Business always targets uninterrupted services to accomplish greater proficiency and productivity. Incident management is the initial step embraced by most enterprises for achieving a speedy recovery. ITIL defines the incident as “An unplanned interruption to a service, or the failure of a component of a service that hasn’t yet impacted service.” In this article, we will discuss ITIL incident management and its associated process, roles, and responsibilities to understand efficient IT service management practices.
What is ITIL Incident Management?
When an incident occurs, the major goal of the management is to get the service restored to a normal level of operation within agreed service level agreements. It is the main component of ITIL service support. Though certain operations fail to resolve or configure to normal operations, they are considered an incident. Even if a similar incident occurs multiple times, then a record of the problem should be made.
Since several incidents can occur, it is impractical to solve all of them simultaneously. So, it should be ranked on a priority basis from high, medium, and low priority assigned on the basis of the impact caused by its urgency or interruption. A problem that ranks high on an impact and urgency basis is given a high priority as it can affect the functioning of an enterprise.
ITIL Incident Management Function
Various functions are involved in incident management and the most important one is the service desk. The service desk is the single point of contact for the users to report any incidents. Without the availability of a service desk, users will have to contact support staff without prioritization. It means the staff might handle low-priority incidents overlooking high-priority incidents.
Thus, having a structured service desk enables support staff to handle all issues promptly, gather IT data, and support problem management in an efficient way.
ITIL Incident Management Process
Incident management plays a vital role in the day-to-day processes of an organization to encourage efficient workflow and deliver the best results for providers and customers. To ensure your IT support team is competent, implement a structured process flow from reporting the incident to resolving the issue.
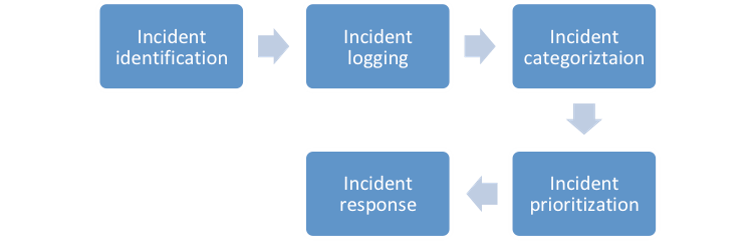
The main process steps involved in incident management:
Incident Identification
The incident comes from the users in whatever form the enterprise allows. The service desk decides whether the issue is strictly an incident or just a request. In the case of requests, they are categorized and handled more diversely than incidents, and they fall under request fulfillment.
Incident Logging
After identifying the issue, the service desk logs the incident as a ticket. The ticket should contain information such as the user’s name, contact details, incident description, and other related details. Ideally, the incident logging process would comprise prioritization, categorization, and other steps followed by the service desk.
Incident Categorization
Once you have logged the ticket, the issue needs to be classified to determine how actually the issue has to be handled. The process helps the team to sort out and model the incidents more easily based on their categories. It allows some of the issues to be automatically prioritized. The process makes it easier for the service desk team to track and identify the incidents and prevent them accordingly.
Incident Prioritization
Incident prioritization is an essential part of the incident management process as it helps you to determine how best to prioritize any issue. An incident priority is determined by its influence on the users and its urgency on the business. An incident having high impact and high urgency should be worked on before something with low impact and low urgency.
Incident Response
Rather than closing out an incident, the service desk personnel need to ensure with the end-user whether the incident was handled acceptably or not. If so, the issue can be closed, else the service desk personnel should check whether it is a recurring problem or not.
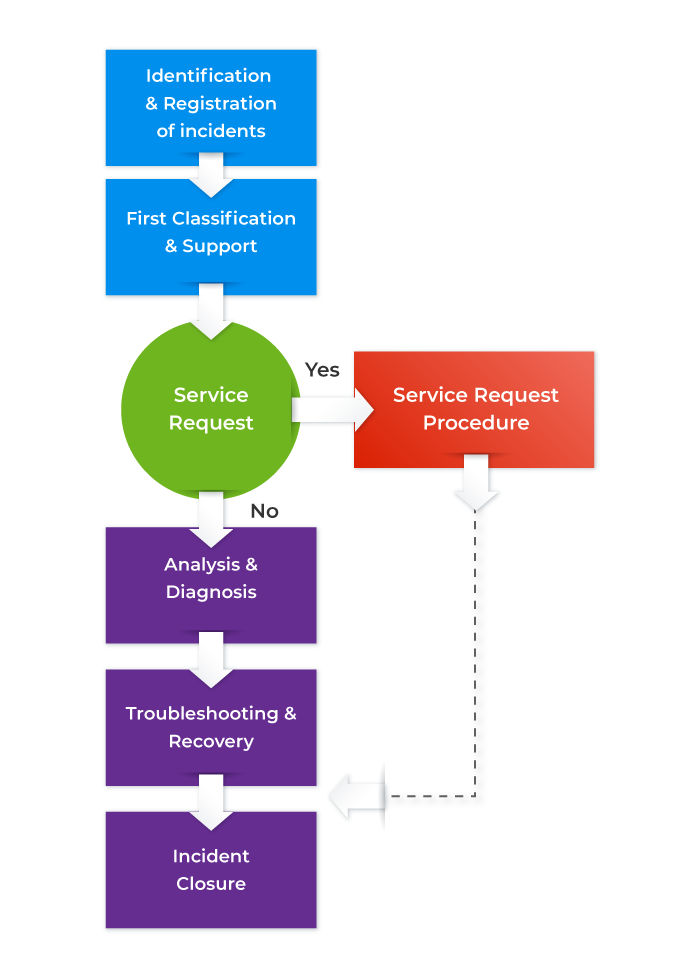
Incident Management Process Life Cycle Flow Diagram
The incident management life cycle comprises a set of instructions that allows and encourages IT professionals, to work together to achieve effective IT service delivery. Irrespective of the size or type of industry, the incident management life cycle is flexible and can be easily structured in a way it can cater to the industry requirements.
Incident Management Roles and Responsibilities
Four separate roles are allocated during the incident management handling process. Here, we describe some major incident management roles and responsibilities that are associated with each of the job titles:
1st Level Technical Support
They are the major contact persons for any incident reports within an organization. Usually, they staff the IT service desk by taking incident reports from clients in registering, categorizing, and taking an immediate effort to restore the service interruption at the earliest.
When the 1st-level technical support can’t resolve the interruption within the given time frame, the issue is escalated to the 2nd-level support. Though 1st-level support technicians might be accountable for restoring the IT service in case of a major incident, they are not accountable for managing with the incident team.
Incident Manager
An incident manager is held responsible for the complete incident management process within an enterprise, which comprises all major incidents reported and to be resolved. Once the issue is escalated either by 1st or 2nd level staff, then the incident management should identify what resources and proficiency are needed to resolve the incident and form a major incident team that can solve the issues as soon as possible.
IT Operator
IT operators are responsible for performing day-to-day operations within organizations like maintaining servers, backing up data, and ensuring that scheduled tasks are performed. They are used as extra labor to address major service interruptions.
Major Incident Team
The role of the major incident team in addressing major IT interruptions is to restore the services quickly using accessible resources. The size of the team depends on the nature of the service interruption and the level of expertise required to restore the service.
The Scope of ITIL Incident Management
Incident management includes events that might cause disruption of services in an organization. This disruption can be anything from power failures, software bugs, and hardware damage to severe crashes. All the events need not have to be incidents. Many events are not at all related to disruption but are indicators of normal operations.
All these aspects come under the scope of incident management and can be systematically resolved by assigning priorities.
The Procedure of ITIL Incident Management
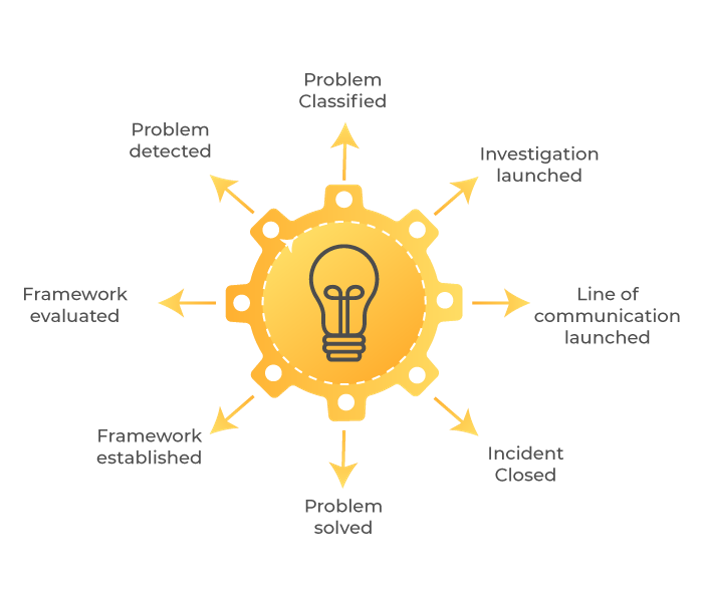
The following procedure is followed in incident management:
- Problem Detected
The problem is detected in the initial phase and its characteristics are recorded accordingly. - Problem Classified
The incident is categorized according to its type and initial support is provided. - Investigation Launched
An investigation is launched to identify the cause of the issue. The data obtained finally is evaluated and considered. - Line of Communication Launched
The incident is then resolved using data obtained in the previous phase. The final solution obtained is documented for further reference. - Incident Closed
The incident raised is authoritatively closed once it is resolved and then the system is restored to its normal working criteria. - Problem Solved
The line of communication is gradually maintained to ensure that the issue doesn’t arise again. And the system is periodically tracked to check the probabilities of further disruptions. - Framework Established
A framework is established for reference that is supposed to be used to resolve similar incidents. - Framework Evaluated
The incident framework is further evaluated to ensure a hassle-free and proficient way to resolve the disruption.
What is the Purpose of ITIL Incident Management?
The main purpose of ITIL incident management is to restore normal service operations as soon as possible and to minimize the adverse effect of disruption on normal business operations. The term normal service operation refers to an optimal level wherein the services are performed within the agreed operational levels.
Incident Management Examples
Some of the common types of incidents can be categorized as follows:
Application
- If a specific error is unavailable, then it establishes an application error and needs to be rectified by the concerned team.
- Unavailability of data and data corruption can affect the hassle-free function of an organization.
- A bug in the software used by the system or by any website in an online company can seriously cause a major loss of revenue and divert potential customer streams.
Hardware
- A company’s server is accountable for handling and hosting its digital content. During a server crash, if an issue is not resolved at the earliest, then it can halt the working of the entire company.
- Having issues with the internet can disrupt video conferencing, email, and other such online activities which could be the core components of the company’s functionality.
- Failure of computer systems can cause loss of productivity within the department of the company. In such a scenario, a backup system is essential to ensure that work is not affected.
Conclusion
Incident management tracks incidents via the service desk to follow the trends in the incident categories and also the time taken at each stage. The final module of incident management involves assessing the data gathered. The data gathered guides the organizations to enhance the quality of the service delivered and reduce the overall incidents.
Incident management promptly succeeds in responding, analyzing, and documenting the incidents, whilst ensuring customer satisfaction is met. By using a professional approach, it communicates and resolves the incidents quickly thereby improving the business perception. Give yourself a chance to grow in your Service Management career with the ITIL 4 Foundation certification training, and gain useful skills and best practices.
Know more about Service Management best practices through Invensis Learning’s IT Service Management certification training on ITIL Foundation Course, SIAM Foundation, SIAM professional, VeriSM, etc.