Quality management system (QMS) constitutes a set of processes and standards meticulously crafted to fulfill customer needs and elevate satisfaction. These systems are delineated through articulated goals, objectives, and processes crucial for sustaining and improving business operations. Implementing QMS boosts overall productivity and augments a business’s performance, fostering heightened trust among its intended audience.
Across industries, various types of QMS have evolved into international standards, each designed to ensure excellence in specific areas.
A prominent example is ISO 9001:2015, an international standard that outlines the standards and requisites for effective quality management practices.
As organizations embrace these frameworks, they pave the way for enhanced customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and the establishment of enduring credibility in their respective markets.
Table of Contents
- Types of Quality Management Systems (QMS)
- Integrating Various Quality Management Types to Create a Cohesive System
- Conclusion
Types of Quality Management Systems (QMS)
Quality Management Systems (QMS) play a crucial role in ensuring that organizations meet and exceed the expectations of their customers while continuously improving their processes. One widely recognized QMS is the ISO 9001 standard, which provides a framework for implementing quality management principles.
However, the quality management system is diverse, and various industries and sectors may require specialized approaches. This section explores different types of Quality Management Systems beyond ISO 9001. These systems cater to specific needs and regulatory requirements, tailoring their frameworks to address unique challenges within diverse sectors.
ISO 9001
ISO 9001, an internationally recognized standard for quality management systems, was introduced by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1987 and underwent updates in subsequent years, with the latest version released in 2015.
This standard outlines the requirements for organizations to establish effective quality management systems, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continual improvement.
Over a million companies across more than 170 countries presently hold ISO 9001 certification, utilizing its principles to enhance product design, conduct specific testing, and create robust quality management processes.
The framework’s foundation lies in the Plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle, providing organizations with a systematic approach to ensure consistent quality and meet customer expectations.
ISO 9001 certification is a hallmark of an organization’s commitment to delivering high-quality products and services. The standard offers valuable guidance on designing effective processes, managing resources efficiently, and fostering a culture of continual improvement.
By aligning with ISO 9001, companies build trust with their customer base and gain a competitive edge in the global market by demonstrating to international quality management standards.
AIFT 16949
AIFT 16949 is a significant technical standard designed to establish and improve quality management systems within the aerospace industry. Formulated by the Aerospace Industry Association (AIA) and the Technical Committee of ISO, this protocol is tailored to address the unique challenges and requirements of the aerospace supply chain and manufacturing processes.
Introduced to promote continuous improvement, AIFT 16949 strongly emphasizes defect prevention and waste reduction.
This standard comprehensively covers various aspects of aerospace products, including design, production, development, installation, and servicing. Organizations in the aerospace sector seeking AIFT 16949 certification demonstrate their commitment to delivering high-quality products and services while adhering to stringent industry standards.
Similar to IATF 16949, the AIFT 16949 certification is typically valid for three years and involves annual confirmation by auditors certified by the AIA.
This ensures that aerospace organizations maintain and continually enhance their quality management systems to meet the industry’s evolving demands.
ISO 13485
ISO 13485, a quality management system standard, was introduced by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to address the manufacturing design and quality of medical devices specifically.
First published in 1996, with subsequent revisions, the present version of ISO 13485 was released on 1 March 2016. Unlike general quality management systems, ISO 13485 tailors its focus to the unique and critical requirements of the medical device industry.
This specialized quality system places paramount importance on product safety, incorporating stringent measures to ensure the well-being of patients and users.
It also emphasizes comprehensive risk management activities throughout the production process, acknowledging the critical nature of medical devices.
ISO 13485 establishes specific requirements and quality standards for implantable devices, recognizing the specialized considerations required for these critical medical technology components.
Adhering to ISO 13485 standards allows organizations in the medical device industry to demonstrate their commitment to producing safe and effective products while complying with various regulatory requirements.
ISO 22000
ISO 22000 is an important quality system centered around food security and safety management. Developed and issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), this standard is instrumental in enhancing overall performance in food safety across the global food supply chain.
ISO 22000 encompasses comprehensive guidelines for managing food safety and traceability throughout the food industry.
Within the ISO 22000 framework, various sub-sections address distinct aspects of food safety, ensuring a proper approach.
- ISO 22001: Providing guidelines tailored for the food and drink industry, focusing on specific requirements and best practices within this sector.
- ISO 22002: Offering guidelines for different segments of food safety, with specialized parts dedicated to Food Manufacturing, Food Catering, Farming, and Food Packaging Manufacturing.
- ISO 22003: Establishing food safety guidelines, with Part 1 focusing on requirements for organizations providing audits and certifications for food safety, and Part 2 covering requirements for organizations providing certification of products.
- ISO 22004: A food safety management system that concentrates on the practical application of ISO 22000, ensuring seamless integration and implementation.
- ISO 22005: Dedicated to traceability and tracking in the food and feed supply chain, providing essential protocols to enhance transparency and accountability.
- ISO 22006: Guiding the application of ISO 9002:2000 specifically for crop production, offering tailored insights to address the unique challenges within this sector.
ISO 200000
ISO 20000 is a key standard in Information Technology Service Management (ITSM), outlining specific requirements for organizations to establish, maintain, and continually enhance a technical service management system.
This international standard ensures that IT service providers effectively align their ITSM practices with the business’ needs and objectives.
Aimed at promoting excellence in IT service delivery, ISO 20000 plays a crucial role in establishing a framework for organizations to manage their IT services in a systematic and efficient manner.
By adhering to ISO 20000, IT industries can optimize their processes, enhance service quality, and align IT services with the business’s strategic goals.
This standard serves as a valuable assurance for clients, assuring them that their service requirements will be met successfully and that the IT service provider is committed to continuous improvement in service delivery.
In essence, ISO 20000 provides a benchmark for IT service management and facilitates a structured approach to delivering IT services that meet the dynamic and evolving needs of businesses and clients.
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a cornerstone of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), outlining specific requirements that ISMS providers must uphold. This international standard ensures that organizations establish and maintain robust systems for managing information security risks associated with their data.
Organizations that attain ISO 27001 certification are committed to safeguarding their information assets’ confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The standard provides a comprehensive framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating information security risks, ensuring that sensitive data is protected against unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction.
By adhering to ISO 27001, organizations instill trust in their stakeholders by assuring them that stringent measures are in place to manage and secure valuable information assets.
This certification is particularly crucial in today’s digital landscape, where information security is paramount. ISO 27001 helps organizations mitigate risks and ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements related to information security, reinforcing the overall resilience of an organization’s information management practices.
AS 9100D
AS 9100D stands as a pinnacle in quality management within the aerospace industry, offering a comprehensive framework of requirements specifically tailored for aviation, space, and defense sectors.
As an ISO-certified program, AS 9100D mandates stringent quality management standards that organizations in these industries must adhere to.
This quality management system emphasizes safety requirements, deeming them mandatory for implementation by organizations.
By integrating AS 9100D, aerospace companies are committed to delivering products and services that meet rigorous safety and quality standards. The standard covers a spectrum of criteria, ensuring that design, production, and service processes within the aerospace sector are aligned with the highest industry benchmarks.
AS 9100D is regarded as one of the premier quality management systems in the aerospace domain, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and accountability. Its implementation ensures compliance with international standards and signifies a commitment to excellence in a sector where precision, safety, and reliability are paramount.
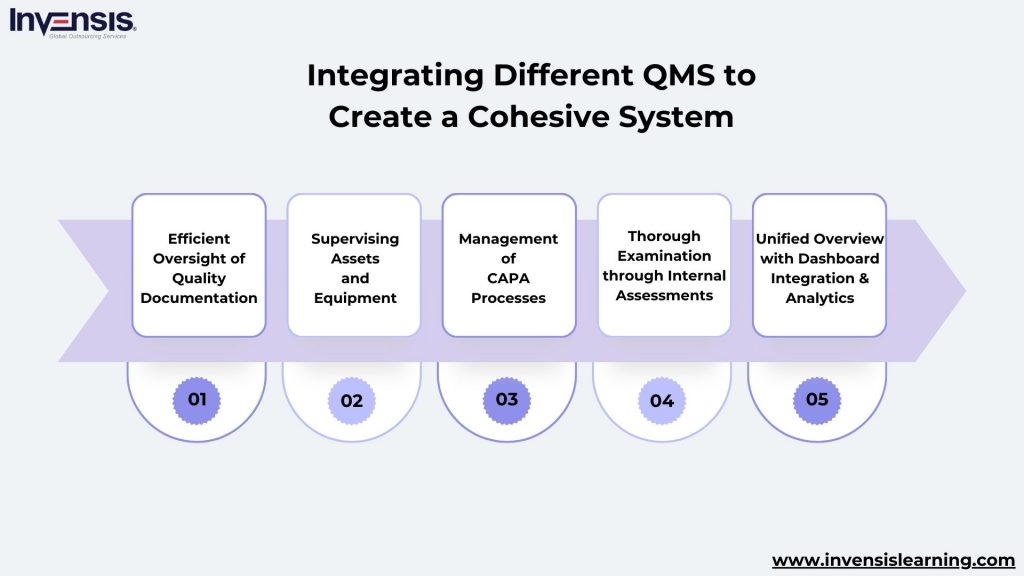
Integrating Various Quality Management Types to Create a Cohesive System
Integrating diverse quality management standards necessitates establishing a cohesive system to uphold all crucial quality components effectively.
A contemporary quality management system adopts a digital format that houses distinct modules and enables companies to meet essential quality standards and accreditations.
These software-based modules encompass various functionalities, including:
-
Efficient Oversight of Quality Documentation
Managing all quality documents, policies, and procedures utilized by employees systematically for documentation, organization, and tracking of internal processes.
-
Supervising Assets and Equipment
Focused on monitoring the equipment and assets intricately connected to production, goods movement, and providing quality services to customers.
-
Management of CAPA Processes (Corrective and Preventive Actions)
An integral component of the quality management system, this module ensures the incorporation of corrective and preventive measures, which are vital for improving quality. Tracking and executing CAPA are fundamental aspects.
-
Thorough Examination through Internal Assessments
A robust quality management system controls versions and creates audit trails for all documents and interactions. Auditors use this information to oversee daily processes and actions implemented.
-
Unified Overview with Dashboard Integration and Analytics
Digital quality management systems automatically consolidate and compile quality data in a format easily presented and monitored. This aids in foreseeing quality patterns over time, improving internal processes.
Conclusion
Quality Management Systems (QMS) is crucial for organizations aspiring to uphold and enhance their operational standards. From the foundational ISO 9001 to specialized frameworks like ISO 13485 for medical devices and AS 9100D for aerospace, each QMS type offers unique guidelines to ensure quality compliance within specific industries.
The advent of digital technology introduces sophisticated solutions such as ISO 20000 for IT service management and ISO 27001 for information security, further streamlining processes in today’s dynamic business environment.
As businesses strive for continuous improvement and regulatory compliance, choosing and implementing an appropriate QMS becomes pivotal for operational efficiency, building stakeholder confidence, and demonstrating unwavering commitment to delivering high-quality products and services. Embracing these diverse QMS frameworks is a strategic imperative for organizations seeking success and resilience.
Advance your career with Invensis Learning’s Six Sigma Certifications and Quality Management Courses. Gain expertise in ISO standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 13485. Enroll now for professional growth and organizational excellence.