The Critical Chain and Critical Path are nothing but methods of managing projects. Critical chain as a new approach is gaining popularity and poses challenges to the traditional method that uses the critical path. Project management takes increasing importance while the percentage of work in the assigned project continues to grow. For over fifty years, the “critical path,” has been the governing principle for planning and superintending projects and has been progressive in management thinking. Today, the “critical path” method is extensively used in enterprises that adopt Project Management best practices.
What is a Critical Path?
The process in which the occurrence of each of the tasks can be decided based on the priority with respect to the dependencies they have on each other is known as the critical path method. The following steps are included in the critical path method.
- Identify all tasks in the first place.
- Calculate how much time each task would take. And mark the dependencies of each task onto one another.
- After this, calculate the time that can be divided among the tasks. And prioritize the most critical tasks to minimize the project delivery time.
The main focus of the critical path method is to calculate the critical path in which the project will be executed so that the minimum time is taken to complete it.
What is a Critical Chain?
A method of planning and managing projects, Critical Chain Project Management highlights the assets required to implement the project activities duties.
An ongoing Project Management technique, the Critical Path Method simplifies critical and non-critical tasks errands with the target of maintaining a strategic distance from period issues and process limited access. The Critical Path Method is ideally suited for projects that comprise various functions that work together complexly.
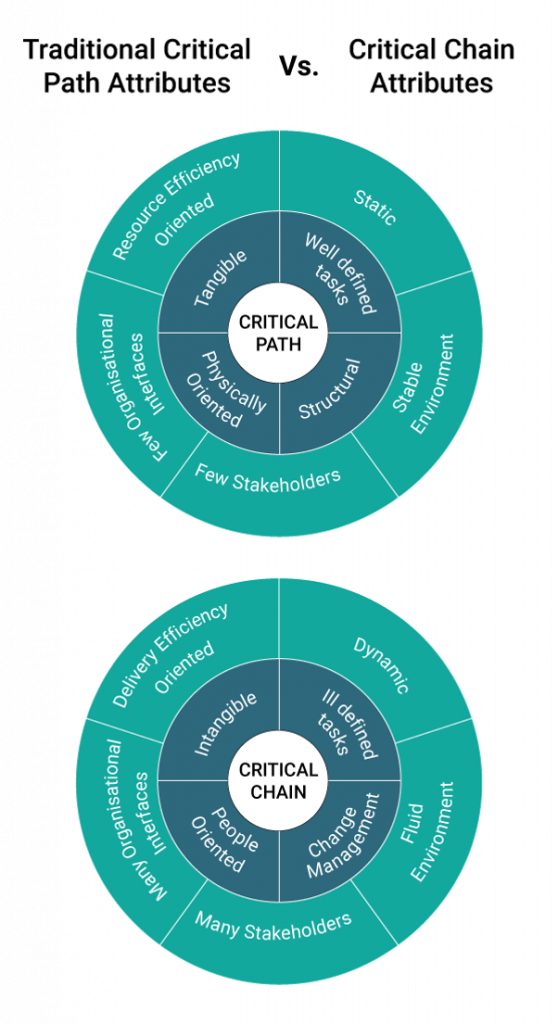
Critical Path vs Critical Chain Method
Let’s try to understand both methods separately for a better understanding.
Critical Path Method
It calculates the early start and finishes dates along with the late start and finish dates for all scheduled activities. This method initiates a forward pass analysis and a backward pass analysis that executes through the project schedule network paths. The critical path is the most extended way through the schedule with either zero or negative total float.
Critical Path Method Advantages
A significant objective in the Critical Path Method is to complete the project in the shortest time possible; here are few advantages of critical path methods:
- The Critical Path Method offers a visual representation of the project activities
- Provides time to complete the tasks and the overall project
- The Critical Path Method helps in tracking critical activities
Critical Chain Method
It modifies the project schedule to legitimize the restricted assets by including duration buffers that are sophisticated schedule activities to maintain focus on the planned activity durations. The critical chain is completed after determining the critical path by entering resource availability, and the resulting schedule produces a resource-constrained critical path, which usually alters from the original. The critical chain focuses on managing the remaining buffer durations against the remaining durations of task chains.
Critical Chain Method Advantages
- According to the PMBOK guide, the Critical Chain Method helps in planning and controlling processes
- Theory of Constraints: Removes bottleneck to resolve constraints
- Lean: Eliminate waste
- In Critical Chain Method, six sigma reduces variations
| Looking forward to enhancing your Project Management skills? Enroll in Project Management Certification now, and take your career to new heights. |
Critical Path Methodology
Specify Each Activity
Utilize the Work Breakdown Structure, it’s imperative for the project team to distinguish each activity that is associated with the venture. The particular list of the activity ought to incorporate more high-level activities. The critical path analysis may become difficult to retain and manage.
Establish Dependencies (Activity Sequence)
Certain activities in the project are reliant on the completion of other projects. Listing the prompt predecessors of every activity will enable you to recognize the right request. To effectively distinguish exercises and their priority, the Project Management team, should keep track of each progression of the tasks that they are performing.
Draw the Network Diagram
Create a Critical Path Analysis chart (CPA) otherwise called the system outline after you’ve recognized the exercises and their conditions. The network diagram is a visual portrayal of the request of your activities dependent on dependencies.
Estimate Activity Completion Time
Utilizing the knowledge or the experience of a qualified colleague, you should now evaluate the time required to finish every activity. If you are dealing with a smaller project, you will in all likely estimate time in days. On the off chance that you are working on a project that is challenging, you may need to quantify time in weeks. You can use the 3-point estimation technique, which is intended to put more weight on the most reasonable time frame.
Identify the Critical Path
There are two different ways you would now be able to identify the critical path.
- Identify the longest path all through the system after you’ve completed drawing your network diagram (guarantee you explore the longest path in regards to most expanded duration in days, not the way with the most boxes or nodes).
- You can likewise recognize critical activities with the Forward Pass/Backward Pass technique, the earliest start and finish times, and the latest start and finish times for each activity.
-
- Earliest Start Time(ES) -> The earliest time an activity can start once the previous dependent activities are over.
- Earliest Finish Time(EF) -> (ES + Activity Duration)
- Latest Finish Time(LF) -> The latest time an activity can finish without delaying the project.
- Latest Start Time(LS) -> (LF – Activity Duration)
-
Update the Critical Path Diagram to Show Progress
As the project progresses, you will take in the actual activity completion times. The system chart would then be able to update to incorporate the data (rather than proceeding to utilize estimations).
By updating the network diagram as new data develops, you may recalculate an alternate critical path. You will likewise have a progressively realistic perspective of the project completion due date and will be able to tell if you are on track or falling behind.
| Enroll in our PMP Online Certification Training today, and develop a strong foundation in the principles of Project Management. |
Critical Chain Methodology
The critical chain is a series of occasions that are predetermined to set aside the longest time for fruition. These projects are set apart as ‘critical’ to isolate them from the ones with a lower prerequisite. The following stage is to send your resources reliant on their excellent accessibility with the end goal that they can focus on conveying the critical tasks first.
While the traditional triple constraints of time, scope, and costs still stand, an added project constraint is the critical chain itself. The following points are characteristic of the CCPM:
- It contains four buffers to control the project schedule, which are project, feeding, capacity, and resource buffers.
- If a resource offers his/her effort estimates, the CCPM cuts out 50% of the activity time and slots it into a buffer. As a result, you get sharpened task estimates based on definitive end-dates.
- It links projects to teams of resources that can account for variations in the activity duration.
- It eliminates multitasking by considering resource constraints before resource-leveling.
- Of these, you’d certainly want to prevent your resources from overworking themselves on multiple efforts or alternately, reworking existing tasks from scratch.
Since the path factors in resource and project inter-dependencies, the project execution carries on as planned.
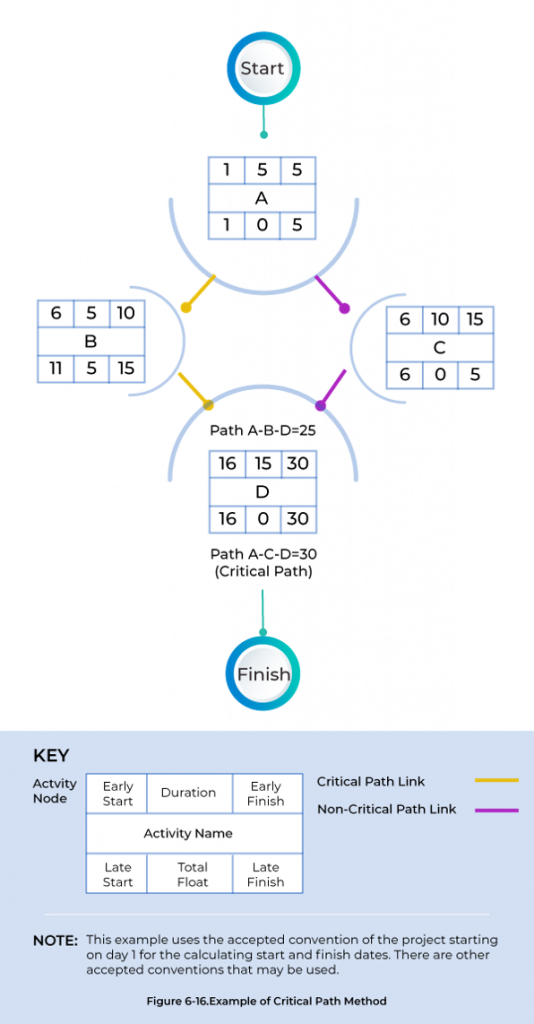
How to Calculate Critical Path Method?
Created through the sequence of activities from the start to the end, the Critical Path is the longest way in a project schedule network diagram and is the SHORTEST possible duration for the project.
To find the critical path, first, we will draw the network diagram. Then we will define each possible path in this network diagram from the start of the project until the end, and then we will define the longest path in this network diagram, which will give us the critical path.
Here is a simple 4-step process to calculate the critical path:
- Build Schedule Network Diagram
- Find activities
- Find All Possible Paths
- Calculate the Duration for each Path
Conclusion
Despite everything, you have to consolidate a few parts of the critical path to ensure a productive task. Project management as practice regularly includes various strategies to be productive. Over the long haul, in any case, the critical path offers a superior possibility of progress each time that you utilize it. However, you should set up to change any procedure you employ with the goal that it fits your organization. Learn about more such methods and skills and give yourself a chance to gain professional expertise in Project Management with the best PMP Online Training.
Know more about Project Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s Project Management certification training on PMP Certification, PMI CAPM Certification Training, Prince2 Training Course, Project Management Fundamentals, etc.