Agile Product Management is an iterative and flexible approach to developing and managing products, emphasizing collaboration, adaptability, and customer feedback.
In the Agile framework, product development is carried out in small, incremental stages called sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. The process allows for frequent reassessment and adjustments based on evolving priorities and customer needs.
Cross-functional teams, comprising members from various departments such as development, marketing, and design, collaborate closely to deliver small, functional pieces of the product in short cycles.
Continuous customer feedback is integrated into each iteration, allowing quick responses to changing market conditions and ensuring that the final product aligns more closely with customer expectations.
This methodology promotes transparency, responsiveness, and the ability to deliver value to users more dynamically and efficiently.
Table of Contents
- What is Product Management?
- Understanding Agile Product Management
- Best Practices of Agile Product Management
- Agile Product Management Tools
- Future of Product Management
- Pros and Cons of an Agile Product Management
- Conclusion
What is Product Management?
Product Management is a diverse approach that includes looking after a product throughout the process, from when it’s first thought up to when it’s eventually taken off the market. Effective product management requires strategic thinking, communication skills, and a customer-centric mindset.
Product managers serve as the bridge between various stakeholders, including customers, development teams, and business executives. They are responsible for defining the product strategy, gathering and prioritizing requirements, and ensuring that the final product meets the needs of both the market and the company.
Product managers collaborate with cross-functional teams to drive the product’s success. They must possess a deep understanding of market trends, user needs, and business goals to make informed decisions that lead to the creation of successful and competitive products.
Product managers often use tools and methodologies such as market research, user feedback, and agile development processes to iterate and improve their products continuously.
The role demands adaptability and the ability to balance competing priorities as product managers work to deliver value to customers while aligning with the organization’s overall business objectives.
Understanding Agile Product Management
Agile product management is a crucial aspect of the collaborative approach to product development that has revolutionized the industry. Agile methodology emphasizes flexibility, customer feedback, and iterative progress, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements and deliver high-value products.
Some common frameworks used in Agile Product Management include Scrum and Kanban, which provide structures for planning, executing, and reviewing work in short cycles.
Continuous feedback, open communication, and a focus on delivering incremental value to customers are fundamental to Agile Product Management. This method allows teams to be more responsive, adaptive, and efficient in delivering products that meet customer expectations.
Best Practices of Agile Product Management
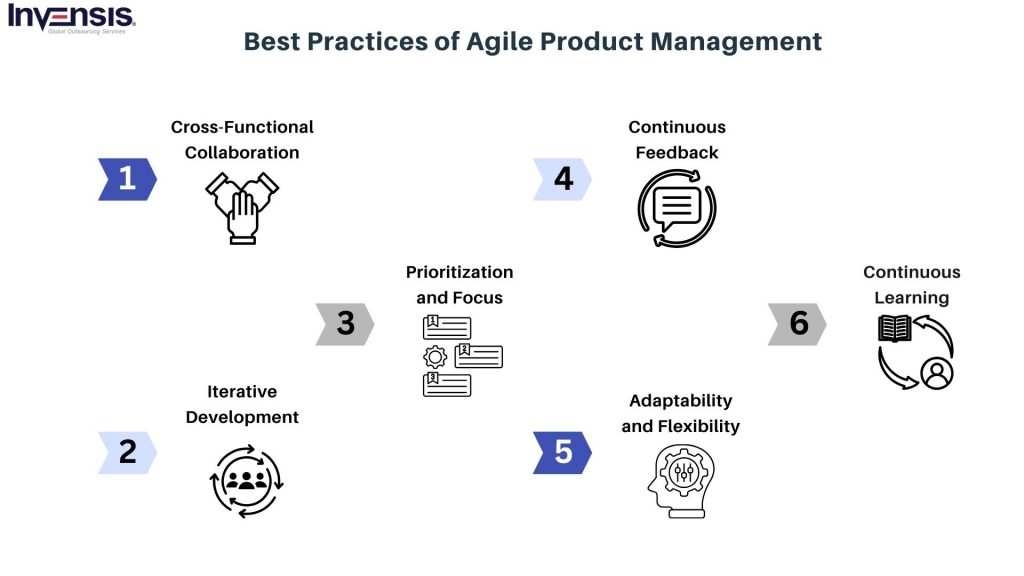
Explore the essentials of Agile Product Management’s best practices. Learn how balancing flexibility and efficiency is the key to success, guiding you to adapt, collaborate, and iterate for products that go beyond expectations.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Cross-functional collaboration involves bringing together individuals with diverse skills and expertise to collaborate on a project. In the context of Agile Product Management, it means assembling teams that include members from various departments, such as development, design, marketing, and quality assurance.
This collaborative approach ensures a holistic understanding of the product and promotes the exchange of ideas, leading to more well-rounded solutions. Effective communication and shared responsibility among team members foster a sense of ownership and alignment toward common goals.
Iterative Development
Iterative development is a fundamental concept in Agile that involves breaking the product development process into small, manageable cycles called iterations or sprints. Instead of attempting to complete the entire project simultaneously, teams focus on delivering a subset of features in each iteration.
This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement, regular assessment of progress, and the flexibility to adapt to changing requirements. It also facilitates the early delivery of valuable features, enabling quicker responses to customer needs and market changes.
Prioritization and Focus
Prioritization and focus are crucial in Agile Product Management to ensure the team works on the most important tasks. Product managers and teams collaborate to prioritize features and user stories based on factors such as customer value, business goals, and dependencies.
By focusing on high-priority items, Agile teams can deliver a minimum viable product (MVP) quickly, providing customer value sooner. This approach also helps manage resources efficiently and mitigates the risk of scope creep.
Continuous Feedback
Continuous feedback involves regularly gathering input from stakeholders, customers, and team members throughout the product development lifecycle. It ensures that the product remains aligned with customer expectations and market needs.
Feedback includes demos, user testing, surveys, and direct communication. Agile teams use this feedback to make informed decisions, refine product features, and address issues promptly. The emphasis on continuous feedback promotes a customer-centric mindset and enables quick adjustments to enhance the product.
Adaptability and Flexibility
Adaptability and flexibility are core principles in Agile Product Management. The Agile approach acknowledges that change is inevitable and embraces the ability to adapt plans and processes accordingly.
Teams remain open to modifying requirements, features, or priorities based on evolving market conditions, customer feedback, or internal insights. This flexibility allows Agile teams to respond quickly to emerging opportunities or challenges, ensuring that the product stays relevant and meets the dynamic needs of the business environment.
Continuous Learning
Continuous learning emphasizes an ongoing commitment to improvement and knowledge acquisition within the Agile team. It involves regularly reflecting on experiences, successes, and challenges to identify areas for enhancement.
Agile teams conduct retrospectives, assessing what worked well, what could be improved, and how to implement those improvements in the next iteration. This culture of continuous learning fosters a mindset of curiosity and adaptability, contributing to the team’s ability to innovate, refine processes, and deliver increasingly better results over time.
Agile Product Management Tools
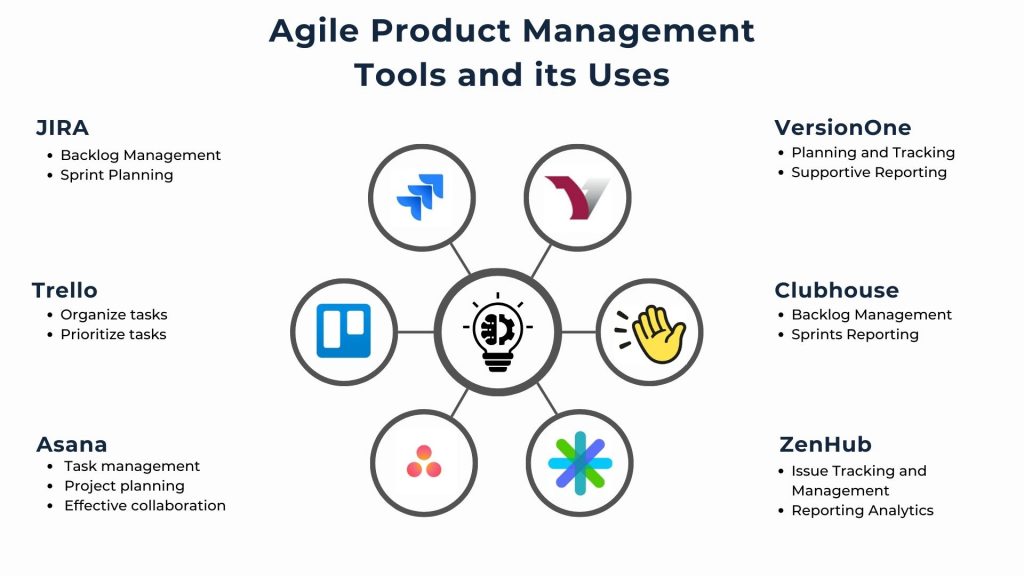
There are numerous Agile Product Management tools available, each catering to different needs and preferences. Here are some widely used and highly regarded Agile Product Management tools.
Jira Software
Jira software is one of the most popular Agile product management tools. It supports various Agile methodologies, including Scrum and Kanban, and provides features for backlog management, sprint planning, and reporting.
Trello
Trello is known for its visual approach to product management. It uses boards, lists, and cards to help teams organize and prioritize tasks. While straightforward, it may suit smaller teams or less complex projects.
Asana
Asana is a versatile product management tool that supports both Agile and traditional product management methodologies. It provides a collaborative platform for task management, project planning, and communication.
VersionOne
VersionOne is an enterprise-level Agile product management tool that offers end-to-end support for Agile development. It covers planning, tracking, collaboration, and reporting, making it suitable for larger organizations.
Clubhouse
Clubhouse is an Agile product management tool designed for simplicity and flexibility. It provides backlog management, sprints, and reporting features, making it suitable for teams practicing Scrum or Kanban.
ZenHub
ZenHub is a product management extension for GitHub designed to integrate seamlessly with development workflows. It adds features like task boards, burndown charts, and release reports directly to GitHub.
Future of Product Management
Here are some potential aspects that could influence the future of product management:
Integration of Advanced Technologies
As technology progresses, product managers are expected to incorporate cutting-edge technologies like (AI), (ML), and (IoT) into the product development process. These advanced technologies can potentially improve personalization, automate various processes, and offer valuable insights into user behavior.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Social Impact
The future of product management is likely to see a greater emphasis on sustainability and social responsibility. Product managers may focus on creating products with minimal environmental impact, ethical sourcing, and a commitment to social impact.
Consumers increasingly value brands that are aligned with their values, and product managers will respond by incorporating sustainability into product strategies.
Shift Towards Outcome-Focused Metrics
Product managers may increasingly move away from traditional output metrics (such as features delivered) to outcome-focused metrics. The emphasis will be on measuring the impact of products on key business objectives and customer satisfaction.
This shift aligns with a more holistic view of product success beyond the mere completion of tasks.
Global Collaboration and Remote Work
The trend towards remote work continues, and product managers must navigate global collaboration with distributed teams. Advanced collaboration tools, virtual communication platforms, and agile methodologies tailored for remote work will become integral to successful product management.
Increased Importance of User Experience (UX) and Design
User experience and design will play an even more critical role in the future of product management. Product managers will collaborate closely with UX designers to create seamless and intuitive product experiences. Understanding user behaviour and incorporating design thinking will be essential for delivering products that resonate with customers.
Also read our blog on Incorporating Agile in UX and Product Design to get insights on implementing Agile for better customer experience!
Pros and Cons of an Agile Product Management
Agile product management is an iterative and flexible product development approach emphasizing collaboration, customer feedback, and continuous improvement. It has its advantages and challenges. Here are some pros and cons of Agile product management
Pros
Flexibility and Adaptability
Agile allows teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements, priorities, and market conditions. It accommodates changes during the development process.
Customer-Centric
Agile strongly emphasizes customer feedback and involvement throughout the development cycle, ensuring that the product meets customer needs and expectations.
Early Delivery of Value
Incremental development and regular releases enable the early delivery of features, providing value to customers sooner and allowing for quicker validation of product assumptions.
Collaboration and Communication
Agile fosters collaboration among cross-functional teams, and regular meetings and feedback sessions enhance teamwork. Encourage teamwork and ensure everyone talks and shares information openly.
Continuous Improvement
Agile encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Teams regularly reflect on their methods and performance, making adjustments to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Cons
Resistance to Change
Traditional organizational structures and individuals accustomed to a waterfall approach may resist the cultural and procedural changes required for successful Agile implementation.
Resource Intensive
Agile methodologies can be more resource-intensive due to the need for frequent communication, planning, and collaboration. This might be challenging for teams with limited resources.
Uncertainty in Planning
The flexible nature of Agile can make long-term planning challenging, as priorities and requirements may change during the development cycle.
Lack of Documentation
Agile’s focus on working software over comprehensive documentation may be a drawback in environments where detailed documentation is crucial.
Dependency on Team Collaboration
Success in Agile relies heavily on effective collaboration within the team. If there are communication or coordination issues, it can negatively impact the development process.
Conclusion
Agile Product Management offers a forward-thinking and adaptable framework for product development, empowering teams to deliver value incrementally while remaining responsive to the ever-changing landscape of customer needs and market dynamics. In the coming years, adopting Agile Product Management is key to success.
It’s like a smart approach that helps organizations thrive in a world that loves new ideas, teamwork, and making customers happy.
Embrace the future with Agile certification courses at Invensis, your key to success in a dynamic world. Elevate your skills with agile courses for a deeper understanding. Succeed in innovation, teamwork, and customer satisfaction.