For an organization to be successful, it is essential for them to have a set of overall objectives which are clearly defined and a sound business strategy associated with those ideas. This business strategy explains how exactly the organization will achieve its overall objectives over a period of time. This is underpinned by a set of individual strategies made for each unit in the organization. Business and IT strategies are dependent on each other. A business strategy defines the IT strategy, and the IT strategy supports and validates the business strategy. Multiple aspects are covered by the ITIL strategy, which includes IT Service Strategy, and IT Technology Strategy.
Watch this ITIL 4 Tutorial For Beginners for Complete Understand of the Concept

The Focus of ITIL Service Strategy
The focus of the ITIL Service Strategy is on the concepts that can be used by an IT service provider in order to build their IT strategy. An IT Service strategy that is successful has clear objectives and expectations regarding performance for the IT service provider as it aims to serve its targeted customers.
Process Areas of ITIL Service Strategy
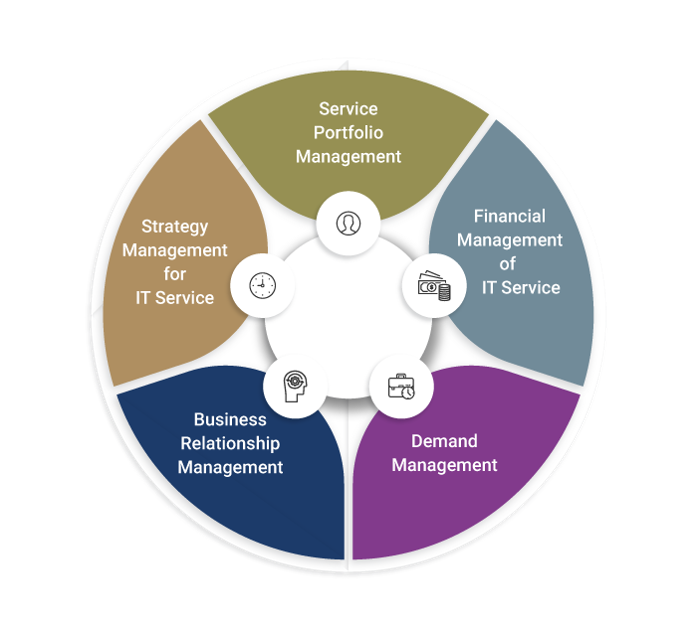
The process areas of service strategy include:
- Service portfolio management
- Financial management of IT service
- Demand management
- Business relationship management
- Strategy management for IT services
Purpose of ITIL Service Strategy
The main purpose of the ITIL Service Lifecycle service strategy stage is to define the perspective, position, plan, and patterns that are needed by a service provider to meet the business objectives of the organization.
The Objective of ITIL Service Strategy
The service strategy should identify:
- How the service provider aims to become and remain valuable to their customers in a unique way
- The objectives it aims to achieve in terms of the business outcomes it wants to enable
- The intended unique approach of the service provider for the creation and delivery of value to the customers
- The constraints and the competitive alternatives that the service provider should work with
The objectives of the service strategy stage of the ITIL lifecycle involve providing the service provider with the following:
- A thorough understanding of what exactly is a strategy. The required processes to:
- Define its service strategy
- Identify the service which they need to provide in order to achieve their strategy
- Predict the expected levels of service demand which are a result of its service strategy
- Find out the level of investment that is required to achieve the service strategy
- Enable a working relationship between the service provider and its customers
- An understanding of the organizational capability that is required to deliver the service strategy
- A clear definition of the services it provides and the customers who use them.
- Clear articulation about the creation, funding, and delivery of services, the target customers for the service, and how each service delivers value
- A clear idea regarding which service assets are used for delivering each value and how their performance can be optimized.
Scope of ITIL Service Strategy
The ITIL service strategy is intended for usage by both internal and external service providers. The scope of service strategy includes:
- Defining a strategy where a service provider can deliver services to meet the business outcomes of the customer
- Defining a sound strategy for managing the services
Value of ITIL Service Strategy
An investment that is made in service strategy by a service provider should deliver sufficient business value in return. Some of the benefits typically obtained by the adoption and implementation of service strategy best practices include:
- An increased ability to understand and express the links between the IT service assets of the service provider, its activities, and the crucial outcomes achieved by its customers as a result of using their services
- A flexible and timely ability to adapt its IT services to take preventive action and meet the changing business needs to ensure an increased competitive advantage over time
- The service provider is seen as contributing to value and cost by its organization and its customers
- A maintained portfolio of qualified services
- Improved IT investment usage where the investment in service development is driven mainly by business priorities and a proper return on investment (ROI) analysis
Conclusion
IT Service Strategy gives an explanation regarding how IT Services will be utilized to enable the IT department to achieve the required objectives. It explains how IT services underpin the overall business strategy, which makes it a vital part of IT service operations today.
Learn more about Service Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s IT Service Management certification training on ITIL 4 Foundation Online, SIAM Foundation, SIAM professional, VeriSM, etc.