Process Management is a key discipline for enterprises that work tirelessly to Continual Service Improvement. ITIL Continual Service Improvement embraces every aspect of the ITIL service lifecycle and can be applied to deliver a sustained improvement in IT performance. The most vital phase of understanding how to improve is by knowing what to measure and understanding how those measures can be evaluated and analyzed to deliver improvements to the clients.
Continual Service Improvement is one of the qualifications within the ITIL Service Lifecycle. It uses a metrics-driven methodology to recognize the opportunities for improvement that supports business processes and to measure the influence of those improvement efforts. And, It delivers guidance on creating and maintaining value for the customers through better design, strategy, transition, and operation of services. It combines principles, practices, and methods from quality management, change management, and capability improvement.
What is ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)?
Continual Service Improvement is a type of process which utilizes techniques from quality management so as to learn from prior successes and failures and aims constantly to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of IT services and processes.
Objectives of ITIL Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
ITIL Continual Service Improvement should predominantly focus on maximizing the effectiveness and also increasing the efficiency of the IT Service Management Process. Listed below are a few objectives of ITIL Continual Service Improvement:
- To evaluate, analyze, and make necessary recommendations to improve the existing opportunities in each phase of the ITIL Service Lifecycle such as Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, and Service Operation.
- Increasing the cost-effectiveness and process efficiency of the IT service.
- To ascertain and implement activities to increase the quality of the IT service and improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the IT service management process.
- In order to increase the cost-effectiveness of IT service delivery while maintaining the same level of customer satisfaction.
- To ensure that a standard and relevant method is used for quality management.
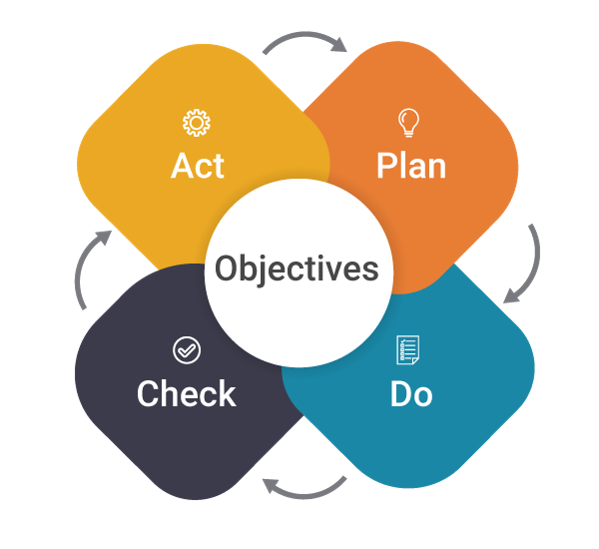
The Deming cycle-The PDCA cycle
The Deming Cycle (also known as the PDCA cycle) is used as the foundation for quality improvement activities across various types of enterprises. It is used in various industries for controlling and measuring results and taking appropriate steps based on the results to come up with a better output in the later steps.
The PDCA cycle is a four-part lifecycle and thus constitutes the acronym PDCA cycle: Plan, do, check, and act.
- Plan: The first step of the process involves planning the improvements. A gap analysis is undertaken and a plan is made to overcome the gap through a series of improvement steps.
- Do: The second phase refers to the Implementation of improvements. A project is instigated to close the gaps identified in the previous phase. This phase includes a series of changes to improve the process.
- Check: This phase is more accurately defined as monitoring, measuring, and reviewing. The end result of the implemented improvements is associated with the measures for success identified and approved in the planning phase.
- Act: The identified improvements are entirely implemented in this step.
The PDCA cycle can be utilized to improve any of the ITIL Service Management processes.
ITIL Continual Service Improvement – 7 Step Improvement Process
The focus of Continual Service Improvement is on service improvement to support business processes. To accomplish this, Continual Service Improvement uses a seven-step process plan for improvement which is crucial for CSI and other stages in the ITIL lifecycle.
The main purpose of this process is to define and manage the steps required to identify, define, gather, process, analyze, present, and implement the improvements which have been made over a period of time.
The 7 step improvement process is essential in supporting CSI and operates across the entire service lifecycle. It focuses on identifying the improvement opportunities, not merely for processes and services, but for all the disciplines implemented as a part of the IT Service Lifecycle.
Scope of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
The scope of the CSI seven-step improvement process contains the following areas:
- The seven-step improvement process includes an analysis of the performance and actual capabilities of the services and processes throughout the lifecycle, partners, and technology.
- It includes continuously aligning the portfolio of IT services of the organization to the present and future business requirements.
- It makes the best use of whatever technology the organization possesses and tries to acquire and utilize new technology when a business case demands it.
- To determine the capabilities of the personnel in the enterprise and to inquire if the right people with the relevant skills are working in appropriate positions.
Continual Service Improvement: Value of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
With the help of the aforementioned seven-step Improvement processes in ITIL Continuous Service improvement, current and future business requirements are met by constant monitoring and analyzing service delivery. Indeed, it also enables repetitive assessment of the present situation against business requirements and identifies the opportunities available for improving the provision of service to the customers.
Principles and Basic Concepts of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
Continual Service Improvements should center on increasing efficiency, maximizing effectiveness, reducing the cost of service, and underlying IT service management. And the only way to accomplish the task is to ensure that the improvement opportunities are identified throughout the service lifecycle.
- The service providers operate in a very competitive market and they need to assess their services against the expectations in the market persistently.
- New delivery mechanisms such as cloud computing can increase the efficiency of the service and need to be considered for implementation.
- The service provided must be compared to the present market offerings to ensure that the service adds actual business value to the clients so that the service provider remains competitive.
- The services must be regularly reviewed to keep up with the latest technological advances to ensure that the services they are delivering are the most efficient.

Continual Service Improvement: Stages in the Seven-Step Improvement Process
The below-mentioned seven steps constitute what is known as a knowledge spiral. The knowledge gathered from one level becomes the input to the other level. It moves from operational management to tactical management and finally strategic management.
Feedback from any stage of the service lifecycle can be used to identify improvement opportunities for any other stage of the lifecycle.
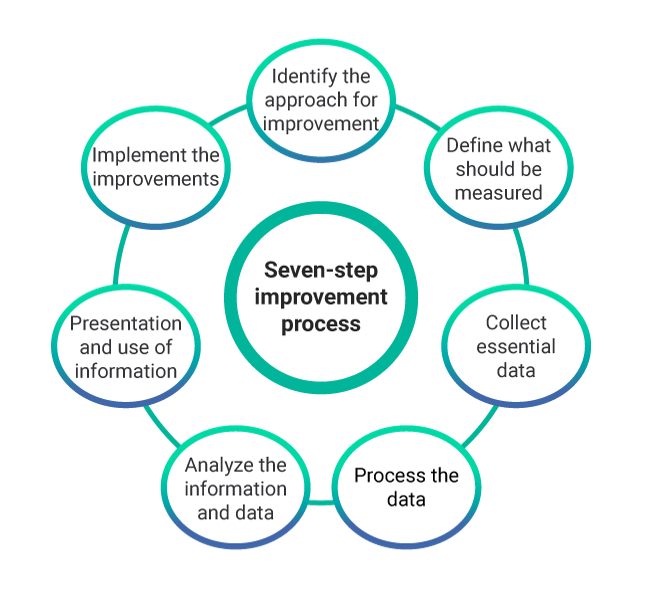
Stages of the Seven-Step Improvement Process
- Identify the approach for improvement: Prior to implementing an improvement strategy, it’s necessary to understand the necessity for continuous improvement. We must take into account the final goals we have set for the business and see how the IT organization can assist in achieving those targets through continuous improvements. Whilst accomplishing this, consider future and present plans as well.
- Define what should be measured: A comparison should be made between what we can ideally measure and what we can actually measure. Gaps should be identified and a realistic measurement plan should be incorporated to support the strategy for improvement.
- Collect the essential data: Data is gathered through persistent monitoring. The process of monitoring can be done either manually or technology can be utilized to the fullest to automate the entire process and simplify it.
- Process the data: Once the data is collected through continuous monitoring, it is then converted into the form required by the audience. This can be considered as a conversion of metrics into Key Performance Indicator (KPI) results and changing the available data into information.
- Analyze the information and data: The multiple sources of data are combined to transform the information into knowledge, which is further analyzed to find the gaps and their impact on the overall business. The information is further evaluated by considering all the relevant internal and external factors. It also helps to answer questions regarding something that is good or bad and whether is it expected and in line with the targets.
- Proper presentation and utilization of information: The information which is gathered and analyzed needs to be presented in a proper manner with the right amount of detail so that the information is comprehensible and provides the required amount of detail to support informed decision-making.
- Implement the improvements: A change implemented with continuous improvement sets a new baseline for the entire process. The knowledge obtained should be combined with previous experience and used to make informed decisions and necessary improvements. The improvements which are made must focus on optimizing and correcting the services, processes, and tools.
Conclusion
The 7-step improvement process is a vital process of CSI and thus identifies the opportunities available for improving services, tools, processes, etc. The process initiates service measurement, service reporting, and improvement. This helps to define the service baseline and processes, metrics, KPIs, critical success factors, and corrective measures to identify and improve the gaps in IT service management. ITIL CSI desires a commitment from the people working throughout the service lifecycle. It requires enduring attention to monitoring, analyzing, a well-thought plan, and reporting results aiming towards improvement.
Know more about Service Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s IT Service Management certification training on ITIL 4 Course Online, SIAM Foundation, SIAM professional, VeriSM, etc.