Agile Release Train (ART) plays a key role in defining an enterprise’s success by a combination of criteria. One of the most important reasons companies use Agile frameworks is to establish a strong culture of collaboration, interaction, and accountability within the organization while taking an iterative approach to creating, delivering, and deploying.
This realization has propelled the widespread adoption of Agile frameworks, where an iterative approach to development, delivery, and deployment takes center stage.
As the buzz surrounding Agile and Scaled Agile methodologies continues to grow, professionals find themselves navigating a sea of new terms from the expansive Agile universe.
One such term that frequently captures curiosity is the “Agile Release Train” (ART). In this article, we will understand the concept of an Agile Release Train (ART), its principles, and the structure that governs its dynamics.
Table of Contents
- What is an Agile Release Train (ART)?
- Principles of Agile Release Trains
- Structure of an Agile Release Train
- Agile Release Train (ART) Roles and Responsibilities
- Technologies Used to Manage and Streamline Agile Release Train
- Conclusion
What is an Agile Release Train (ART)?
The Agile Release Train (ART) stands as a persistent assembly of agile teams collaborating with various stakeholders to craft and deliver value iteratively. The ART plays a crucial role in aligning efforts and mitigating risks and dependencies by offering program-level cadence and synchronization.
ART includes all the teams with the necessary expertise for implementing, testing and releasing software and other deliverables. Agile Release Train Engineers (Agile RTE) are responsible for ensuring the seamless collaboration of Agile release trains and adherence to SAFe processes for the successful execution of extensive development programs.
The ART operates within a predefined time frame called a Program Increment (PI), typically lasting 8-12 weeks. During a PI, cross-functional teams collaborate to collectively achieve a set of predefined objectives aligned with the overall business goals.
This synchronized effort enables efficient planning, coordination, and integration of work across teams, fostering a cohesive and streamlined approach to product development.
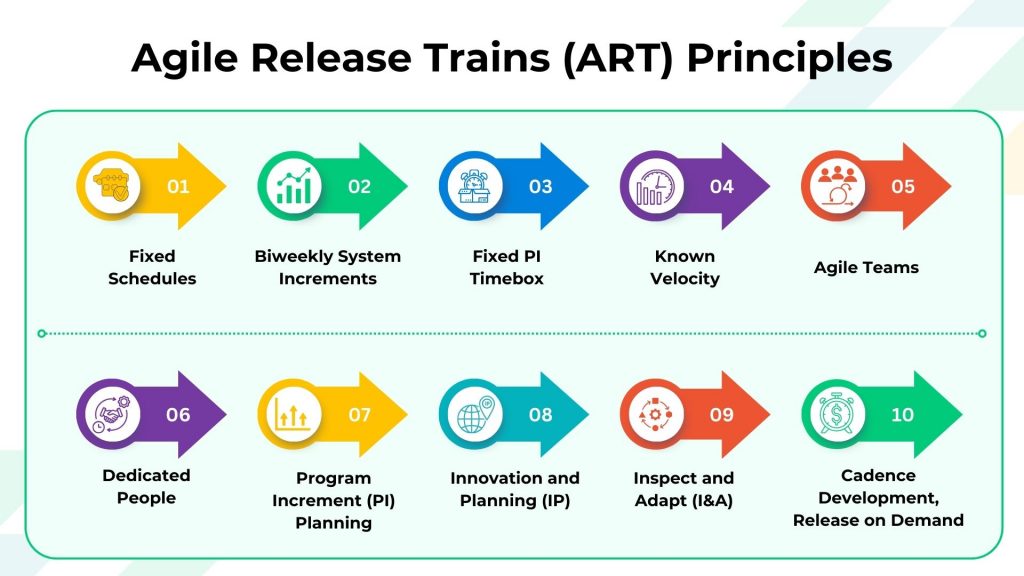
Principles of Agile Release Trains (ART)
Agile Release Trains (ART) principles form the foundational guidelines that guide the functioning and effectiveness of these collaborative teams within the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe).
Here are key principles that underpin the operation of an ART:
- Fixed Schedules: Agile Release Trains adhere to set schedules, ensuring predictability in development processes, facilitating coordination, and maintaining a steady flow of value delivery
- Biweekly System Increments: ART delivers working product increments every two weeks, promoting continuous integration, quick feedback loops, and a consistent rhythm in software development
- Fixed PI Timebox: The Program Increment (PI) timebox, lasting 8-12 weeks, provides a structured framework for planning and executing activities within a predefined time frame, fostering focused and goal-oriented development
- Known Velocity: Agile Release Trains (ART) work with a known velocity, understanding their capacity to deliver work within a specific timeframe, aiding in realistic planning and commitment to sustainable workloads
- Agile Teams: Agile Release Trains consist of cross-functional and self-organizing Agile teams, fostering collaboration and leveraging diverse skills to maximize efficiency and innovation in product development
- Dedicated People: Emphasizing commitment, Agile Release Trains encourage team members to stay dedicated for the duration of the program increment, fostering ownership, accountability, and continuity within the team
- Program Increment (PI) Planning: PI Planning is a collaborative event where teams align their efforts, discuss priorities, and commit to shared goals for the upcoming Program Increment, ensuring everyone is on the same page
- Innovation and Planning (IP): IP time within the program increment allows teams to focus on innovation, exploration, and future feature planning, fostering creativity and balancing the need for both execution and forward-thinking
- Inspect and Adapt (I&A): The I&A event at the end of each program increment facilitates reflection, feedback gathering, and identification of areas for improvement, contributing to the continuous enhancement of the ART
- Cadence Development, Release on Demand: RTE Agile teams remove releasing from development to reduce the inherent uncertainty in creating new things
Enroll in Invensis Learning’s Agile Certification Courses Now and master Agile Release Train principles!
Structure of an Agile Release Train
The Agile Release Train (ART) functions as a collaborative unit of multiple Agile teams undertaking diverse tasks such as design, testing, solution-building, deployment, release, and operations.
Depending on their preferences, these teams may adopt various Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, or Extreme Programming (XP). Within each Agile team, the roles of Scrum Master and Product Owner play pivotal roles.
Inherently cross-functional, Agile Release Trains are strategically organized around developmental value streams. Adhering to SAFe® guidelines, the composition of teams is structured to ensure an uninterrupted flow of value throughout the development process.
This organizational approach is geared towards optimizing collaboration, enhancing efficiency, and facilitating the seamless delivery of value within a dynamic Agile framework.
To ensure an uninterrupted flow of value within the Agile Release Train (ART), the following SAFe® guidelines on the composition of teams come into practice:
- Cross-Functional Nature: Agile Release Trains are inherently cross-functional, incorporating diverse skills within each team to cover various aspects of the development lifecycle, from design to deployment.
- Organized Around Developmental Value Streams: The structure of Agile Release Trains is strategically organized around developmental value streams, aligning teams with specific business objectives and ensuring a cohesive flow of value delivery.
- Adherence to SAFe® Principles: Teams within the ART are expected to adhere to the principles outlined in the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe®), emphasizing collaboration, alignment with business goals, and continuous improvement.
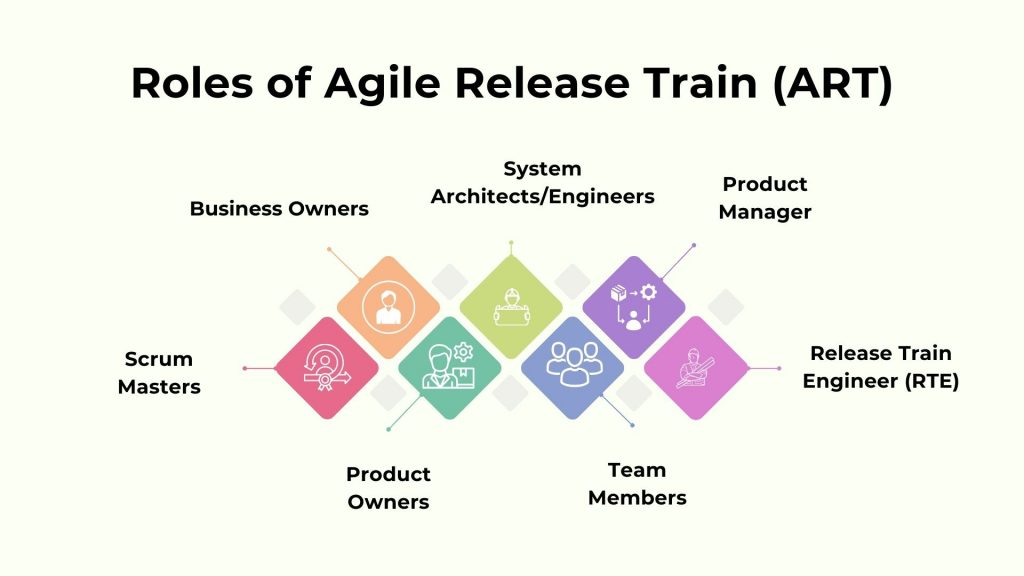
Agile Release Train (ART) Roles and Responsibilities
Roles and responsibilities within an Agile Release Train (ART) are pivotal in successfully implementing Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) principles. ART consists of 5 to 12 high-performing Agile teams (50 to 150 people).
It comprises dedicated full-time team members, providing stability for the training and possibilities for team members to advance. Scrum masters and product owners are members of teams. Here’s an overview of key roles and their associated responsibilities within an ART:
Scrum Masters
Scrum Masters act as facilitators for Agile Teams. They ensure the team adheres to Agile principles, remove impediments, and foster an environment of continuous improvement. Their goal is to optimize team efficiency and effectiveness.
Product Owners
Product Owners are accountable for defining and prioritizing features within the Agile Release Train. They work closely with stakeholders, ensuring the team delivers valuable, high-quality solutions aligned with business objectives.
Team Members
Team members, often comprising developers, testers, and other specialists, collaborate to deliver the features and solutions defined by the Product Owners. They self-organize, commit to the work, and continuously improve their processes.
Release Train Engineers (RTEs), System Architects / Engineers, Product Managers, and Business Owners are some of the other roles that Agile Release Trains frequently use.
Release Train Engineer (RTE)
The Release Train Engineer serves as a servant leader and coach for the Agile Release Train (ART). They facilitate communication, coordinate activities, manage risks, and ensure adherence to SAFe principles, fostering a smooth and efficient operation of the train.
Product Manager
Product Managers oversee the strategic direction of the product or solution. They collaborate with Product Owners, define overall priorities, and ensure that the delivered solutions align with the organization’s business strategy and goals.
System Architects/Engineers
System Architects and Engineers provide technical leadership within the ART. They guide the overall system architecture, address technical challenges, and ensure that the technical solutions align with organizational standards.
Business Owners
Business Owners represent the interests of the business or enterprise. They provide input on priorities, align the ART with overall business goals, and make key decisions to ensure that the delivered solutions meet strategic objectives.
Technologies Used to Manage and Streamline Agile Release Train
Agile Release Trains (ARTs) serve as the driving force behind scaled Agile, addressing the organization’s paramount priorities and ensuring accelerated and predictable delivery.
Achieving value in this manner necessitates both practice and the adoption of technology and solutions that facilitate alignment and coordination across the entire journey, from strategic planning to final delivery.
By harnessing appropriate technology processes and maintaining visibility for informed decision-making, the team can operate cohesively, functioning as a fully integrated release train.
Enterprise Kanban
Enterprise Kanban tools are crucial in visualizing workflow, status, and context, enhancing velocity, and fostering team unity for continuous improvement and timely deliveries. By utilizing digital Kanban boards to prioritize, manage, and track work, teams gain clarity on tasks and maintain seamless communication within a shared view.
Dependency Management
For effective Dependency Management, teams can plan and coordinate across the Agile Release Train (ART) using interconnected boards that map epics to features and other milestones. This approach enables visualization, communication, and effective management of dependencies between teams and across multiple teams.
Work Tool and Agile Methodology of Choice
Teams can choose their preferred Agile execution tools, such as Atlassian Jira, Rally Software, Microsoft Azure DevOps, or Digital.ai. The ideal enterprise Agile tool seamlessly integrates with an ART Kanban board, allowing teams to continue delivering value without disruptions.
Data Analytics and Reporting for Agile Release Trains
In terms of Data Analytics and Reporting, selecting tools that offer meaningful metrics for measuring the effectiveness of Agile Release Trains is crucial. The right tools provide insights into delivery trends across teams and individual levels, fostering continuous improvement and enabling organizations to track progress and scale Agile effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Agile Release Trains (ARTs) emerge as vital catalysts for implementing Agile at scale, adeptly addressing the organization’s key priorities with accelerated and predictable delivery.
The success of ARTs hinges on a combination of practice, technology, and strategic solutions, ensuring seamless alignment and coordination throughout the development journey. By leveraging the right tools and processes and transparent decision-making, ARTs function as fully integrated release trains, embodying the collaborative spirit of Agile methodologies.
As organizations embrace the principles of ARTs, they unlock the potential for sustained value delivery, fostering innovation, adaptability, and continuous improvement at every level of their Agile framework.
If you’re seeking to implement Agile Release Train into your team, Invensis Learning can help you get started. Embark on your Agile journey with confidence by exploring Agile Certification Courses. Gain a deep understanding of Agile Release Trains, enhance coordination skills, and unlock the potential for accelerated, value-driven project delivery.