for major ‘partnering’ relationships which involve senior managers sharing strategic information which is confidential in order to facilitate long-term plans.
- Tactical: They are for the relationships which involve a significant amount of commercial activity and business interaction.
- Operational: They are for suppliers of operational products and services.
- Commodity: They are for suppliers who provide low-value or easily available products or services.
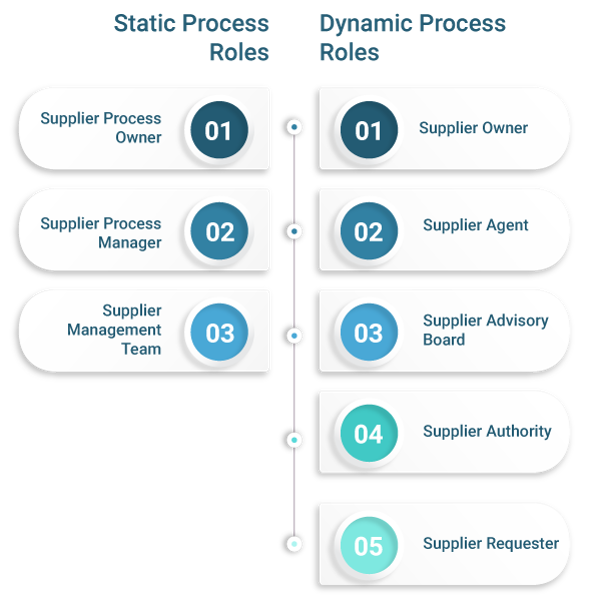
Supplier Management Roles and Functions
The following roles are vital for the supplier management process:
Static Process Roles
- Supplier Process Owner: The supplier process owner initiates the supply process and is responsible for defining the strategic goals and for allocating all the resources which are required for a process.
- The Supplier Process Manager: The supplier process manager is in charge of the entire process and is responsible for the effectiveness and efficiency of the process.
- Supplier Management Team: This is the team that is associated with the supplier management process.
Dynamic Process Roles
- Supplier Owner: The supplier owner is responsible for managing the overall supply process and ensuring it is carried out as per requirements. The supplier owner can be changed with the help of a hierarchical escalation.
- Supplier Agent: The supplier agent is responsible for an activity or a task within the activity of the supplier. They can be changed by a functional escalation if needed.
- Supplier Advisory Board: The supplier advisory board is the consulting body for category 2 and category 3 supplies. The members of the supplier advisory board are defined under the activity called Supplier Strategy.
- Supplier Authority: The duty of the supplier authority is to authorize a supplier based on their credentials.
- The Supplier Requester: A supplier requester triggers a supplier using a Request for Supplier (RFS) form which can be identical to a service or customer-specific role.
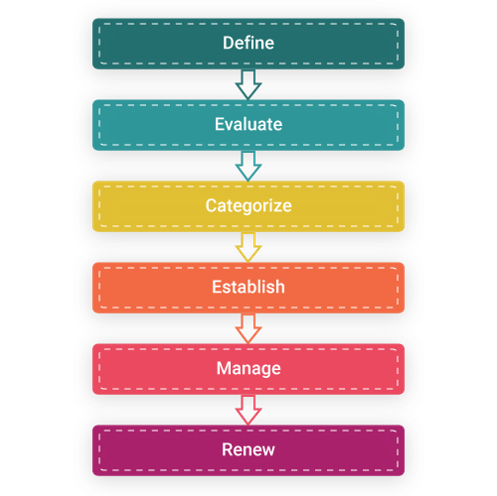
Supplier Management Process Activities
The process activities of supplier management involve the following steps:
Define New Supplier
To define the new supplier and the requirements of the contract. The needs of the business are identified by:
- Generating a Statement of Requirement (SOR) or Invitation To Tender (ITT)
- Making sure that they conform to the overall business strategy
- Preparing the initial business case with all the details such as costs, targets, timescales, benefits, and risk analysis
Evaluate New Suppliers
To evaluate the new suppliers and contracts to make sure that they align with the requirements of the organization. This is done by:
- Identifying the method of procurement
- Establishing the criteria against which the product/service will be evaluated
- Evaluating the alternatives available
- Selecting the most favorable alternative
Categorize The Suppliers
To categorize the suppliers and contracts and perform maintenance on the supplier and contract management information system (SCIMS). This is done by:
- Assessing the supplier and contract
- Making sure that the changes are passed through service transition
- Categorizing the supplier
- Updating the Supplier and Contract Database
- Performing maintenance on the Supplier and Contract Database
Establish New Suppliers
To establish the new suppliers and contracts as per the policy. This is done by:
- Setting up the supplier service and contract
- Preparing for the transition to the service
- Finally establishing contacts and relationships
Manage The Contract
To manage the contract and performance of the supplier. This is done by:
- Managing and controlling the operation and delivery of the service or product
- Monitoring and reporting the service quality and the costs incurred
- Reviewing and improving the service
- Managing the relationship with the supplier
- Planning for possible renewal or termination of the contract
Renew The Contract
To renew the contract if the quality of service delivered by the supplier is favorable or to terminate the contract if unfavorable.
Challenges of Supplier Management
The following challenges are faced by supplier management:
- The needs of the business and IT industry are constantly changing. Managing this change and delivering services simultaneously is a challenge.
- Working with an imposed contract that has poor targets or non-existent definitions of supplier performance targets.
- Inadequate retention of expertise in an organization.
- Interference in the running of operations.
- Losing the strategic perspective and focusing on operational issues results in a lack of focus on strategic relationship objectives.
Risks of Supplier Management
The following risks are encountered by supplier management:
- Unavailability of resources or budget for the process.
- A lack of commitment from the senior management to the supplier management.
- Supplier personnel or organizational culture which is not aligned with the requirements of the business.
- Lack of cooperation from suppliers who are not willing to take part in the supplier management process.
- Contracts that are badly written and do not support the needs of the business.
Conclusion
Supplier management thus ensures that maximum value is obtained for the money spent and the contracts with the suppliers are in line with the business needs. By managing the relationships with the various suppliers it helps to monitor their performance. Learn about more such processes and practices in service management with ITIL 4 Foundation certification training, and take your service management career with expert professional capabilities.
Know more about Service Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s IT Service Management certification training on ITIL 4 Foundation, SIAM Foundation, SIAM professional, VeriSM, etc.