Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- What is Operations Management?
- What is Project Management?
- The Connection Between Operations Management and Project Management
- Operations Management vs Project Management: Differences
- Project Management vs Operations Management: Similarities
- Conclusion
Introduction
With operational excellence and a well-defined strategy, businesses can succeed in keeping up and achieving their goals in a dynamic marketplace. Two key areas where these elements are most evident are Operations Management and Project Management. Although they share common goals of optimizing performance and ensuring smooth processes, they serve distinct purposes and require unique skill sets. Operations Management focuses on the continuous and systematic design, execution, and control of processes that produce and deliver a company’s goods or services. Project Management, on the other hand, revolves around the planning, initiation, execution, control, and closing of projects, which are temporary endeavours aimed at creating unique products, services, or results.
Understanding the differences and intersections between these two disciplines is crucial for businesses striving to achieve excellence and adaptability in today’s fast-paced environment. In this blog, we delve into the core distinctions, similarities, and collaborative potential of operations management and project management, providing insights to help you leverage both for optimal organizational performance.

What is Operations Management?
Operations management is a significant factor in any organization focused on efficiently managing the processes of producing and delivering goods or services. It involves a range of activities such as planning, organizing, coordinating, and controlling all the resources required to produce a company’s products or services. The primary objective of operations management is to ensure that business operations are efficient, effective, and capable of meeting customer demands.
Key responsibilities within operations management include managing the supply chain, overseeing production processes, maintaining quality control, and optimizing inventory levels. Operations managers strive to minimize costs while maximizing productivity and quality. They also work to improve processes through continuous improvement initiatives and the implementation of best practices. By effectively managing these operational aspects, businesses can achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction, reduce waste, and improve overall profitability.
What is Project Management?
Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. It involves a systematic approach to planning, organizing, and executing the tasks necessary to turn a brilliant idea into a tangible product, service, or deliverable. This structured methodology ensures that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the specified quality standards.
Key aspects of project management include:
- Defining Project Scope: Outlining the project’s boundaries, objectives, and deliverables to manage stakeholder expectations and prevent scope creep
- Identifying Deliverables: Specifying the tangible and intangible outputs the project will produce, including requirements, acceptance criteria, and timelines
- Managing Risks: Identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and developing strategies to mitigate or avoid them
- Effective Communication Across Teams: Ensuring clear and consistent communication among team members, stakeholders, and external partners to foster collaboration and keep everyone aligned toward the project’s goals
By focusing on these key aspects, project management provides a framework that enhances the likelihood of project success, enabling organizations to deliver value, achieve strategic objectives, and drive innovation.
The Connection Between Operations Management and Project Management
A project’s management lifecycle progresses through phases such as initiation, planning, execution, control & monitoring, and closure. During these stages, projects often intersect with ongoing operations, particularly:
- At the phase of developing a new product, expanding outputs, or upgrading a product
- During the product development process or while improving operations
- Until the end of the product life cycle
- At closeout phase
According to Karen R. J. White’s “Practical Project Management for Agile Nonprofits,” both operations and project managers share responsibility in four key areas:
- Budget Management
- Schedule Coordination
- Staff Management
- Skills Development
These areas highlight the collaborative efforts required between project and operations management to ensure projects align with organizational goals and operational capabilities throughout their life cycle.
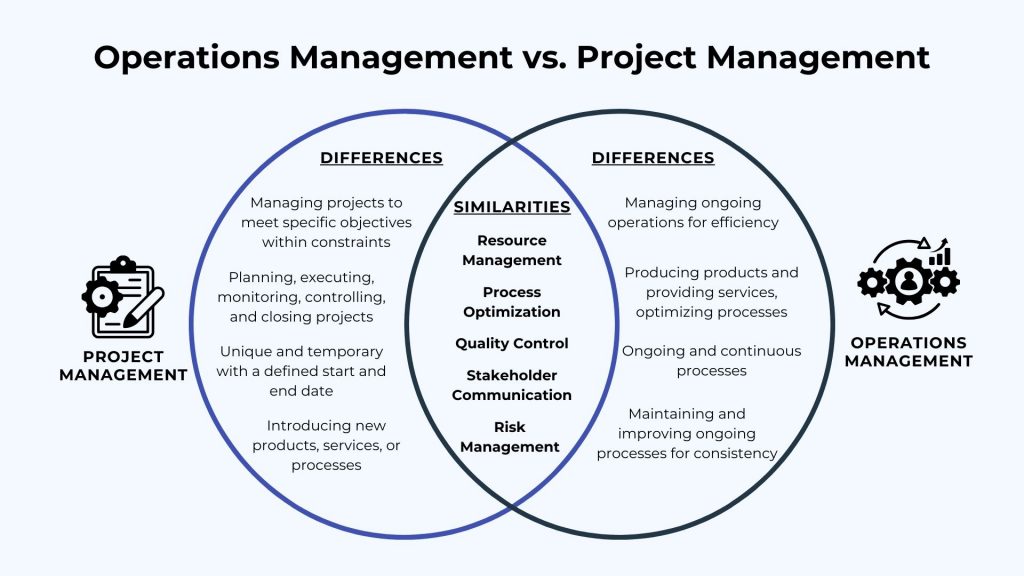
Operations Management vs Project Management: Differences
Operations management and project management are two crucial functions within an organization, but they differ in their focus and objectives. The responsibilities shared by operations and project managers—budget, schedule, staff management, and skills development—remain consistent, though their specific duties within these areas vary. Below is a detailed breakdown of how operations and project managers handle these responsibilities:
-
Budget Management
For operations management, budget management focuses on maintaining and optimizing the budget for ongoing operational activities. Operations managers allocate resources across daily operations, ensuring efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adherence to financial plans. They monitor costs, adjust budgets as needed, and prioritize spending to support operational objectives and long-term sustainability.
In project management, budget management is a process that involves creating, monitoring, and controlling the project’s financial resources. Project managers are responsible for estimating costs, developing budgets, and tracking expenses throughout the project lifecycle. They ensure that funds are allocated properly to tasks, manage variances, and make adjustments to stay within budget constraints.
-
Schedule
Operations managers establish and maintain standardized schedules for ongoing operational activities. They ensure smooth workflow and resource allocation to meet production targets and delivery deadlines. Compared to the well-defined timelines of projects, operational schedules require a more dynamic approach, allowing for adaptions based on shifts in demand or unexpected events.
Project managers create detailed schedules that break down the project into phases and tasks with defined timelines. They actively manage these timelines, coordinating with team members and stakeholders to ensure tasks are completed on time and dependencies between tasks are met. This active management is a key factor in the successful progress of the project.
-
Staff Management
The responsibility of an operations manager is wider in terms of managing staff. Their responsibilities include:
- Recruiting people into the department
- Onboarding new staff
- Allotting people to projects according to their qualities and characteristics
They are also responsible for approving leave applications, dealing with absences due to sickness or personal problems, and all the other HR duties. They oversee projects but are also responsible for ensuring performance on everything that is not related to projects.
The project manager is not responsible for any HR issues like hiring or firing. They are just responsible for overseeing the performance of their teammates on the project work that they are managing. But they cannot take any action if any team member is performing badly. All they can do is report the situation to the team member’s manager. Then, it will be the responsibility of the operational manager of that team member to look at the performance issue.
-
Skills Development
Project managers require a diverse skill set that encompasses planning, organization, communication, risk management, and budget control. They often participate in professional development opportunities to stay updated on the latest project management methods and best practices.
Operations managers require a strong understanding of production processes, quality control, and cost analysis. They also need leadership skills to manage teams, motivate employees, and promote a culture of continuous improvement. To optimize operational efficiency, operations managers may focus on developing skills in areas like lean manufacturing or Six Sigma.
Project Management vs Operations Management: Similarities
Even though project management and operations management are distinct, they share several key similarities essential for organizational success. Both fields emphasize the coordinated application of resources, processes, and activities to achieve predetermined objectives and deliver value to the organization. Efficient resource management and process optimization are crucial in both domains, ensuring optimal personnel, equipment, and materials utilization to maximize efficiency and productivity.
Quality control and risk management are critical in both fields, focusing on maintaining standards and mitigating risks. Both disciplines align their activities with the organization’s strategic goals and emphasize effective stakeholder communication. Recognizing these similarities fosters better collaboration between project and operations teams, improving overall performance and success.
Conclusion
A project manager and an operations manager have different roles, even though they share some responsibilities. An operations manager operates within a broader scope, handling management duties and related functions, allowing the project manager to focus exclusively on the current project. Both roles are essential together. The project manager depends on the operations manager to allocate resources and provide support, which is crucial for project success. At the same time, the operations manager depends on project managers to deliver high-quality results in their projects.
Both roles are integral to organizational success, leveraging their unique strengths to achieve strategic objectives. Enhancing your skills through PMP Certification Training equips you with the best practices and expertise to excel in project management, ensuring your projects thrive and contribute effectively to organizational goals.